Abstract
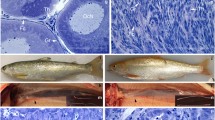
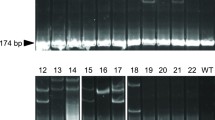
Gene targeting is a powerful tool for analyzing gene function. Recently, new technology for gene targeting using engineered zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs) has been described in fish species. However, it has not yet been widely used for cold water and slow developing species, such as Salmonidae. Here, we present the results of successful ZFN-mediated disruption of the sex-determining gene sdY (sexually dimorphic on the Y chromosome) in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Three pairs of ZFN mRNA targeted to different regions of the sdY gene were injected into fertilized rainbow trout eggs. Sperm from 1-year-old male founders (parental generation one or P1) carrying a ZFN-induced mutation in their germline were then used to produce F1 non-mosaic animals. In these F1 populations, we characterized 14 different mutations in the sdY gene, including one mutation leading to the deletion of leucine 43 (L43) and 13 mutations at other target sites that had different effects on the SdY protein, i.e., amino acid insertions, deletions, and frameshift mutations producing premature stop codons in the mRNA. The gonadal phenotype analysis of the F1-mutated animals revealed that the single L43 amino acid deletion did not lead to a male-to-female sex reversal, but all other mutations induced a clear ovarian phenotype. These results show that targeted gene disruption using ZFN is efficient in rainbow trout but depends on the ZFN design. We also characterized new sdY mutations resulting in male-to-female sex reversal, and we conclude that L43 seems dispensable for SdY function.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amacher SL (2008) Emerging gene knockout technology in zebrafish: zinc-finger nucleases. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 7:460–464
Ansai S, Ochiai H, Kanie Y, Kamei Y, Gou Y, Kitano T, Yamamoto T, Kinoshita M (2012) Targeted disruption of exogenous EGFP gene in medaka using zinc-finger nucleases. Dev Growth Differ 54:546–556
Beumer K, Bhattacharyya G, Bibikova M, Trautman JK, Carroll D (2006) Efficient gene targeting in Drosophila with zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics 172:2391–2403
Bibikova M, Golic M, Golic KG, Carroll D (2002) Targeted chromosomal cleavage and mutagenesis in Drosophila using zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics 161:1169–1175
Boonanuntanasarn S, Yoshizaki G, Takeuchi T (2003) Specific gene silencing using small interfering RNAs in fish embryos. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 310:1089–1095
Boonanuntanasarn S, Yoshizaki G, Takeuchi Y et al (2002) Gene knock-down in rainbow trout embryos using antisense morpholino phosphorodiamidate oligonucleotides. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 4:256–266
Le Cam A, Bobe J, Bouchez O, Cabau C, Kah O, Klopp C, Lareyre JJ, Le Guen I, Lluch J, Montfort J, Moreews F, Nicol B, Prunet P, Rescan PY, Servili A, Guiguen Y (2012) Characterization of rainbow trout gonad, brain and gill deep cDNA repertoires using a Roche 454-Titanium sequencing approach. Genetics 500:32–39
Capecchi MR (2005) Gene targeting in mice: functional analysis of the mammalian genome for the twenty-first century. Nat Rev Genet 6:507–512
Carroll D (2011) Genome engineering with zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics 188:773–782
Chevassus B, Devaux A, Chourrout D, Jalabert B (1988) Production of YY rainbow trout males by self-fertilization of induced hermaphrodites. J Hered 79:89–92
Dillin A (2003) The specifics of small interfering RNA specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:6289–6291
Dong Z, Ge J, Li K, Xu Z, Liang D, Li J, Li J, Jia W, Li Y, Dong X, Cao S, Wang X, Pan J, Zhao Q (2011) Heritable targeted inactivation of myostatin gene in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) using engineered zinc finger nucleases. PloS one 6:e28897
Doyon Y, McCammon JM, Miller JC, Faraji F, Ngo C, Katibah GE, Amora R, Hocking TD, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Amacher SL (2008) Heritable targeted gene disruption in zebrafish using designed zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 26:702–708
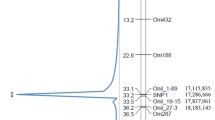
Gharbi K, Gautier A, Danzmann RG, Gharbi S, Sakamoto T, Høyheim B, Taggart JB, Cairney M, Powell R, Krieg F, Okamoto N, Ferguson MM, Holm LE, Guyomard R (2006) A linkage map for brown trout (Salmo trutta): chromosome homeologies and comparative genome organization with other salmonid fish. Genetics 172:2405–2419
Govoroun M, Le Gac F, Guiguen Y (2006) Generation of a large scale repertoire of expressed sequence tags (ESTs) from normalised rainbow trout cDNA libraries. BMC genomics 7:196
