Abstract
Background
Activation of the intrarenal renin–angiotensin system (RAS) plays a critical role in the pathophysiology of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and hypertension. It has been reported that reactive oxygen species (ROS) are important components of intrarenal RAS activation. Melatonin is recognized as a powerful antioxidant, and we recently reported that impaired nighttime melatonin secretion correlates negatively with urinary angiotensinogen excretion, the surrogate marker of intrarenal RAS activity in patients with CKD. However, whether melatonin supplementation ameliorates the augmentation of intrarenal RAS in CKD has remained unknown. We aimed to clarify whether exogenous melatonin ameliorates intrarenal RAS activation via the reduction of ROS production.
Methods
5/6 Nephrectomized (Nx) rats were used as a chronic progressive CKD model and compared with sham-operated control rats. The Nx rats were divided into untreated Nx rats and melatonin-treated Nx rats. The levels of intrarenal RAS, ROS components, and renal injury were evaluated after 4 weeks of treatment.
Results
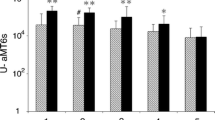
Compared with the control rats, the untreated Nx rats exhibited significant increases in intrarenal angiotensinogen, angiotensin II (AngII) type 1 receptors, and AngII, accompanied by elevated blood pressure, higher oxidative stress (8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine), lower antioxidant (superoxide dismutase) activity, and increased markers of interstitial fibrosis (α-smooth muscle actin, Snail, and type I collagen) in the remnant kidneys. Treatment with melatonin significantly reversed these abnormalities.
Conclusion
Antioxidant treatment with melatonin was shown to ameliorate intrarenal RAS activation and renal injury in a 5/6 Nx rat model.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kobori H, Nangaku M, Navar LG, Nishiyama A. The intrarenal renin–angiotensin system: from physiology to the pathobiology of hypertension and kidney disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2007;59:251–7.
Navar LG, Harrison-Bernard LM, Nishiyama A, Kobori H. Regulation of intrarenal angiotensin II in hypertension. Hypertension. 2002;39:316–22.
Miyata K, Ohashi N, Suzaki Y, Katsurada A, Kobori H. Sequential activation of the reactive oxygen species/angiotensinogen/renin–angiotensin system axis in renal injury of type 2 diabetic rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2008;35:922–7.
Ohashi N, Urushihara M, Kobori H. Activated intrarenal reactive oxygen species and renin angiotensin in IgA nephropathy. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2009;61:55–66.
Kamiyama M, Urushihara M, Morikawa T, Konishi Y, Imanishi M, Nishiyama A, Kobori H. Oxidative stress/angiotensinogen/renin–angiotensin system axis in patients with diabetes nephropathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:23045–62.
Ohashi N, Katsurada A, Miyata K, Satou R, Saito T, Urushihara M, Kobori H. Role of activated intrarenal reactive oxygen species and renin–angiotensin system in IgA nephropathy model mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009;36:750–5.
Luo H, Wang X, Chen C, Wang J, Zou X, Li C, Xu Z, Yang X, Shi W, Zen C. Oxidative stress causes imbalance of renal renin angiotensin system (RAS) components and hypertension in obese Zucker rats. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015;4:e001559.
Xue H, Yuan P, Ni J, Li C, Shao D, Liu J, Shen Y, Wang Z, Zhou L, Zhang W, Huang Y, Yu C, Wang R, Lu L. H2S inhibits hyperglycemia-induced intrarenal renin–angiotensin system activation via attenuation of reactive oxygen species generation. PLoS One. 2013;8:e74366.
Russcher M, Koch B, Nagtegaal E, van der Putten K, ter Wee P, Gaillard C. The role of melatonin treatment in chronic kidney disease. Front Biosci. 2012;17:2644–56.
Quiroz Y, Ferrebuz A, Romero F, Vaziri ND, Rodriguez-Iturbe B. Melatonin ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation, proteinuria, and progression of renal damage in renal mass reduction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;294:F336–44.
