Abstract
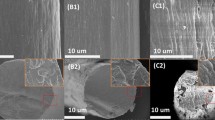
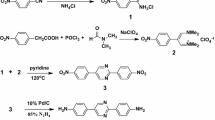
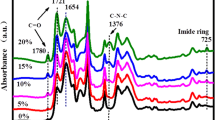
A series of polyamic acid copolymers (co-PAAs) with para-hydroxyl groups was synthesized using two diamine monomers, namely p-phenylenediamine (p-PDA) and 5-amino-2-(2-hydroxy-5-aminobenzene)-benzoxazole (m-pHBOA), of different molar ratios through copolymerization with 3,3′,4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA) in N,N-dimethyacetamine (DMAc). The co-PAA solutions were used to fabricate fibers by dry-jet wet spinning, and thermal imidization was conducted to obtain polyimide copolymer (co-PI) fibers. The effects of the m-pHBOA moiety on molecular packing and physical properties of the prepared fibers were investigated. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic results confirmed that intra/intermolecular hydrogen bonds originated from the hydroxyl group and the nitrogen atom of the benzoxazole group and/or the hydroxyl group and the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group of cyclic imide. As-prepared PI fibers displayed homogenous and smooth surface and uniform diameter. The glass transition temperatures (Tgs) of PI fibers were within 311−337 °C. The polyimide fibers showed 5% weight loss temperature (T5%) at above 510 °C in air. Two-dimensional wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WXRD) patterns indicated that the homo-PI and co-PI fibers presented regularly arranged polymer chains along the fiber axial direction. The ordered molecular packing along the transversal direction was destroyed by introducing the m-pHBOA moiety. Moreover, the crystallinity and orientation factors increased with increasing draw ratio. Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) results showed that it is beneficial to reduce defects in the fibers by increasing the draw ratio. The resultant PI fibers exhibited excellent mechanical properties with fracture strength and initial modulus of 2.48 and 89.73 GPa, respectively, when the molar ratio of p-PDA/m-pHBOA was 5/5 and the draw ratio was 3.0.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, F.; Huang, L.; Shi, Y.; Jin, X.; Wu, Z.; Shen, Z.; Chuang, K.; Lyon, R. E.; Harris, F. W.; Cheng S. Z. D. Thermal degradation mechanism and thermal mechanical properties of two high-performance aromatic polyimide fibers. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B: Phys. 2016, 38, 107–122.
Zhao, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, G.; Dai, X.; Liu, F.; Ma, X.; Qiu, X. Atomic oxygen resistance of polyimide fibers with phosphorus-containing side chains. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 5437–5444.
Dong, J.; Yang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Q. Facile method for fabricating low dielectric constant polyimide fibers with hyperbranched polysiloxane. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 2818–2825.
Zhao, Y.; Feng, T.; Li, G.; Liu, F.; Dai, X.; Dong, Z.; Qiu, X. Synthesis and properties of novel polyimide fibers containing phosphorus groups in the main chain. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 42482–42494.
Penn, L.; Larsen, F. Physicochemical properties of Kevlar-49 fiber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1979, 23, 59–73.
Yang, H. in Kevlar ara id fiber, Wiley, 1993.
Choe, E. W.; Kim, S. N. Synthesie, spining and fiber mechanical properties of poly(p-phenylenebenzobisoxazole). Macromolecules 1981, 14, 920–924.
Sikkema, D. J. Design, synthesis and properties of a novel rigid rod polymer, PIPD or ‘M5’: High modulus and tenacity fibres with substantial compressive strength. Polymer 1998, 39, 5981–5986.
Afshari, M.; Sikkema, D. J.; Lee, K.; Bogle, M. High performance fibers based on rigid and flexible polymers. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 230–274.
Eashoo, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, A.; Shen, D.; Tse, C.; Harris, F. W.; Cheng, S. Z. D.; Gardner, K. H.; Hsiao, B. S. High performance aromatic polyimide fibers, 3. A polyimide synthesized from 3, 3′, 4, 4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride and 2, 2′-dimethyl-4, 4′-diaminobiphenyl. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1994, 195, 2207–2225.