Guiguen Y, Baroiller JF, Ricordel MJ, Iseki K, Mcmeel OM, Martin SA, Fostier A (1999) Involvement of estrogens in the process of sex differentiation in two fish species: the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and a tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Mol Reprod Dev 54:154–162
Heasman J (2002) Morpholino oligos: making sense of antisense? Dev Biol 243:209–214
Koop BF, von Schalburg KR, Leong J, Walker N, Lieph R, Cooper GA, Robb A, Beetz-Sargent M, Holt RA, Moore R, Brahmbhatt S, Rosner J, Rexroad CE 3rd, McGowan CR, Davidson WS (2008) A salmonid EST genomic study: genes, duplications, phylogeny and microarrays. BMC genomics 9:545
McManus MT, Sharp PA (2002) Gene silencing in mammals by small interfering RNAs. Nature Rev Genet 3:737–747
Meng X, Noyes MB, Zhu LJ, Lawson ND, Wolfe SA (2008) Targeted gene inactivation in zebrafish using engineered zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 26:695–701
Metzker ML (2010) Sequencing technologies—the next generation. Nat Rev Genet 11:31–46
Nakajima K, Nakajima T, Takase M, Yaoita Y (2012) Generation of albino Xenopus tropicalis using zinc-finger nucleases. Dev Growth Differ 54:777–784
Rexroad CE, Lee Y, Keele JW, Karamycheva S, Brown G, Koop B, Gahr SA, Palti Y, Quackenbush J (2003) Sequence analysis of a rainbow trout cDNA library and creation of a gene index. Cytogenet Genome Res 102:347–354
Salem M, Rexroad CE, Wang J, Thorgaard GH, Yao J (2010) Characterization of the rainbow trout transcriptome using Sanger and 454-pyrosequencing approaches. BMC Genomics 11:564
Shukla VK, Doyon Y, Miller JC, DeKelver RC, Moehle EA, Worden SE, Mitchell JC, Arnold NL, Gopalan S, Meng X, Choi VM, Rock JM, Wu YY, Katibah GE, Zhifang G, McCaskill D, Simpson MA, Blakeslee B, Greenwalt SA, Butler HJ, Hinkley SJ, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD (2009) Precise genome modification in the crop species Zea mays using zinc-finger nucleases. Nature 459:437–441
Thorgaard GH, Bailey GS, Williams D, Buhler DR, Kaattari SL, Ristow SS, Hansen JD, Winton JR, Bartholomew JL, Nagler JJ, Walsh PJ, Vijayan MM, Devlin RH, Hardy RW, Overturf KE, Young WP, Robison BD, Rexroad C, Palti Y (2002) Status and opportunities for genomics research with rainbow trout. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 133:609–646
Tuschl T (2002) Expanding small RNA interference. Nature Biotechnol 20:446–448
Watanabe M, Umeyama K, Matsunari H, Takayanagi S, Haruyama E, Nakano K, Fujiwara T, Ikezawa Y, Nakauchi H, Nagashima H (2010) Knockout of exogenous EGFP gene in porcine somatic cells using zinc-finger nucleases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 402:14–18
Whyte JJ, Zhao J, Wells KD, Samuel MS, Whitworth KM, Walters EM, Laughlin MH, Prather RS (2011) Gene targeting with zinc finger nucleases to produce cloned eGFP knockout pigs. Mol Reprod Dev 78:2
Yano A, Guyomard R, Nicol B, Jouanno E, Quillet E, Klopp C, Cabau C, Bouchez O, Fostier A, Guiguen Y (2012) An immune-related gene evolved into the master sex-determining gene in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Curr Biol 22:1423–1428
Yano A, Nicol B, Jouanno E, Quillet E, Fostier A, Guyomard R, Guiguen Y (2013) The sexually dimorphic on the Y-chromosome gene (sdY) is a conserved male-specific Y-chromosome sequence in many salmonids. Evol Appl. doi:10.1111/eva.12032
Yoshizaki G, Oshiro T, Takashima F (1991) Introduction of carp α-globin gene into rainbow trout. Nippon Suisan Gakk 57:819–824
Young JJ, Cherone JM, Doyon Y, Ankoudinova I, Faraji FM, Lee AH, Ngo C, Guschin DY, Paschon DE, Miller JC, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Harland RM, Zeitler B (2011) Efficient targeted gene disruption in the soma and germ line of the frog Xenopus tropicalis using engineered zinc-finger nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:7052–7057
Yu S, Luo J, Song Z, Ding F, Dai Y, Li N (2011) Highly efficient modification of beta-lactoglobulin (BLG) gene via zinc-finger nucleases in cattle. Cell Res 21:1638–1640
Acknowledgments
We thank the LPGP experimental facility staff for their help in maintaining our ZFN rainbow trout. This work was supported by funds from INRA, ANR (SVSE 7 2011, project SDS), and the European Commission Seventh Framework Program (222719–LIFECYCLE). A.Y. and B.N were supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from the INRA GA and PHASE departments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yano, A., Nicol, B., Jouanno, E. et al. Heritable Targeted Inactivation of the Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Master Sex-Determining Gene Using Zinc-Finger Nucleases. Mar Biotechnol 16, 243–250 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-013-9546-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-013-9546-8