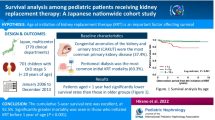
Abstract
Background
Some pediatric patients on maintenance dialysis may need end-of-life care in the future because of being excluded from the indication of kidney transplantation and experiencing difficulty in continuation of their dialysis. This study aimed to thoroughly elucidate mortality outcomes of children on maintenance dialysis including the cause of death and clinical background of exclusion from indication of transplantation.
Patients and methods
This single-center retrospective study enrolled 53 children who received kidney transplantation (5) or maintenance peritoneal dialysis (PD, 48) as initial renal replacement therapy (RRT). We examined the selected RRT modalities, mortality outcomes, clinical backgrounds of cause of death, and risk factors of excluding from future the indication of transplantation.
Results
Nine (17%) of all 53 patients, all receiving PD (9/48, 19%), were finally excluded from next RRT indication—7 were excluded due to severe extrarenal complications that indicated high risk for transplantation and 2 were excluded due to severe psychomotor retardation and at the guardians’ discretion. Patients who were excluded from the indication had a younger age at PD induction and higher proportion of cerebral and cardiac complications or psychomotor retardation than patients who were included in the indication. Of the nine patients, seven died; of which, one patient died due to fatal progression of extrarenal complications and six died due to infectious or noninfectious dialysis-related complications.
Conclusion
Patients with severe extrarenal complications or psychomotor retardation tend to be excluded from the indication of transplantation. Their condition becomes fatal because of the complications of long-term dialysis and progression in extrarenal complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
McDonald SP, Craig JC. Long-Term survival of children with end-stage renal disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2654–62. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa031643.
Gallyeva DB, Jackson CA, Wild SH, Burns S, Hughes D, Taynor JP, Metcalfe W, Halbesma N. Long-term all-cause mortality and cardiovasular outcomes in Scottish children after initiation of renal replacement therapy: a national cohort study. Pediatric Nephrol. 2020;35:677–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-019-04430-4.
Chesnaye N, Bonthuis M, Schaefer F, Groothoff JW, Verrina E, Heaf JG, Jankauskiene A, Lukosiene V, Molchanova EA, Mota C, Peco-Antić A, Ratsch I-MM, Bjerre A, Roussinov DL, Sukalo A, Topaloglu R, Van Hoeck K, Zagozdzon I, Jager KJ, Van Stralen KJ. Demographics of paediatric renal replacement therapy in Europe: a report of the ESPN/ERA-EDTA registry. Pediatr Nephrol. 2014;29:2403–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2884-6.
Chesnaye NC, Schaefer F, Groothoff JW, Bonthusis M, Reusz G, Heaf JG, Lewis M, Maurer E, Paripović D, Zagozdzon I, van Stralen KJ, Jaher KJ. Mortality risk in European children with end-stage renal disease on dialysis. Kidney Int. 2020;89:1355–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2016.02.016.
Mitsnefes MM, Laskin BL, Dahhou M, Zhang X, Foster BJ. Mortality risk among children initially treated with dialysis for end-stage kidney disease. JAMA. 2013;309:1921–9. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.4208.
Boudville N, Kemp A, Clayton P, Lim W, Badve SV, Hawley CM, McDonald SP, Wiggins KJ, Bannister KM, Brown FG, Johnson DW. Recent peritonitis associates with mortality among patients treated with peritoneal dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:1398–405. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2011121135.
Ye H, Zhou Q, Fan L, Guo Q, Mao H, Huang F, Yu X, Yang X. The impact of peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis on mortality in peritoneal dialysis patients. BMC Nephrol. 2017;18:186. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-017-0588-4.
Alexander RT, Foster BJ, Tonelli MA, Soo A, Nettel-Aguirre A, Hemmelgarn BR, Samuel SM. Survival and transplantation outcomes of children less than 2 years of age with end-stage renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012;27:1975–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-012-2195-8.
Mekahli D, Shaw V, Ledermann SE, Rees L. Long-term outcome of infants with severe chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5:10–7. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.05600809.
Neu AM, Sander A, Borzych-Duzalka D, Watson AR, Vallés PG, Ha IS, Patel H, Askenazi D, Balasz-Chmielewska I, Lauronen J, Groothoff JW, Feber J, Schaefer F, Warady BA. Comorbidities in chronic pediatric peritoneal dialysis patients: a report of the international pediatric peritoneal dialysis network. Perit Dial Int. 2012;32:410–8. https://doi.org/10.3747/pdi.2012.00124.
Shroff R, Rees L, Trompeter R, Hutchinson C, Ledermann S. Long-term outcome of chronic dialysis in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2006;21:257–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-2067-6.
Renal Physicians Association Clinical Practice Guideline. Shared decision-making in the appropriate initiation of and withdrawal from dialysis. 2nd ed. Maryland: Rockville; 2010.
Harambat J, Ekulu PM. Inequalities in access to pediatric ESRD care: a global health challenge. Pediatr Nephrol. 2016;31:353–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3263-7.
Mong Hiep TT, Janssen F, Ismaili K, Khai Minh D, Vuong Kiet D, Robert A. Etiology and outcome of chronic renal failure in hospitalized children in ho chi Minh City, Vietnam. Pediatr Nephrol. 2008;23:965–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-0752-y.
Gulati S, Mittal S, Sharma RK, Gupta A. Etiology and outcome of chronic renal failure in Indian children. Pediatr Nephrol. 1999;13:594–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670050750.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by SH, KT, and NF. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SH, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee at which the study was conducted (IRB approval number 2020023) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
The participants have consented to the submission of the article to the journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Hibino, S., Kitagata, R., Nishimura, T. et al. Mortality outcomes and clinical background of children on maintenance dialysis without receiving kidney transplantation. Clin Exp Nephrol 26, 198–204 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-021-02132-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-021-02132-6