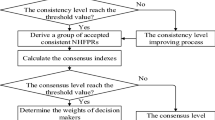
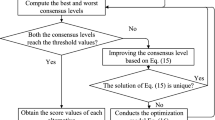
Abstract
In some actual decision-making problems, experts may be hesitant to judge the performances of alternatives, which leads to experts providing decision matrices with incomplete information. However, most existing estimation methods for incomplete information in group decision-making (GDM) neglect the hesitant judgments of experts, possibly making the group decision outcomes unreasonable. Considering the hesitation degrees of experts in decision judgments, an approach is proposed based on the triangular intuitionistic fuzzy numbers (TIFNs) and TODIM (interactive and multiple criteria decision-making) method for GDM and consensus measure. First, TIFNs are applied to handle incomplete information due to the hesitant judgments of experts. Second, considering the risk attitudes of experts, a decision-making model is proposed to rank alternatives for GDM with incomplete information. Subsequently, based on measuring the concordance between solutions, a consensus model is presented to measure the group’s and individual’s consensus degrees. Finally, an illustrative example is presented to show the detailed implementation procedure of the proposed approach. The comparisons with some existing estimation methods verify the effectiveness of the proposed approach for handling incomplete information. The impacts and necessities of experts’ hesitation degrees are discussed by a sensitivity analysis.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Wan S, Cheng X, Dong J (2023) Group decision-making with interval multiplicative preference relations. Knowl Inf Syst 65:2305–2346
Xu X, Hou Y, He J, Zhang Z (2020) A two-stage similarity clustering-based large group decision-making method with incomplete probabilistic linguistic evaluation information. Soft Comput 24(22):16869–16883
Chen XG, Yu GF, Wu J, Yang Y (2020) A minimum trust discount coefficient model for incomplete information in group decision making with intuitionistic fuzzy soft set. Int J Fuzzy Syst 22(6):2025–2040
Liu P, Wang P, Pedrycz W (2021) Consistency-and consensus-based group decision-making method with incomplete probabilistic linguistic preference relations. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29(9):2565–2579
Krishankumar R, Nimmagadda SS, Rani P, Mishra AR, Ravichandran KS, Gandomi AH (2021) Solving renewable energy source selection problems using a q-rung orthopair fuzzy-based integrated decision-making approach. J Clean Prod 279:123329
Raghunathan K, Soundarapandian RK, Gandomi AH, Ramachandran M, Patan R, Madda RB (2021) Duo-stage decision: a framework for filling missing values, consistency check, and repair of decision matrices in multicriteria group decision making. IEEE Trans Eng Manag 68(6):1773–1785
Li Z, Zhang Z, Yu W (2022) Consensus reaching with consistency control in group decision making with incomplete hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Comput Ind Eng 170:108311
Chen Z, Pan Z, Ma Q, Hou T, Zhao P (2022) An MAGDM method for design concept evaluation based on incomplete information. Plos one 17(11):e0277964
Dou Y, Jing L, Cai X, Lu C, Lv T, Jiang S (2023) A concept evaluation approach based on incomplete information: considering large-scale criteria and risk attitudes. Adv Eng Inform 58:102234
Ren J, Gao Y (2011) Discrete fuzzy-stochastic multi-criterion decision-making method with incomplete information. Syst Eng Theory Pract 31(1):122–130. https://doi.org/10.12011/1000-6788(2011)1-122
Shi ZH, Zhang D, Lin K (2012) A TOPSIS method based on incomplete intuitionistic fuzzy information. Math Practice Theory 42(12):234–240. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2012.19.035
Xue ZA, Xin XW, Yuan YL, Xue TY (2018) Intuitionistic fuzzy possibility measure-based three-way decisions for incomplete data. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 35(5):5657–5666
Wen TC, Chung HY, Chang KH, Li ZS (2021) A flexible risk assessment approach integrating subjective and objective weights under uncertainty. Eng Appl Artif Intell 103:104310
Zhang C, Bai W, Li D, Zhan J (2022) Multiple criterion group decision making based on multigranulation probabilistic models, MULTIMOORA and TPOP in incomplete q-rung orthopair fuzzy information systems. Int J Approx Reason 143:102–120
