Abstract
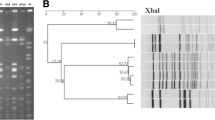
An outbreak of Klebsiella pneumoniae resistant to broadspectrum cephalosporins occurred in a hospital in the Kinki area in Japan. During 18 months, from February 1998 to July 1999, 23 strains were isolated from 21 patients (10 with pneumonia, 4 with urinary tract infection, 1 with sepsis, 1 with vaginosis, 1 with a wound infection, and 1 with both pneumonia and sepsis; 3 patients showed noninfective colonization with K. pneumoniae) in seven wards, including the intensive care unit. MEN-1-derived gene was detected by polymerase chain reaction from the majority of the strains. Ninety-nine strains of K. pneumoniae were isolated during this period. The isolation rate of K. pneumoniae resistant to broad spectrum cephalosporins was 21%. We distinguished three clones by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis, and one of them was isolated from 18 patients. The presence of an R-plasmid of more than 160 kb was confirmed by plasmid analysis, but it was not possible to obtain transconjugants from all strains. This outbreak of K. pneumoniae was immediately confirmed by genetic analysis, and it was promptly ended by the infection control procedures. This is the first hospital outbreak of MEN-1-producing K. pneumoniae in Japan.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: August 17, 2000 / Accepted: January 16, 2001
About this article
Cite this article
Komatsu, M., Ikeda, N., Aihara, M. et al. Hospital outbreak of MEN-1-derived extended spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae . J Infect Chemother 7, 94–101 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s101560100015
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s101560100015