Abstract
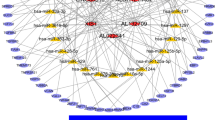
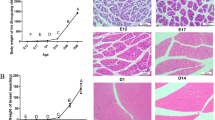
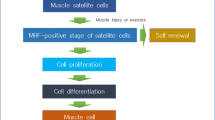
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is an X-linked genetic neuromuscular disease that is characterized by progressive muscle wasting and by defects in the regenerative capacity and inflammatory infiltration of muscle. Many noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) participate in the pathophysiological mechanisms of this disease. To explore the role of circular RNAs (circRNAs), a type of ncRNAs, in DMD, microarray analysis was performed to explore the expression patterns of circRNAs in the gastrocnemius muscles in mdx mice, a DMD animal model, and C57 mice. The microarray data were validated by qRT-PCR. Further, gene ontology (GO) and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis were performed to predict the function of the differentially expressed circRNAs (DEcRNAs). A circRNA/microRNA (miRNA) interaction network was predicted by bioinformatics. We also predicted the protein-coding ability of the circRNAs based on their N6-methyladenosine motifs and open-reading frames. We identified 197 differentially expressed circRNAs between mdx mice and C57 mice. Of the 197 DEcRNAs, 6 circRNAs were randomly selected to validate the microarray data, and twenty-two circRNAs were randomly selected to construct a circRNA/miRNA interaction network. Bioinformatics analysis showed that the linear counterparts of the DEcRNAs were mainly associated with muscle structure, nervous system development, and the cAMP signaling pathway. A total of 189 circRNAs were predicted to have protein-coding potential, and there were 98 circRNAs that could potentially be translated into polypeptides with 150 or more amino acids. This work described the expression pattern of circRNAs in mdx mice and indicated that circRNAs may play pivotal roles in the pathophysiological mechanisms of DMD.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aranmolate A, Tse N, Colognato H (2017) Myelination is delayed during postnatal brain development in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. BMC Neurosci 18:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-017-0381-0
Ashwal-Fluss R et al (2014) circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 56:55–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.019
Batchelor CL, Winder SJ (2006) Sparks, signals and shock absorbers: how dystrophin loss causes muscular dystrophy. Trends Cell Biol 16:198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2006.02.001
Bulaklak K et al (2018) MicroRNA-206 downregulation improves therapeutic gene expression and motor function in mdx mice. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 12:283–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2018.05.011
Campbell KP, Kahl SD (1989) Association of dystrophin and an integral membrane glycoprotein. Nature 338:259–262. https://doi.org/10.1038/338259a0
Chen R et al (2018) Expression of circular RNAs during C2C12 myoblast differentiation and prediction of coding potential based on the number of open reading frames and N6-methyladenosine motifs. Cell Cycle 17:1832–1845. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2018.1502575
Costelli P, Reffo P, Penna F, Autelli R, Bonelli G, Baccino FM (2005) Ca(2+)-dependent proteolysis in muscle wasting. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:2134–2146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2005.03.010
Dey BK, Mueller AC, Dutta A (2014) Long non-coding RNAs as emerging regulators of differentiation, development, and disease. Transcription 5:e944014. https://doi.org/10.4161/21541272.2014.944014
Doorenweerd N et al (2014) Reduced cerebral gray matter and altered white matter in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann Neurol 76:403–411. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24222
Ervasti JM, Ohlendieck K, Kahl SD, Gaver MG, Campbell KP (1990) Deficiency of a glycoprotein component of the dystrophin complex in dystrophic muscle. Nature 345:315–319. https://doi.org/10.1038/345315a0
Greco S, Cardinali B, Falcone G, Martelli F (2018) Circular RNAs in muscle function and disease. Int J Mol Sci:19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113454
Hentze MW, Preiss T (2013) Circular RNAs: splicing’s enigma variations. EMBO J 32:923–925. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2013.53
Hoffman EP, Brown RH Jr, Kunkel LM (1987) Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell 51:919–928
Huganir RL, Miles K (1989) Protein phosphorylation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 24:183–215. https://doi.org/10.3109/10409238909082553
Jeck WR et al (2013) Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 19:141–157. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.035667.112
Johnson BD, Scheuer T, Catterall WA (2005) Convergent regulation of skeletal muscle Ca2+ channels by dystrophin, the actin cytoskeleton, and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:4191–4196. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0409695102
