Abstract
Background
The renal resistive index (RI) is a Doppler-derived measure that reportedly correlates with renal histological changes and renal disease severity and outcome. The aim of this study was to investigate the factors related to the RI elevation in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods
Using Doppler ultrasonography, RIs were determined in 30 patients with CKD, after which they were correlated with interstitial fibrosis, arteriosclerosis, arteriolosclerosis and peritubular capillary (PTC) density. PTC-positive areas were determined based on CD34 immunostaining. Interstitial fibrosis was detected with Masson trichrome staining. All histological markers were assessed using quantitative and semi-quantitative analyses and evaluated statistically using Pearson correlation tests, unpaired t tests and stepwise multiple regression analysis.
Results
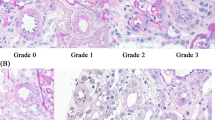
RI correlated positively with age (r = 0.603, p = 0.0004), systolic blood pressure (r = 0.775, p < 0.0001), diastolic blood pressure (r = 0.575, p = 0.001), interstitial fibrosis (r = 0.381, p = 0.038) and arteriosclerosis (r = 0.520, p = 0.003), and negatively with creatinine clearance (r = −0.471, p = 0.009) and CD34+ (PTC) areas (r = −0.437, p = 0.016). Patients with hypertension or diabetes mellitus showed higher RIs (p < 0.05) than those without the ailments. Multivariate analysis showed PTC and arteriosclerosis to be independent variables correlating with RI (r 2 = 0.321, p < 0.05).
Conclusions
To our knowledge, this is the first report of using RI measurements to evaluate peritubular capillary loss. Our findings indicate that increases in RI are associated with both arteriosclerosis and loss of PTCs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rifkin MD, Needleman L, Pasto ME, Kurtz AB, Foy PM, McGlynn E, et al. Evaluation of renal transplant rejection by duplex Doppler examination: value of the resistive index. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987;148:759–62.
Radermacher J, Mengel M, Ellis S, Stuht S, Hiss M, Schwarz A, et al. The renal arterial resistance index and renal allograft survival. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:115–24.
Terry JD, Rysavy JA, Frick MP. Intrarenal Doppler: characteristics of aging kidneys. J Ultrasound Med. 1992;11:647–51.
Shimizu Y, Itoh T, Hougaku H, Nagai Y, Hashimoto H, Sakaguchi M, et al. Clinical usefulness of duplex ultrasonography for the assessment of renal arteriosclerosis in essential hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res. 2001;24:13–7.
Florczak E, Januszewicz M, Januszewicz A, Prejbisz A, Kaczmarska M, Michałowska I, et al. Relationship between renal resistive index and early target organ damage in patients with never-treated essential hypertension. Blood Press. 2009;18:55–61.
Soldo D, Brkljacic B, Bozikov V, Drinkovic I, Hauser M. Diabetic nephropathy. Comparison of conventional and duplex Doppler ultrasonographic findings. Acta Radiol. 1997;38:296–302.
Ishimura E, Nishizawa Y, Kawagishi T, Okuno Y, Kogawa K, Fukumoto S, et al. Intrarenal hemodynamic abnormalities in diabetic nephropathy measured by duplex Doppler sonography. Kidney Int. 1997;51:1920–7.
Sugiura T, Wada A. Resistive index predicts renal prognosis in chronic kidney disease: results of a 4-year follow-up. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011;15:114–20.
Bigé N, Lévy PP, Callard P, Faintuch JM, Chigot V, Jousselin V, et al. Renal arterial resistive index is associated with severe histological changes and poor renal outcome during chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2012;13:139.
Rigler AA, Vizjak A, Ferluga D, Kandus A, Buturović-Ponikvar J. Ultrasonography parameters and histopathology findings in transplanted kidney. Transplant Proc. 2013;45:1630–4.
Sugiura T, Nakamori A, Wada A, Fukuhara Y. Evaluation of tubulointerstitial injury by Doppler ultrasonography in glomerular diseases. Clin Nephrol. 2004;61:119–26.
Platt JF, Rubin JM, Ellis JH. Lupus nephritis: predictive value of conventional and Doppler US and comparison with serologic and biopsy parameters. Radiology. 1997;203:82–6.
Ikee R, Kobayashi S, Hemmi N, Imakiire T, Kikuchi Y, Moriya H, et al. Correlation between the resistive index by Doppler ultrasound and kidney function and histology. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;46:603–9.
Mostbeck GH, Kain R, Mallek R, Derfler K, Walter R, Havelec L, et al. Duplex Doppler sonography in renal parenchymal disease histopathologic correlation. J Ultrasound Med. 1991;10:189–94.
Platt JF, Ellis JH, Rubin JM, DiPietro MA, Sedman AB. Intrarenal arterial Doppler sonography in patients with nonobstructive renal disease: correlation of resistive index with biopsy findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990;154:1223–7.
Nangaku M. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial injury in the kidney: final common pathways to end-stage renal failure. Intern Med. 2004;43:9–17.
Choi YJ, Chakraborty S, Nguyen V, Nguyen C, Kim BK, Shim SI, et al. Peritubular capillary loss is associated with chronic tubulointerstitial injury in human kidney: altered expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Hum Pathol. 2000;31:1491–7.
Kang D-H, Kanellis J, Hugo C, Truong L, Anderson S, Kerjaschki D, et al. Role of the microvascular endothelium in progressive renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:806–16.
Basile DP, Donohoe D, Roethe K, Osborn JL. Renal ischemic injury results in permanent damage to peritubular capillaries and influences long-term function. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001;281:F887–99.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, N., Kimura, H., Takahashi, N. et al. Renal resistive index correlates with peritubular capillary loss and arteriosclerosis in biopsy tissues from patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 19, 1114–1119 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-015-1116-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-015-1116-0