Cheng, S. Z. D.; Wu, Z.; Mark, E. A high-performance aromatic polyimide fibre: 1. Structure, properties and mechanical-history dependence. Polymer 1991, 32, 1803–1810.
Dong, J.; Yin, C.; Luo, W.; Zhang, Q. Synthesis of organ-soluble copolyimides by one-step polymerization and fabrication of high performance fibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 7594–7602.
Park, S. K.; Farris, R. J. Dry-jet wet spinning of aromatic polyamic acid fiber using chemical imidization. Polymer 2001, 42, 10087–10093.
Dorogy, W. E.; St Clair, A. K. Wet spinning of solid polyamic acid fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 43, 501–519.
Zhang, E.; Dai, X.; Dong, Z.; Qiu, X.; Ji, X. Critical concentration and scaling exponents of one soluble polyimide from dilute to semidilute entangled solutions. Polymer 2016, 84, 275–285.
Xiang, H.; Huang, Z.; Liu, L.; Chen, L.; Zhu, J.; Hu, Z.; Yu, J. Structure and properties of polyimide (BTDA-TDI/MDI copolyimide) fibers obtained by wet-spinning. Macromol. Res. 2011, 19, 645–653.
Yang, W.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, E.; Qiu, X.; Ji, X. Influence of thermal treatment on the structure and mechanical properties of one aromatic BPDA-PDA polyimide fiber. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 96, 429–442.
Yin, C.; Dong, J.; Tan, W.; Lin, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q. Straininduced crystallization of polyimide fibers containing 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzimidazole moiety. Polymer 2015, 75, 178–186.
Dong, J.; Yin, C.; Lin, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q. Evolution of the microstructure and morphology of polyimide fibers during heat-drawing process. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 44666–44673.
Yang, W.; Liu, F.; Zhang, E.; Qiu, X.; Ji, X. Influence of atmosphere and force during thermal imidization on the structure and properties of BPDA-PDA polyimide fibers. Chem. J. Chinese U-Chinese 2017, 38, 150–158.
Yan, X.; Zhang, M.; Qi, S.; Tian, G.; Niu, H.; Wu, D. A highperformance aromatic co-polyimide fiber: Structure and property relationship during gradient thermal annealing. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 2193–2207.
Yang, W.; Liu, F.; Li, G.; Zhang, E.; Xue, Y.; Dong, Z.; Qiu, X.; Ji, X. Comparison of different methods for determining the imidization degree of polyimide fibers. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 34, 209–220.
Sukhanova, T.; Baklagina, Y. G.; Kudryavtsev, V.; Maricheva, T.; Lednicky, F. Morphology, deformation and failure behaviour of homo-and copolyimide fibres: 1. Fibres from 4, 4′-oxybis(phthalic anhydride) (DPhO) and p-phenylenediamine (PPh) or/and 2, 5-bis(4-aminophenyl)-pyrimidine (2, 5PRM). Polymer 1999, 40, 6265–6276.
Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Sun, Q.; Li, J. Synthesis and properties of poly(imide-benzoxazole) fibers from 4, 4′-oxydiphthalic dianhydride in polyphosphoric acid. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 64, 108–117.
Yin, C.; Dong, J.; Zhang, D.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Q. Enhanced mechanical and hydrophobic properties of polyimide fibers containing benzimidazole and benzoxazole units. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 88–98.
Cheng, Y.; Dong, J.; Yang, C.; Wu, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Q. Synthesis of poly(benzobisoxazole-co-imide) and fabrication of high-performance fibers. Polymer 2017, 133, 50–59.
Gan, F.; Dong, J.; Zhang, D.; Tan, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Q. High-performance polyimide fibers derived from wholly rigidrod monomers. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 5477–5489.
Niu, H.; Huang, M.; Qi, S.; Han, E.; Tian, G.; Wang, X.; Wu, D. High-performance copolyimide fibers containing quinazolinone moiety: Preparation, structure and properties. Polymer 2013, 54, 1700–1708.
