Abstract
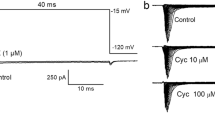
The actions of benzodiazepines were studied on the responses to GABA of the fast coxal depressor (Df) motor neurone of the cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Ro5-4864, diazepam and clonazepam were investigated. Responses to GABA receptors were enhanced by both Ro5-4864 and diazepam, whereas clonazepam, a potent-positive allosteric modulator of human GABA(A) receptors, was ineffective on the native insect GABA receptors of the Df motor neurone. Thus, clear pharmacological differences exist between insect and mammalian native GABA-gated chloride channels with respect to the actions of benzodiazepines. The results enhance our understanding of invertebrate GABA-gated chloride channels which have recently proved important in (a) comparative studies aimed at identifying human allosteric drug-binding sites and (b) understanding the actions of compounds used to control ectoparasites and insect crop pests.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MD, Celniker SE et al (2000) The genome gequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287(5461):2185–2195
Bai D, Zhu G et al (2001) Distinct functional and pharmacological properties of tonic and quantal inhibitory postsynaptic currents mediated by gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors in hippocampal neurons. Mol Pharmacol 59(4):814–824
Barnard EA, Skolnick P et al (1998) International union of pharmacology. XV. Subtypes of γ-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors: classification on the basis of subunit structure and receptor function. Pharmacol Rev 50(2):291–313
Benavides J, Malgouris C et al (1983a) “Peripheral type” benzodiazepine binding sites in rat adrenals: binding studies with [3H]PK 11195 and autoradiographic localization. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 266(1):38–49
Benavides J, Quarteronet D et al (1983b) Labelling of “peripheral-type” benzodiazepine binding sites in the rat brain by using [3H]PK 11195, an isoquinoline carboxamide derivative: kinetic studies and autoradiographic localization. J Neurochem 41(6):1744–1750
Benavides J, Menager J et al (1985) Characterization of solubilized “peripheral type” benzodiazepine binding sites from rat adrenals by using [3H]PK 11195, an isoquinoline carboxamide derivative. Biochem Pharmacol 34(2):167–170
Bonin RP, Martin LJ et al (2007) α5 GABAA receptors regulate the intrinsic excitability of mouse hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 98(4):2244–2254
Buckingham SD, Biggin PC et al (2005) Insect GABA receptors: splicing, editing, and targeting by antiparasitics and insecticides. Mol Pharmacol 68(4):942–951
Chelli B, Falleni A et al (2001) Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor ligands: mitochondrial permeability transition induction in rat cardiac tissue. Biochem Pharmacol 61(6):695–705
Costa B, Salvetti A et al (2006) Peripheral benzodiazepine receptor: characterization in human T-lymphoma Jurkat cells. Mol Pharmacol 69(1):37–44
David JA, Sattelle DB (1990) Ionic basis of membrane potential and of acetylcholine-induced currents in the cell body of the cockroach fast coxal depressor motor neurone. J Exp Biol 151(1):21
De Souza EB (1990) Neuroendocrine effects of benzodiazepines. J Psychiatr Res 24(Suppl 2):111–119
Decaudin D (2004) Peripheral benzodiazepine receptor and its clinical targeting. Anticancer Drugs 15(8):737–745
Dennis T, Dubois A et al (1988) Distribution of central omega 1 (benzodiazepine1) and omega 2 (benzodiazepine2) receptor subtypes in the monkey and human brain. An autoradiographic study with [3H]flunitrazepam and the omega 1 selective ligand [3H]zolpidem. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247(1):309–322
Es-Salah Z, Lapied B et al (2008) RNA editing regulates insect γ-aminobutyric acid receptor function and insecticide sensitivity. Neuroreport 19(9):939–943
Ffrench-Constant RH (1993) Cloning of the Drosophila cyclodiene insecticide resistance gene: a novel GABAA receptor subtype? Comp Biochem Physiol C 104(1):9–12
Gavish M, Katz Y et al (1992) Biochemical, physiological, and pathological aspects of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. J Neurochem 58(5):1589–1601
