Abstract
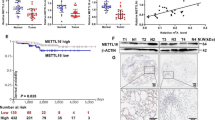
In this study, we aimed to explore the molecular role of Deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 4 (DTX4) in thyroid cancer (TC) both in vitro and in vivo. The expression level of DTX4 in TC tissues was compared using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. We subsequently evaluated cell proliferation and migration in DTX4 knock down or DTX4 overexpression TC cell lines (TPC-1 and K1) by CCK-8, cell colony formation, and transwell assays. RNA sequencing and KEGG analysis were employed to identify potential genes that interact with DTX4. Our results showed that DTX4 was expressed at higher levels in both TC tissues and cells compared to normal controls. Knock down of DTX4 expression significantly inhibited TC cell progression in vitro. Furthermore, knockdown of endogenous DTX4 by shDTX4 markedly abrogated tumor growth, with significantly smaller tumor size and lower tumor weight in the shDTX4 group compared to the shCtrl group. Conversely, overexpression of DTX4 enhanced TC cell proliferation and migration. Through RNA sequencing, we identified 590 Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs), with stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD) ranking as the top gene. A positive correlation between DTX4 and SCD was observed in TC samples. Additionally, treatment with an SCD inhibitor, A939572, significantly rescued the enhanced growth effect induced by DTX4 overexpression. In conclusion, this study demonstrated that DTX4 promotes TC progression through SCD, indicating that the DTX4/SCD axis could be a promising target for TC therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset used and/or analyzed in this study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Burger AM, Seth AK (2004) The ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation pathway in cancer: therapeutic implications. Eur J Cancer 40:2217–2229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2004.07.006
Cui J, Li Y, Zhu L, Liu D, Songyang Z, Wang HY, Wang RF (2012) NLRP4 negatively regulates type I interferon signaling by targeting the kinase TBK1 for degradation via the ubiquitin ligase DTX4. Nat Immunol 13:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2239
Deng M, Tam JW, Wang L et al (2020) TRAF3IP3 negatively regulates cytosolic RNA induced anti-viral signaling by promoting TBK1 K48 ubiquitination. Nat Commun 11:2193. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16014-0
Du L, Zhao Z, Zheng R et al (2020) Epidemiology of thyroid cancer: Incidence and mortality in China, 2015. Front Oncol 10:1702. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.01702
He TS, Huang J, Chen T, Zhang Z, Cai K, Yu J, Xu LG (2021) The Kinase MAP4K1 inhibits cytosolic RNA-induced antiviral signaling by promoting proteasomal degradation of TBK1/IKKepsilon. Microbiol Spectr 9:e0145821. https://doi.org/10.1128/Spectrum.01458-21
da Huang W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Igal RA (2016) Stearoyl CoA desaturase-1: New insights into a central regulator of cancer metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 1861:1865–1880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.09.009
Kanehisa M (2002) The KEGG database. Novartis Found Symp 247:91–101; discussion 101–103, 119–128, 244–152. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12539951
Li J, Hou H, Sun J, Ding J, Xu Y, Li G (2023) Systematic pan-cancer analysis identifies transmembrane protein 158 as a potential therapeutic, prognostic and immunological biomarker. Funct Integr Genomics 28;23(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01032-0
Lin X, Sun B, Zhu D et al (2016) Notch4+ cancer stem-like cells promote the metastatic and invasive ability of melanoma. Cancer Sci 107:1079–1091. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12978
Liu M, Zhu K, Qian X, Li W (2016) Identification of miRNA/mRNA-Negative regulation pairs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Med Sci Monit 22:2215–2234. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.896047
Liu WM, Laux H, Henry JY, Bolton TB, Dalgleish AG, Galustian C (2010) A microarray study of altered gene expression in colorectal cancer cells after treatment with immunomodulatory drugs: differences in action in vivo and in vitro. Mol Biol Rep 37:1801–1814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9614-3
Liu X, Xian Y, Xu H, Hu M, Che K, Liu X, Wang H (2021) The associations between Deltex1 and clinical characteristics of breast cancer. Gland Surg 10:3116–3127. https://doi.org/10.21037/gs-21-739
Oatman N, Dasgupta N, Arora P et al. (2021) Mechanisms of stearoyl CoA desaturase inhibitor sensitivity and acquired resistance in cancer. Sci Adv 7. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abd7459