Ozbek E, Ilbey Y, Ozbek M, Simsek A, Cekmen M, Somay A. Melatonin attenuates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal injury by reducing oxidative stress, iNOS, MAPK, and NF-kB expression. J Endourol. 2009;23:1165–73.
Nava M, Quiroz Y, Vaziri N, Rodriguez-Iturbe B. Melatonin reduces renal interstitial inflammation and improves hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;284:F447–54.
Escribano BM, Moreno A, Tasset I, Tunez I. Impact of light/dark cycle patterns on oxidative stress in an adriamycin-induced nephropathy model in rats. PLoS One. 2014;9:e97713.
Ishigaki S, Ohashi N, Isobe S, Tsuji N, Iwakura T, Ono M, Sakao Y, Tsuji T, Kato A, Miyajima H, Yasuda H. Impaired endogenous nighttime melatonin secretion relates to intrarenal renin–angiotensin system activation and renal damage in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016;20:878–84.
Koch BC, Van Der Putten K, Van Someren EJ, Wielders JP, TerWee PM, Nagtegaal JE, Gaillard CA. Impairment of endogenous melatonin rhythm is related to the degree of chronic kidney disease (CREAM study). Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:513–9.
Hosgood SA, Mohamed IH, Nicholson ML. The two layer method does not improve the preservation of porcine kidneys. Med Sci Monit. 2011;17:BR27–33.
Baskett JJ, Cockrem JF, Antunovich TA. Sulphatoxymelatonin excretion in older people: relationship to plasma melatonin and renal function. J Pineal Res. 1998;24:58–61.
Isobe S, Ohashi N, Ishigaki S, Tsuji T, Sakao Y, Kato A, Miyajima H, Fujigaki Y, Nishiyama A, Yasuda H. Augmented circadian rhythm of the intrarenal renin–angiotensin systems in anti-thymocyte serum nephritis rats. Hypertens Res. 2016;39:312–20.
Kobori H, Katsurada A, Miyata K, Ohashi N, Satou R, Saito T, Hagiwara Y, Miyashita K, Navar LG. Determination of plasma and urinary angiotensinogen levels in rodents by newly developed ELISA. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;294:F1257–63.
Huang Y, Yamamoto T, Misaki T, Suzuki H, Togawa A, Ohashi N, Fukasawa H, Fujigaki Y, Ichihara A, Nishiyama A, Senbonmatsu T, Ikegaya N, Hishida A. Enhanced intrarenal receptor-mediated prorenin activation in chronic progression anti-thymocyte serum nephritis rats on high salt intake. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012;303:F130–8.
Ohashi N, Isobe S, Ishigaki S, Suzuki T, Ono M, Fujikura T, Tsuji T, Kato A, Ozono S, Yasuda H. Intrarenal renin–angiotensin system activity is augmented after initiation of dialysis. Hypertens Res. 2017;40:364–70.
Ohashi N, Yamamoto T, Huang Y, Misaki T, Fukasawa H, Suzuki H, Togawa A, Suzuki S, Fujigaki Y, Nakagawa T, Nakamura Y, Suzuki F, Kitagawa M, Hishida A. Intrarenal RAS activity and urinary angiotensinogen excretion in anti-thymocyte serum nephritis rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;295:F1512–8.
Zhou H, Kato A, Miyaji T, Yasuda H, Fujigaki Y, Yamamoto T, Yonemura K, Takebayashi S, Mineta H, Hishida A. Urinary marker for oxidative stress in kidneys in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:616–23.
Kobori H, Ozawa Y, Suzuki Y, Nishiyama A. Enhanced intrarenal angiotensinogen contributes to early renal injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:2073–80.
Nishiyama A, Konishi Y, Ohashi N, Morikawa T, Urushihara M, Maeda I, Hamada M, Kishida M, Hitomi H, Shirahashi N, Kobori H, Imanishi M. Urinary angiotensinogen reflects the activity of intrarenal renin–angiotensin system in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26:170–7.
Urushihara M, Ohashi N, Miyata K, Satou R, Acres OW, Kobori H. Addition of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker to CCR2 antagonist markedly attenuates crescentic glomerulonephritis. Hypertension. 2011;58:586–93.