Gisselmann G, Plonka J et al (2004) Drosophila melanogaster GRD and LCCH3 subunits form heteromultimeric GABA-gated cation channels. Br J Pharmacol 142(3):409–413
Harrison JB, Chen HH et al (1996) Immunocytochemical mapping of a C-terminus anti-peptide antibody to the GABA receptor subunit, RDL in the nervous system in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Tissue Res 284(2):269–278
Hosie AM, Sattelle DB (1996) Allosteric modulation of an expressed homo-oligomeric GABA-gated chloride channel of Drosophila melanogaster. Br J Pharmacol 117(6):1229–1237
Hosie AM, Aronstein K et al (1997) Molecular biology of insect neuronal GABA receptors. Trends Neurosci 20(12):578–583
Hosie AM, Buckingham SD et al (2001) Alternative splicing of a Drosophila GABA receptor subunit gene identifies determinants of agonist potency. Neuroscience 102(3):709–714
Hosie AM, Wilkins ME et al (2006) Endogenous neurosteroids regulate GABAA receptors through two discrete transmembrane sites. Nature 444(7118):486–489
Jones AK, Buckingham SD et al (2009) Splice-variant- and stage-specific RNA editing of the Drosophila GABA receptor modulates agonist potency. J Neurosci 29(13):4287–4292
Korpi ER, Debus F et al (2007) Does ethanol act preferentially via selected brain GABAA receptor subtypes? the current evidence is ambiguous. Alcohol 41(3):163–176
Lees G, Beadle DJ et al (1987) Responses to GABA by isolated insect neuronal somata: pharmacology and modulation by a benzodiazepine and a barbiturate. Brain Res 401(2):267–278
Lummis SC, Sattelle DB (1985) Insect central nervous system gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors. Neurosci Lett 60(1):13–18
Marangos PJ, Patel J et al (1982) Characterization of peripheral-type benzodiazepine binding sites in brain using [3H]Ro 5–4864. Mol Pharmacol 22(1):26–32
Mathers DA, Wan X et al (2007) Barbiturate activation and modulation of GABAA receptors in neocortex. Neuropharmacology 52(4):1160–1168
Nimmich ML, Heidelberg LS et al (2009) RNA editing of the GABAA receptor α3 subunit alters the functional properties of recombinant receptors. Neurosci Res 63(4):288–293
Olsen RW, Sieghart W (2009) GABAA receptors: subtypes provide diversity of function and pharmacology. Neuropharmacology 56(1):141–148
Quinlan JJ, Firestone LL et al (2000) Mice lacking the long splice variant of the γ2 subunit of the GABAA receptor are more sensitive to benzodiazepines. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66(2):371–374
Reynolds DS (2008) The value of genetic and pharmacological approaches to understanding the complexities of GABA(A) receptor subtype functions: the anxiolytic effects of benzodiazepines. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 90(1):37–42
Rudolph U, Möhler H (2004) Analysis of GABAA receptor function and dissection of the pharmacology of benzodiazepines and general anesthetics through mouse genetics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 44(1):475–498
Sattelle DB (1990) GABA receptors of insects. Adv Insect Physiol 22:1–113
Sattelle DB, Pinnock RD et al (1988) GABA receptors on the cell-body membrane of an identified insect motor neuron. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 232(1269):443–456
Sattelle DB, Lummis SCR et al (1991) Pharmacology of insect GABA receptors. Neurochem Res 16(3):363
Sigel E (2005) The benzodiazepine recognition site on GABAA receptors. Medicin Chem Rev Online 2(3):251–256
Sine SM, Engel AG (2006) Recent advances in Cys-loop receptor structure and function. Nature 440(7083):448–455
Timothy R, David M et al (1986) γ-Aminobutyric acid receptor complex of insect CNS: characterization of a benzodiazepine binding site. J Neurochem 47(6):1955–1962
Verma A, Snyder SH (1989) Peripheral type benzodiazepine receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 29:307–322
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buckingham, S.D., Higashino, Y. & Sattelle, D.B. Allosteric modulation by benzodiazepines of GABA-gated chloride channels of an identified insect motor neurone. Invert Neurosci 9, 85–89 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10158-009-0091-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10158-009-0091-0