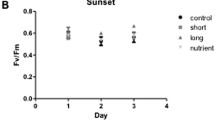
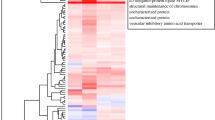
Abstract
Coral bleaching is caused by the loss of symbiont zooxanthellae and/or decrease in their pigments. Since the algal symbionts provide the energy basis for corals and whole reefs, their loss or impairment of function leads to widespread mortality. This phenomenon has been documented numerous times in recent years, and has extensively damaged coral reefs all over the world. Temperature has been found to be the major cause of bleaching, and rising sea temperatures have increased the frequency of these catastrophic episodes. To characterize the response of zooxanthellae to temperature stress at the molecular level, we used the mRNA differential display technique to monitor changes in the abundance of specific mRNA species in the cell under different temperature conditions. Axenically grown zooxanthellae were exposed to a range of temperatures (21.7, 17, 26°C) before extraction of their mRNA. Of numerous differentially expressed sequences, seven mRNA species were amplified by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequenced. One of those sequences was positively identified as encoding a multifunction cell surface aminopeptidase, dipeptidyl peptidase IV, which is active in cell matrix adhesion. Our work illustrates the power of the differential display technique as a useful tool to study the response of zooxanthellae to stressors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
SF Altschul MS Boguski W Gish JC Wootton (1994) ArticleTitleIssues in searching molecular sequence databases Nat Genet 6 119–129 Occurrence Handle10.1038/ng0294-119
A Banaszak TC LaJeunesse RK Trench (2000) ArticleTitleThe synthesis of mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) by cultured, symbiotic dinoflagellates J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 249 219–233 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-0981(00)00192-1
E Banin Y Ben-Haim T Israely Y Loya E Rosenberg (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of the environment on the bacterial bleaching of corals Water Air Soil Pollut 123 337–352 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1005274331988
B Bauvois (1988) ArticleTitleA collagen-binding glycoprotein on the surface of mouse fibroblasts is identified as dipeptidyl peptidase-IV Biochem J 252 723–731
Y Ben-Haim E Banim A Kushmaro Y Loya E Rosenberg (1999) ArticleTitleInhibition of photosynthesis and bleaching of zooxanthellae by the coral pathogen Vibrio shiloi Environ Microbiol 1 223–229 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1462-2920.1999.00027.x
R Bhagooli M Hidaka (2003) ArticleTitleComparison of stress susceptibility of in hospite and isolated zooxanthellae among five coral species J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 291 181–197
NA Black R Voellmy AM Szmant (1995) ArticleTitleHeat shock protein induction in Montastraea faveolata and Aiptasia pallida exposed to elevated temperature Biol Bull 188 234–240
O Choresh E Ron Y Loya (2001) ArticleTitleThe 60-kDa heat shock protein (HSP60) of the sea anemone Anemonia viridis: a potential early warning system for environmental changes Mar Biotechnol 3 501–508 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10126-001-0007-4
F Corpet (1988) ArticleTitleMultiple sequence alignment with hierarchical-clustering Nucleic Acids Res 16 10881–10890
AE Douglas (2003) ArticleTitleCoral bleaching—how and why? Mar Pollut Bull 46 385–392 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00037-7
K Fitt BE Brown ME Warner RP Dunne (2001) ArticleTitleCoral bleaching: interpretation of thermal tolerance limits and thermal thresholds in tropical corals Coral Reefs 20 51–65 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003380100146
RD Gates G Baghdasarian L Muscatine (1992) ArticleTitleTemperature stress causes host cell detachment in symbiotic cnidarians—implications for coral bleaching Biol Bull 182 324–332
MG Gleason (1993) ArticleTitleEffects of disturbance on coral communities bleaching in Moorea, French Polynesia Coral Reefs 12 193–201 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00334479
PW Glynn (1993) ArticleTitleCoral reef bleaching: ecological perspective Coral Reefs 12 1–17 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00303779
O Hoegh-Guldberg (1999) ArticleTitleCoral bleaching, climate change and the future of the world's coral reefs Mar Freshwater Res 50 839–866 Occurrence Handle10.1071/MF99078
O Hoegh-Guldberg (2000) ArticleTitleGlobal climate change and the thermal tolerance of corals Galaxea, JCRS 2 1–12
O Hoegh-Guldberg GJ Smith (1989) ArticleTitleThe effect of sudden changes in temperature, light and salinity on the population density and export of zooxanthellae from the reef corals Stylophora pistillata Esper and Seriatopora hystrix Dana J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 129 279–303 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-0981(89)90109-3
M Ishikura K Hagiwara K Takishita M Haga K Iwai T Maruyama (2004) ArticleTitleIsolation of new Symbiodinium strains from Tridacnid giant clam (Tridacna crocea) and sea slug (Pteraeolidia ianthina) using culture medium containing giant clam tissue homogenate Mar Biotechnol 6 378–385 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10126-004-1800-7
