Abstract
Background. The regulation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) is a key determinant of sodium homeostasis. The effect of cyclic AMP (cAMP) on ENaC activity is tissue-specific, and is controversial when ENaC is ex-pressed in Xenopus oocytes.
Methods. The modulation of ENaC by cAMP in oocytes expressing human or rat ENaC was performed with two-electrode voltage clamping.
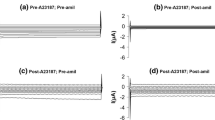
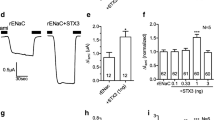
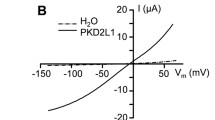
Results. 250 μM 8-(4-chlorophenylthio)-adenosine 3′, 5′-cyclic monophosphate (8-CPT-cAMP) added to the bath significantly increased normalized amiloride-sensitive currents within 60 s in oocytes expressing human α, β, and γ subunits (5 ng cRNA each). The cAMP effect was dose-dependent and was partially inhibited by 200 μM Rp-CPT-cAMP, a competitive cAMP antagonist. A transient effect of 8-CPT-cAMP on rat ENaC activity was also observed. Oocytes expressing rat α subunits with γ subunits (which have a putative protein kinase A phosphorylation site) showed similar increases in amiloride-sensitive current with 250 μM 8-CPT-cAMP, while oocytes expressing rat α subunits with β subunits were not activated by 8-CPT-cAMP. Further, rat ENaC (but not human ENaC)-expressing oocytes were not activated by cAMP when oocytes were continuously superfused during electrophysiological recordings, suggesting that rat ENaC activation by cAMP is dependent upon the condition of oocytes during cAMP stimulation.
Conclusion. The present results suggest that ENaC expressed in Xenopus oocytes can be activated by cAMP, and that the γ subunit confers sensitivity to cAMP modulation of rat ENaC activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: February 21, 2002 / Accepted: June 26, 2002
Acknowledgments We thank Dr. M.J. Welsh for providing the human ENaC clones and Dr. B.C. Rossier for providing the rat ENaC clones. We sincerely appreciate the technical help of Dr. Sunil Saxena and Mr. Darryl Morin. We also thank Martha Yeager for her secretarial support. This work was supported in part by grants from the National Institute of Health, NS-34877 (YO), DK-19407, and DK-53161 (DGW); the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation MMFDP (JKT); and the WM Keck Foundation (MWQ).
Correspondence to:K. Tamba
About this article
Cite this article
Tamba, K., Oh, Y., Tucker, J. et al. Epithelial sodium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes are activated by cyclic-AMP. Clin Exp Nephrol 6, 0195–0201 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s101570200034
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s101570200034