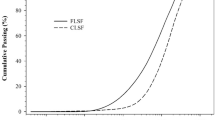
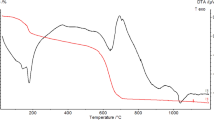
Abstract
In recent years, the incorrect disposal of industrial solid wastes is one of the main reasons for serious environmental pollution. The appropriate recycle of these waste materials in commercial purpose is the key way to protect the environment. In the present study, the suitability of gypsum waste (GW) from ceramics factory as a filler in epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) was explored. Most importantly, the properties of ENR/GW composites were compared with those of ENR composites filled with most widely used non-reinforcing filler calcium carbonate (CaCO3). In both ENR/GW and ENR/CaCO3 composites, the values of torque difference, hardness and tensile modulus increased steadily with increasing filler content. However, at same filler loading level, the mechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of ENR/GW composites were better as compared to those of ENR/CaCO3 composites. ENR/GW composite also exhibited considerably higher thermal stability as compared to either unfilled ENR or ENR/CaCO3 composite. As a whole, GW could be used as a cost-effective semi-reinforcing filler in ENR composites.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ismail H, Nasaruddin MN, Ishiaku US (1999) White rice husk ash filled natural rubber compounds: the effect of multifunctional additive and silane coupling agents. Polym Test 18:287–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9418(98)00030-0
Chuayjuljit S, Imvittaya A, Na-Ranong N, Potiyaraj P (2002) Effects of particle size and amount of carbon black and calcium carbonate on curing characteristics and dynamic mechanical properties of natural rubber. J Metals Mater Miner 12:51–57
Intiya W, Thepsuwan U, Sirisinha C, Sae-Oui P (2017) Possible use of sludge ash as filler in natural rubber. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 19:774–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-016-0480-5
Thongsang S, Sombatsompop N, Ansarifars A (2008) Effect of fly ash silica and precipitated silica fillers on the viscosity, cure, and viscoelastic properties of natural rubber. Polym Adv Technol 19:1296–1304. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.1129
Mishra S, Shimpi NG (2005) Comparison of nano CaCO3 and fly ash filled with styrene butadiene rubber on mechanical and thermal properties. J Sci Ind Res 64:744–751
Alkadasi NAN, Hundiwale DG, Kapadi UR (2004) Effect of coupling agent on the mechanical properties of fly ash–filled polybutadiene rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 91:1322–1328. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.13280
Sombatsompop N, Thongsang S, Markpin T, Wimolmala E (2004) Fly ash particles and precipitated silica as fillers in rubbers. I. Untreated fillers in natural rubber and styrene–butadiene rubber compounds. J Appl Polym Sci 93:2119–2130. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.20693
Thongsang S, Worakhan W, Wimolmala E, Sombatsompop N (2012) Dynamic mechanical analysis and tribological properties of NR vulcanizates with fly ash/precipitated silica hybrid filler. Tribol Int 53:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2012.04.006
Ahmed K, Nizami SS, Raza NZ (2013) Characteristics of natural rubber hybrid composites based on marble sludge/carbon black and marble sludge/rice husk derived silica. J Ind Eng Chem 19:1169–1176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2012.12.014
Ahmed K, Nizami SS, Riza NZ (2014) Reinforcement of natural rubber hybrid composites based on marble sludge/Silica and marble sludge/rice husk derived silica. J Adv Res 5:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2013.01.008
Sae-oui P, Sirisinha C, Thaptong P (2009) Utilization of limestone dust waste as filler in natural rubber. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 11:166–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-008-0230-4
Sae-oui P, Rakdee C, Thanmathorn P (2002) Use of rice husk ash as filler in natural rubber vulcanizates in comparison with other commercial fillers. J Polym Sci 83:2485–2493. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.10249
Sereda L, Visconte LL, Nunes RCB, Furtado CRG, Riande E (2003) Effect of silica and rice husk ash fillers on the modulus of polysiloxane networks. J Appl Polym Sci 90:421–429. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.12645
Da Costa HM, Visconte LLY, Nunes RCB, Furtado CRG (2003) Rice-husk-ash-filled natural rubber. II. Partial replacement of commercial fillers and the effect on the vulcanization process. J Appl Polym Sci 87:1405–1413. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.11514
Pongdong W, Kummerlöwe C, Vennemann N, Thitithammawong A, Nakason C (2018) A comparative study of rice husk ash and siliceous earth as reinforcing fillers in epoxidized natural rubber composites. Polym Compos 39:414–426. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.23951
Moulin L, Da Silva S, Bounaceur A, Herblot M, Soudais Y (2017) Assessment of recovered carbon black obtained by waste tires steam water thermolysis: an industrial application. Waste Biomass Valor 8:2757–2770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9822-8
Taverna ME, Tassara O, Morán J, Sponton M, Frontini P, Nicolau V, Estenoz D (2019) Effect of kraft lignin from hardwood on viscoelastic, thermal, mechanical and aging performance of high pressure laminates. Waste Biomass Valor 10:585–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0088-6
Yangthong H, Wisunthorn S, Pichaiyut S, Nakason C (2019) Novel epoxidized natural rubber composites with geopolymers from fly ash waste. Waste Manag 87:148–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.02.013
Panitchakarn P, Wikranvanich J, Phisalaphong M (2019) Synthesis and characterization of natural rubber/coal fly ash composites via latex aqueous microdispersion. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21:134–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0774-x
Şaşmaz S, Karaağaç B, Uyanık N (2019) Utilization of chrome-tanned leather wastes in natural rubber and styrene-butadiene rubber blends. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21:166–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0775-9