PL Jokiel (2004) Temperature stress and coral bleaching E Rosenberg Y Loya (Eds) Coral Health and Disease Springer Berlin 401–426
PL Jokiel SL Coles (1990) ArticleTitleResponse of Hawaiian and other Indo-Pacific reef corals to elevated temperature Coral Reefs 8 155–162 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00265006
PL Jokiel RH York SuffixJr (1982) ArticleTitleSolar ultraviolet photobiology of the reef coral Pocillopora damicornis and symbiotic zooxanthellae Bull Mar Sci 32 301–315
RJ Jones (1997) ArticleTitleZooxanthellae loss as a bioassay for assessing stress in corals Mar Ecol Prog Ser 149 163–171
S Karako-Lampert DJ Katcoff Y Achituv Z Dubinsky N Stambler (2005) ArticleTitlePhysiology changes of Symbiodinium microadriaticum clade B as response to different environmental conditions J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 318 11–20 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.jembe.2004.11.024
A Kushmaro Y Loya M Fine E Rosenberg (1996) ArticleTitleBacterial infection and coral bleaching Nature 380 396 Occurrence Handle10.1038/380396a0
MP Lesser (1996) ArticleTitleExposure of symbiotic dinoflagellates to elevated temperatures and ultraviolet radiation causes oxidative stress and inhibits photosynthesis in symbiotic dinoflagellates Limnol Oceanogr 41 271–283 Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.1996.41.2.0271
P Liang AB Pardee (1992) ArticleTitleDifferential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction Science 257 967–971
Y Loya K Sakai K Yamazato Y Nakano H Sambali R Woesik Particlevan (2001) ArticleTitleCoral bleaching: the winners and the losers Ecol Lett 4 122–131 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1461-0248.2001.00203.x
PA Marshall AH Baird (2000) ArticleTitleBleaching of corals on the Great Barrier Reef: differential susceptibilities among taxa Coral Reefs 19 155–163 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003380000086
JJA McLaughlin PA Zahl (1959) ArticleTitleAxentic zooxanthellae from various invertebrate hosts Ann NY Acad Sci 77 55–72
WJ Meehan GK Ostrander (1997) ArticleTitleCoral bleaching: a potential biomarker of environmental stress J Toxicol Environ Health 50 529–552 Occurrence Handle10.1080/009841097160258
MB Morgan TW Snell (2002) ArticleTitleCharacterizing stress gene expression in reef-building corals exposed to the mosquitoside dibrom Mar Pollut Bull 44 1206–1218 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00177-7
L Muscatine JW Porter (1977) ArticleTitleReef corals: mutualistic symbioses adapted to nutrient poor environments BioScience 27 454–460 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1297526
GA Piazza HM Callanan J Mowery DC Hixson (1989) ArticleTitleEvidence for a role of depeptidyl peptidase-IV in fibronectin-mediated interactions of hepatocytes with extracellular-matrix Biochem J 262 327–334
JW Porter SK Lewis KG Porter (1999) ArticleTitleThe effect of multiple stressors on the Florida Keys coral reef ecosystem: a landscape hypothesis and a physiological test Limnol Oceanogr 44 941–949 Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.1999.44.3_part_2.0941
R Rowan (1998) ArticleTitleDiversity and ecology of zooxanthellae on coral reefs J Phycol 34 407–417 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1529-8817.1998.340407.x
R Rowan N Knowlton A Baker J Jara (1997) ArticleTitleLandscape ecology of algal symbionts creates variation in episodes of coral bleaching Nature 388 265–269 Occurrence Handle10.1038/40843
N Stambler Z Dubinsky (1987) ArticleTitleEnergy relationships between Anemonia sulcata and its endosymbiotic zooxanthellae Symbiosis 3 233–248
DK Stoecker DE Gustafson (2003) ArticleTitleCell-surface proteolytic activity of photosynthetic dinoflagellates Aquatic Microb Ecol 30 175–183
G Taroncher-Oldenburg DM Anderson (2000) ArticleTitleIdentification and characterization of three differentially expressed genes, encoding S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase, methionine aminopeptidase, and a histone-like protein, in the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense Appl Environ Microbiol 66 2105–2112 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.66.5.2105-2112.2000
RK Trench (1987) Dinoflagellates in non-parasitic symbioses FJR Taylor (Eds) The Biology of Dinoflagellates Blackwell Oxford 530–570
ME Warner WK Fitt GW Schmidt (1999) ArticleTitleDamage to photosystem II in symbiotic dinoflagellates: a determinant of coral bleaching Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96 8007–8012 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.96.14.8007
Wilkinson CR (1998) Status of Coral Reefs of the World. Sida: Australian Institute of Marine Science
K Yamazato (1999) ArticleTitleCoral bleaching in Okinawa, 1980 vs. 1998 Galaxea, JCRS 1 83–87
Acknowledgment
This study is a part of Sarit Karako Lampert's research toward her Ph.D. dissertation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karako-Lampert, S., Hershkovits, G., Stambler, N. et al. Differential Gene Expression in Symbiodinium microadriaticum Clade B Following Stress. Mar Biotechnol 8, 268–274 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-005-5008-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-005-5008-2