Legnini I et al (2017) Circ-ZNF609 Is a Circular RNA that can be translated and functions in myogenesis. Mol Cell 66:22–37 e29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.017
Li H et al (2018a) circFGFR4 promotes differentiation of myoblasts via binding miR-107 to relieve its inhibition of Wnt3a. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 11:272–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2018.02.012
Li H et al (2018b) CircFUT10 reduces proliferation and facilitates differentiation of myoblasts by sponging miR-133a. J Cell Physiol 233:4643–4651. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26230
Luise M, Presotto C, Senter L, Betto R, Ceoldo S, Furlan S, Salvatori S, Sabbadini RA, Salviati G (1993) Dystrophin is phosphorylated by endogenous protein kinases. Biochem J 293(Pt 1):243–247. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2930243
Mendell JR et al (2012) Evidence-based path to newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann Neurol 71:304–313. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.23528
Morgoulis D, Berenstein P, Cazacu S, Kazimirsky G, Dori A, Barnea ER, Brodie C (2019) sPIF promotes myoblast differentiation and utrophin expression while inhibiting fibrosis in Duchenne muscular dystrophy via the H19/miR-675/let-7 and miR-21 pathways. Cell Death Dis 10:82. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1307-9
Pamudurti NR et al (2017) Translation of CircRNAs Mol Cell 66:9-21 e27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.021
Perry MM, Muntoni F (2016) Noncoding RNAs and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Epigenomics 8:1527–1537. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi-2016-0088
Ricotti V et al (2016) Neurodevelopmental, emotional, and behavioural problems in Duchenne muscular dystrophy in relation to underlying dystrophin gene mutations. Dev Med Child Neurol 58:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.12922
Rybak-Wolf A et al (2015) Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant, conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol Cell 58:870–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.027
Song T et al (2019) CircRNA hsa_circRNA_101996 increases cervical cancer proliferation and invasion through activating TPX2 expression by restraining miR-8075. J Cell Physiol 234:14296–14305. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28128
Su H et al (2019) Circular RNA cTFRC acts as the sponge of MicroRNA-107 to promote bladder carcinoma progression. Mol Cancer 18:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0951-0
Turner PR, Westwood T, Regen CM, Steinhardt RA (1988) Increased protein degradation results from elevated free calcium levels found in muscle from mdx mice. Nature 335:735–738. https://doi.org/10.1038/335735a0
Vicens Q, Westhof E (2014) Biogenesis of circular RNAs. Cell 159:13–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.005
Wang R et al (2018) EIF4A3-induced circular RNA MMP9 (circMMP9) acts as a sponge of miR-124 and promotes glioblastoma multiforme cell tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer 17:–166. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0911-0
Wu R et al (2015) MicroRNA-431 accelerates muscle regeneration and ameliorates muscular dystrophy by targeting Pax7 in mice. Nat Commun 6:7713. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8713
Yang Y et al (2017) Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N(6)-methyladenosine. Cell Res 27:626–641. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.31
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jinfu Lin, Hongjie Li, Jingyan Chen, and Baihong Dong for their technical assistance.
Funding
The work was supported by the grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2017A030313850); the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2016A030310283); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81701240); Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Major Neurological Diseases (2017B030314103); The Southern China International Cooperation Base for Early Intervention and Functional Rehabilitation of Neurological Diseases (2015B050501003); Guangdong Provincial Engineering Center for Major Neurological Disease Treatment; and Guangdong Provincial Translational Medicine Innovation Platform for Diagnosis and Treatment of Major Neurological Disease.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Experimentation Committee of Sun Yat-Sen University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Z., Liu, Y., Fang, X. et al. Comprehensive analysis of the expression profile of circRNAs and their predicted protein-coding ability in the muscle of mdx mice. Funct Integr Genomics 20, 397–407 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-019-00724-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-019-00724-w