Fujita H, Fujishima H, Chida S, Takahashi K, Qi Z, Kanetsuna Y, Breyer MD, Harris RC, Yamada Y, Takahashi T. Reduction of renal superoxide dismutase in progressive diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:1303–13.
Cao W, Li A, Wang L, Zhou Z, Su Z, Bin W, Wilcox CS, Hou FF. A salt-induced reno-cerebral reflex activates renin–angiotensin systems and promotes CKD progression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26:1619–33.
Isobe S, Ohashi N, Fujikura T, Tsuji T, Sakao Y, Yasuda H, Kato A, Miyajima H, Fujigaki Y. Disturbed circadian rhythm of the intrarenal renin–angiotensin system: relevant to nocturnal hypertension and renal damage. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2015;19:231–9.
Slominski RM, Reiter RJ, Schlabritz-Loutsevitch N, Ostrom RS, Slominski AT. Melatonin membrane receptors in peripheral tissues: distribution and functions. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;351:152–66.
Brzezinski A. Melatonin in humans. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:186–95.
Hu W, Ma Z, Jiang S, Fan C, Deng C, Yan X, Di S, Lv J, Reiter RJ, Yang Y. Melatonin: dawning of a treatment for fibrosis? J Pineal Res. 2016;60:121–31.
Brezniceanu ML, Liu F, Wei CC, Tran S, Sachetelli S, Zhang SL, Guo DF, Filep JG, Ingelfinger JR, Chan JS. Catalase overexpression attenuates angiotensinogen expression and apoptosis in diabetic mice. Kidney Int. 2007;71:912–23.
Godin N, Liu F, Lau GJ, Brezniceanu ML, Chenier I, Filep JG, Ingelfinger JR, Zhang SL, Chan JS. Catalase overexpression prevents hypertension and tubular apoptosis in angiotensinogen transgenic mice. Kidney Int. 2010;77:1086–97.
Abdo S, Shi Y, Otoukesh A, Ghosh A, Lo CS, Chenier I, Filep JG, Ingelfinger JR, Zhang SL, Chan JS. Catalase overexpression prevents nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 stimulation of renal angiotensinogen gene expression, hypertension, and kidney injury in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2014;63:3483–96.
Cao W, Xu J, Zhou ZM, Wang GB, Hou FF, Nie J. Advanced oxidation protein products activate intrarenal renin–angiotensin system via a CD36-mediated, redox-dependent pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18:19–35.
Laflamme AK, Wu L, Foucart S, de Champlain J. Impaired basal sympathetic tone and alpha 1-adrenergic responsiveness in association with the hypotensive effect of melatonin in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens. 1998;11:219–29.
Girouard H, Chulak C, LeJossec M, Lamontagne D, de Champlain J. Chronic antioxidant treatment improves sympathetic functions and beta-adrenergic pathway in the spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 2003;21:179–88.
Matsusaka T, Niimura F, Shimizu A, Pastan I, Saito A, Kobori H, Nishiyama A, Ichikawa I. Liver angiotensinogen is the primary source of renal angiotensin ΙΙ. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:1181–9.
Navar LG, Kobori H, Prieto MC, Gonzalez-Villalobos RA. Intratubular renin–angiotensin system in hypertension. Hypertension. 2011;57:355–62.
Coffman TM, Crowley SD. Kidney in hypertension: guyton redux. Hypertension. 2008;51:811–6.
Kobori H, Nishiyama A. Effects of tempol on renal angiotensinogen production in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;315:746–50.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from Young Investigator Research Projects of Hamamatsu University School of Medicine in 2015 (Awarded to Sayaka Ishigaki).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Animal Committee of the Hamamatsu University School of Medicine (No. 2015088).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Ishigaki, S., Ohashi, N., Matsuyama, T. et al. Melatonin ameliorates intrarenal renin–angiotensin system in a 5/6 nephrectomy rat model. Clin Exp Nephrol 22, 539–549 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-017-1505-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-017-1505-7