Papadopoulos T, Casemayou A, Neau E et al (2017) Systems biology combining human- and animal-data miRNA and mRNA data identifies new targets in ureteropelvic junction obstruction. BMC Syst Biol 11:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12918-017-0411-7
Paton CM, Ntambi JM (2009) Biochemical and physiological function of stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297:E28-37. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.90897.2008
Schumacher EC, Gotze S, Kordes C, Benes V, Haussinger D (2017) Combined methylome and transcriptome analysis during rat hepatic stellate cell activation. Stem Cells Dev 26:1759–1770. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2017.0128
She K, Fang S, Du W et al (2019) SCD1 is required for EGFR-targeting cancer therapy of lung cancer via re-activation of EGFR/PI3K/AKT signals. Cancer Cell Int 19:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0809-y
Skrypek K, Balog S, Eriguchi Y, Asahina K (2021) Inhibition of Stearoyl-CoA desaturase induces the unfolded protein response in pancreatic tumors and suppresses their growth. Pancreas 50:219–226. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000001737
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK et al. (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15545-15550. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Takano T (2017) Natural history of thyroid cancer [Review]. Endocr J 64:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.EJ17-0026
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C, Zhang Z (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W98–W102. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx247
Tesfay L, Paul BT, Konstorum A et al (2019) Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 protects ovarian cancer cells from ferroptotic cell death. Cancer Res 79:5355–5366. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0369
Viatour P, Ehmer U, Saddic LA et al (2011) Notch signaling inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma following inactivation of the RB pathway. J Exp Med 208:1963–1976. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20110198
Wang C, Shi M, Ji J et al (2020) Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD1) facilitates the growth and anti-ferroptosis of gastric cancer cells and predicts poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Aging (Albany NY) 12:15374–15391. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103598
Wang HC, Perry SS, Sun XH (2009) Id1 attenuates Notch signaling and impairs T-cell commitment by elevating Deltex1 expression. Mol Cell Biol 29:4640–4652. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00119-09
Wang L, Sun X, He J, Liu Z (2021) Functions and molecular mechanisms of deltex family ubiquitin E3 ligases in development and disease. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:706997. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.706997
Wu S, Shen SH, Lu F et al (2022) Bromodomain containing 4 transcriptionally activated Deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 2 contributes to glioma progression and predicts an unfavorable prognosis. Ann Transl Med 10:313. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-22-555
Xie F, Wang J, Zhang B (2023) RefFinder: a web-based tool for comprehensively analyzing and identifying reference genes. Funct Integr Genomics 23:125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01055-7
Xu H, Liang S, Hu J, Liu W, Dong Z, Wei S (2022) Deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 3 inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and regulates cell cycle progression via upregulating E2F transcription factor 1. Mol Biol Rep 49:1661–1668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06916-7
Yu Z, Zhou Y, Li Y, Dong Z (2023) Integration of clinical and spatial data to explore lipid metabolism-related genes for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in gliomas. Funct Integr Genomics 23:2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01010-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZY designed the study. YC carried out the experiment and wrote the paper. JL and NB analyzed the data and discussed the result. YC and ZY revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent participate
Not applicable.
Animal Ethics
The experimental procedure followed the United States National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH Publication No. 85–23, revised 1985). The study protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Center for Integrative and Translational Medicine, Shandong Public Health Clinical Center (NO. ECAESDUSM 20123011).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Y., Luo, J., Bai, N. et al. Deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 4 promotes thyroid cancer progression through stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 280 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01215-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01215-9