de Paiva FFG, de Maria VPK, Torres GB, Dognani G, Santos RJ, Cabrera FC, Job AE (2019) Sugarcane bagasse fiber as semi-reinforcement filler in natural rubber composite sandals. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21:326–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0801-y
Nawi AM, Badarulzaman NA (2015) Effect of plaster of paris waste and sintering temperatures on physical properties of pottery. Proc CIRP 26:752–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.08.019
Radulović D, Terzić A, Andrić L (2017) The construction and ceramics industry waste gypsum valorization possibilities. In: Lee B, Gadow R, Mitic V (eds) Proceedings of the IV advanced ceramics and applications conference, Atlantis Press, Paris, pp 475–491
Godinho-Castro AP, Testolin RC, Janke L, Corrêa AXR, Radetski CM (2012) Incorporation of gypsum waste in ceramic block production: proposal for a minimal battery of tests to evaluate technical and environmental viability of this recycling process. Waste Manag 32:153–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.08.019
Asakura H (2015) Sulfate and organic matter concentration in relation to hydrogen sulphide generation at inert solid waste landfill site–Limit value for gypsum. Waste Manag 43:328–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.06.018
Ko JH, Xu Q, Jang YC (2015) Emissions and control of hydrogen sulfide at landfills: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Techol 45:2043–2083. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2015.1010427
Tounchuen K, Buggakupta W, Panpa W (2014) Characteristics of automotive glass waste-containing gypsum bodies made from used plaster mould. Key Eng Mater 608:91–96. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.608.91
Lee S, Xu Q, Booth M, Townsend TG, Chadik P, Bitton G (2006) Reduced sulfur compounds in gas from construction and demolition debris landfills. Waste Manag 26:526–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2005.10.010
He R, Xia FF, Bai Y, Wang J, Shen DS (2012) Mechanism of H2S removal during landfill stabilization in waste biocover soil, an alterative landfill cover. J Hazard Mater 217–218:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.02.061
Plaza C, Xu QY, Townsend T, Bitton G, Booth M (2007) Evaluation of alternative landfill cover soils for attenuating hydrogen sulfide from construction and demolition (C&D) debris landfills. J Environ Manage 84:314–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.06.001
Xu QY, Townsend T, Reinhart D (2010) Attenuation of hydrogen sulfide at construction and demolition debris landfills using alternative cover materials. Waste Manag 30:660–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2009.10.022
Flynn B (1998) Invisible threat: odors & landfill gas from C&D waste. Waste Age 29:91–97
Edwards S, Alharthi R, Ghaly AE (2011) Removal of hydrogen sulfide from water. Am J Environ Sci 7:295–305
Ahmed A, Soliman AM, El Naggar MH, Kamei T (2015) An assessment of geo-environmental properties for utilization of recycled gypsum in earthwork projects. Soils Found 55:1139–1147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2015.09.014
Ngamsurat S, Boonkerd K, Leela-adisorn U, Potiyaraj P (2011) Curing characteristics of natural rubber filled with gypsum. Energy Procedia 9:452–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2011.09.051
Roy K, Debnath SC, Pongwisuthiruchte A, Pranut Potiyaraj (2019) Natural rubber/microcrystalline cellulose composites with epoxidized natural rubber as compatibilizer. Rubber Chem Technol. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.19.81533
Sierra JDM, Lafita C, Gabaldón C, Spanjers H, van Lier JB (2017) Trace metals supplementation in anaerobic membrane bioreactors treating highly saline phenolic wastewater. Bioresour Technol 234:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.032
Ismail H, Shaari SM (2010) Curing characteristics, tensile properties and morphology of palm ash/halloysite nanotubes/ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM) hybrid composites. Polym Test 29:872–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2010.04.005
Roy K, Potiyaraj P (2018) Development of high performance microcrystalline cellulose based natural rubber composites using maleated natural rubber as compatibilizer. Cellulose 25:1077–1087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1613-2
Ismail H, Ahmad HS (2013) The properties of acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR) composite with halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) and silica or carbon black. Polym Plast Technol Eng 52:1175–1182. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602559.2013.769577
Ahmed K, Nizami SS, Raza NZ, Mahmood K (2012) Mechanical, swelling, and thermal aging properties of marble sludge-natural rubber composites. Int J Ind Chem 3:21
Roy K, Debnath SC, Pranut Potiyaraj (2019) A critical review on the utilization of various reinforcement modifiers in filled rubber composites. J Elastom Plast. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095244319835869
Yang S, Zhou Y, Zhang P, Cai Z, Li Y, Fan H (2017) Preparation of high performance NBR/HNTs nanocomposites using an electron transferring interaction method. Appl Surf Sci 425:758–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.030
Krishnamurthy S, Balakrishnan P (2019) Dynamic mechanical behavior, solvent resistance and thermal degradation of nitrile rubber composites with carbon black-halloysite nanotube hybrid fillers. Polym Compos. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25101
Acknowledgements
One of the authors, Kumarjyoti Roy, would like to thank Ratchadaphiseksomphot Endowment Fund, Chulalongkorn University, for senior postdoctoral fellowship assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, K., Debnath, S.C., Bansod, N.D. et al. Possible use of gypsum waste from ceramics industry as semi-reinforcing filler in epoxidized natural rubber composites. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 22, 285–294 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00939-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00939-w