Abstracts
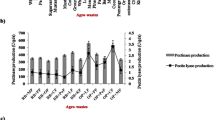
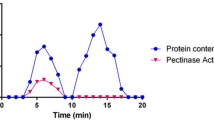
This study armed to determine the expression of protease and pectinase in Bacillus subtilis using the herbal saponin extract as the fermentation substrates and then characterize the fermentation broths. The saponin concentration in the crude extract from four herbs reached to 25% under the extraction conditions of 60 °C, with a pH 9 for 3 h at a solid-liquid ratio of 1:18. In direct fermentation of Bacillus subtilis in the saponin extract, the maximum activities of protease and pectinase in the cell supernatant reached 3984 and 227 U/ml, respectively. Correspondingly, when 5% glucose was added to this extract for the fermentation, the two maximum activities were up to 2451 and 1390 U/ml, respectively. When characterization of the two abovementioned fermentation broths was carried out, it was observed that the luminousness values were increased to 26.9 and 39.2% from 9.7% of the initial value after 32 h of fermentation, respectively, and there was no significant change in the saponin concentration during the fermentation processes. The evaluation values of washing performance were remarkably improved by 8.2 and 21.7%, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aal T, Ped A, Cristianini M (2012) The effect of the high pressure homogenisation on the activity and stability of a commercial neutral protease from Bacillus subtilis. Int J Food Sci Technol 47:716–722
Ahlawat S, Dhiman SS, Battan B, Mandhan RP, Sharma J (2009) Pectinase production by Bacillus subtilis and its potential application in biopreparation of cotton and micropoly fabric. Process Biochem 44:521–526
Brown AE, Adikaram NKB (2010) A role for pectinase and protease inhibitors in fungal rot development in tomato fruits. J Phytopathol 106:239–251
Chen YF, Yang CH, Chang MS, Ciou YP, Huang YC (2010) Foam properties and detergent abilities of the saponins from Camellia oleifera. Int J Mol Sci 11:4417–4425
Cheok CY, Salman HAK, Sulaiman R (2014) Extraction and quantification of saponins: a review. Food Res Int 59:16–40
Chutmanop J, Chuichulcherm S, Chisti Y, Srinophakun P (2008) Protease production by aspergillus oryzae, in solid-state fermentation using agroindustrial substrates. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83:1012–1018
Das KK, Mukherjee AK (2007) Comparison of lipopeptide biosurfactants production by Bacillus subtilis strains in submerged and solid state fermentation systems using a cheap carbon source: some industrial applications of biosurfactants. Process Biochem 42:1191–1199
Daskaya-Dikmen C, Karbancioglu-Guler F, Ozcelik B (2018) Cold active pectinase, amylase and protease production by yeast isolates obtained from environmental samples. Extremophiles 22:599–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-018-1020-0
Kimata H, Nakashima T, Kokubun S et al (2008) Saponins of pericarps of Sapindus mukurossi Gaertn. and solubilization of monodesmosides by bisdesmosides. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 31:1998–2005
Kuo PC, Lin TC, Yang CW, Lin CL, Chen GF, Huang JW (2010) Bioactive saponin from tea seed pomace with inhibitory effects against rhizoctonia solani. J Agric Food Chem 58:8618–8622
Li R, Wu ZL, Wang YJ, Li LL (2013) Separation of total saponins from the pericarp of sapindus mukorossi Gaerten by foam fractionation. Ind Crop Prod 51:163–170
Li Q, Coffman AM, Ju LK (2015) Development of reproducible assays for polygalacturonase and pectinase. Enzym Microb Technol 72:42–48
Liu C, Sun H, Wang WT et al (2015) A new triterpenoid saponin from gleditsia sinensis and its antiproliferative activity. Nat Prod Res 30:2065–2070
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL et al (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Maity JP, Huang YM, Fan CW, Chen CC, Li CY, Hsu CM, Chang YF, Wu CI, Chen CY, Jean JS (2013) Evaluation of remediation process with soapberry derived saponin for removal of heavy metals from contaminated soils in Hai-pu, Taiwan. J Environ Sci (China) 25:1180–1185
Mala M, Srividya S (2010) Partial purification and properties of a laundry detergent compatible alkaline protease from a newly isolated Bacillus species Y. Indian J Microbiol 50:309–317
Manjunath CK, Padmanaban G, Cama HR (1979) Characterization of mitochondrial neutral protease activity and the response of lysosomal enzymes to clofibrate feeding in rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol 28:2929–2934
Muntaha ST, Khan MN (2015) Natural surfactant extracted from Sapindus mukurossi, as an eco-friendly alternate to synthetic surfactant—a dye surfactant interaction study. J Clean Prod 93:145–150
Nakayama K, Fujino H, Kasai R et al (1986) Solubilizing properties of saponins from Sapindus mukurossi Gaertn. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 34:3279–3283
National standards of the People’s Republic of China.GB/T 13174 2008 Determination of detergency and cycle of washing property for laundry detergents
Pathak AP, Deshmukh KB (2012) Alkaline protease production, extraction and characterization from alkaliphilic Bacillus licheniformis kbdl4: a lonar soda lake isolate. Indian J Exp Biol 50:569–576
Rai AK, Sanjukta S, Chourasia R, Bhat I, Bhardwaj PK, Sahoo D (2017) Production of bioactive hydrolysate using protease, β-glucosidase and α-amylase of Bacillus spp. isolated from kinema. Bioresour Technol 235:358–365
Sobucki L, Ramos RF, Daroit DJ (2017) Protease production by the keratinolytic Bacillus sp. CL18 through feather bioprocessing. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:23125–23132
Tanaka O, Tamura Y, Masuda H et al (1996) Application of saponins in foods and cosmetics: saponins of mohave yucca and sapindus mukurossi. Adv Exp Med Biol 405:1–11
Taştan Ö, Baysal T (2017) Chitosan as a novel clarifying agent on clear apple juice production: optimization of process conditions and changes on quality characteristics. Food Chem 237:818–824
Tepe O, Dursun AY (2014) Exo-pectinase production by Bacillus pumilus using different agricultural wastes and optimizing of medium components using response surface methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:9911–9920
Wu Rina (2014) Immobilization of pectinase on cellulosic materials and its application in treatment of specific DCS in papermaking. South China Univ Technol
Yang J, Shih II, Tzeng Y et al (2000) Production and purification of protease from a Bacillus subtilis that can deproteinize crustacean wastes. Enzym Microb Technol 26:406–413
Yin LJ, Hsu TH, Jiang ST (2013) Characterization of acidic protease from Aspergillus niger BCRC 32720. J Agric Food Chem 61:662–666
Zhang Z, Koike K, Jia Z, Nikaido T, Guo D, Zheng J (1999) Triterpenoidal saponins from Gleditsia sinensis. Phytochem 52:715–722
Zhang S, Li H, Uluko H, Liu L, Pang X, Lv J (2015) Investigation of protease production by Pseudomonas fluorescens bj-10 and degradation on milk proteins. J Food Process Preserv 39:2466–2472
Zhoun W, Wang X, Chen C et al (2013) Enhanced soil washing of phenanthrene by a plant-derived natural biosurfactant, Sapindus saponin. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 425:122–128
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Autonomous Region (NO. 2014GXNSFAA118176 and NO. 2012GXNSFAA276037) and Nanning City Science and Technology Plan (20131062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Qiu, J. et al. Co-expression of protease and pectinase in Bacillus subtilis using the herbal saponin extract as substrate. Int Microbiol 21, 223–229 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-018-0019-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-018-0019-9