Borjigin, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Gaines, K.; Riffle, J. S.; Paul, D. R.; Freeman, B. D.; McGrath, J. E. Synthesis and characterization of thermally rearranged (TR) polybenzoxazoles: Influence of isometic structure on gas transport properties. Polymer 2015, 75, 199–210.
Hodgkin, J. H.; Liu, M. S.; Dao, B. N.; Mardel, J.; Hill, A. J. Reaction mechanism and products of the thermal conversion of hydroxy-containing polyimides. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 394–400.
Han, S. H., Lee, J. E.; Lee, K. J.; Park, H. B.; Lee, Y. M. Highly gas permeable and microporous polybenzimidazole membrane by thermal rearrangement. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 357, 143–151.
Dai, X.; Bao, F.; Jiao, L.; Yao, H.; Ji, X.; Qiu, X.; Men, Y. High-performance polyimide copolymer fibers derived from 5-amino-2-(2-hydroxy-4-aminobenzene)-benzoxazole: Preparation, structure and properties. Polymer 2018, 150, 254–266.
Preston, J.; Dewinter, W.; Hofferbert, W. Heterocyclic intermediates for the preparation of thermally stable polymers. II. Benzoxazoles and benzothiazoles. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1968, 5, 269–273.
Klug, H. P.; Alexander, L. E. in X-ray diffraction procedures, Wiley: New York, 1954.
Wilchinsky, Z. Orientation in crystalline polymers related to deformation. Polymer 1964, 5, 271–281.
Ruland, W. Small-angle scattering studies on carbonized cellulose fibers. J. Polym. Sci., Part C: Polym. Symp. 1969, 28, 143–151.
Guiner, A.; Fournet, G.; Walker, C. in Small angle scattering of X-raays, Wiley & Sons, New York, 1955.
Kratky, O.; Porod, G. Diffuse small-angle scattering of X-rays in colloid systems. J. Coll. Sci. 1949, 4, 35–70.
Lin, C.; Kuo, J.; Chen, C.; Fang, J. Investigation of bifurcated hydrogen bonds within the thermotropic liquid crystalline polyurethanes. Polymer 2012, 53, 254–258.
Dong, H.; Xin, Z.; Lu, X.; Lv, Y. Effect of-substituents on the surface characteristics and hydrogen bonding network of polybenzoxazines. Polymer 2011, 52, 1092–1101.
Snyder, R.; Thomson, B.; Bartges, B.; Czerniawski, D.; Painter, P. FTIR studies of polyimides: Thermal curing. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 4166–4172.
Konieczny, J.; Wunder, S. Absence of noncyclic imide formation in PMDA-ODA polyimide. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 7613–7615.
Ma, X.; Kang, C.; Chen, W.; Jin, R.; Guo, H.; Qiu, X.; Gao, L. Effect of multiple H-bonding on the properties of polyimides containing the rigid rod groups. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2016, 54, 570–581.
Luo, L.; Yao, J.; Wang, X.; Li, K.; Huang, J.; Li, B.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.; Liu, X. The evolution of macromolecular packing and sudden crystallization in rigid-rod polyimide via effect of multiple H-bonding on charge transfer (CT) interactions. Polymer 2014, 55, 4258–4269.
Fan, L.; Zhao, D.; Bian, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G. Glass transition temperatures of copolymers from methyl methacrylate, styrene, and acrylonitrile: Binary copolymers. Polym. Bull. 2011, 67, 1311–1323.
Jiang, G.; Huang, W.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Pang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Structure and properties of regenerated cellulose fibers from different technology processes. Carbohyd. Polym. 2012, 87, 2012–2018.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFB0308300) and the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2014CB643603).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
10118_2019_2205_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Preparation and Properties of High-Performance Polyimide Copolymer Fibers Derived from 5-Amino-2-(2-hydroxy-5-aminobenzene)-benzoxazole
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, XM., Gao, H., Zhang, R. et al. Preparation and Properties of High-performance Polyimide Copolymer Fibers Derived from 5-Amino-2-(2-hydroxy-5-aminobenzene)-benzoxazole. Chin J Polym Sci 37, 478–492 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-019-2205-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-019-2205-4