Zhou Y, Zheng C, Wu P, Zhou L (2023) A statistical approach to large-scale group decision making with incomplete hesitant fuzzy linguistic information by incorporating risk attitude. Expert Syst Appl 238:121998
Deng T, Wang X (2013) An object-parameter approach to predicting unknown data in incomplete fuzzy soft sets. Appl Math Model 37(6):4139–4146
Li S, Wei C (2020) A two-stage dynamic influence model-achieving decision-making consensus within large scale groups operating with incomplete information. Knowl-Based Syst 189:105132
Deng J, Zhan J, Wu WZ (2022) A ranking method with a preference relation based on the PROMETHEE method in incomplete multi-scale information systems. Inform Sci 608:1261–1282
Ma X, Han Y, Qin H, Wang P (2023) KNN data filling algorithm for incomplete interval-valued fuzzy soft sets. Int J Comput Intell Syst 16(1):1–15
Li Z, Zhang Q, Liao H (2019) Efficient-equitable-ecological evaluation of regional water resource coordination considering both visible and virtual water. Omega 83:223–235
Cabrerizo FJ, Al-Hmouz R, Morfeq A, Martínez MÁ, Pedrycz W, Herrera-Viedma E (2020) Estimating incomplete information in group decision making: a framework of granular computing. Appl Soft Comput 86:105930
Birjandi AK, Akhyani F, Sheikh R, Sana SS (2019) Evaluation and selecting the contractor in bidding with incomplete information using MCGDM method. Soft Comput 23(20):10569–10585
Liao H, Peng X, Gou X (2020) Medical supplier selection with a group decision-making method based on incomplete probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Int J Fuzzy Syst 23(1):280–294
Capuano N, Chiclana F, Fujita H, Herrera-Viedma E, Loia V (2018) Fuzzy group decision making with incomplete information guided by social influence. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 26(3):1704–1718
Chu J, Wang Y, Liu X, Liu Y (2020) Social network community analysis based large-scale group decision making approach with incomplete fuzzy preference relations. Inf Fusion 60:98–120
Lu Y, Xu Y, Herrera-Viedma E (2022) Consensus progress for large-scale group decision making in social networks with incomplete probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information. Appl Soft Comput 126:109249
Fu YG, Fang GC, Liu YY, Guo LK, Wang YM (2023) Disjunctive belief rule-based reasoning for decision making with incomplete information. Inform Sci 625:49–64
Zhan J, Deng J, Xu Z, Martínez L (2023) A three-way decision methodology with regret theory via triangular fuzzy numbers in incomplete multi-scale decision information systems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 31(8):1–15
Deng J, Zhan J, Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F (2023) Regret theory-based three-way decision method on incomplete multiscale decision information systems with interval fuzzy numbers. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 31(3):982–996
Wang X, Cai J (2017) A group decision-making model based on distance-based VIKOR with incomplete heterogeneous information and its application to emergency supplier selection. Kybernetes 46(3):501–529
Yuan Y, Cheng D, Zhou Z (2021) A minimum adjustment consensus framework with compromise limits for social network group decision making under incomplete information. Inform Sci 549:249–268
Wan S, Yuan H, Dong J (2021) Decision making with incomplete interval multiplicative preference relations based on stochastic program and interval category. Inform Sci 570:403–427
Zhang S, Meng F (2021) A group decision making method with intuitionistic triangular fuzzy preference relations and its application. Appl Intell 51(4):2556–2573
Li X, Zhang S, Meng F (2022) Operation mode selection of public-funded private-run elderly care agencies based on triangular intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations group decision-making. Comput Appl Math 41(8):346
Zhang L, Yang Z, Li T (2023) Group decision making with incomplete interval-valued linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations. Inform Sci 647:119451
Li T, Zhang L, Zhang Z (2023) The consistency and consensus analysis for group decision-making with incomplete linguistic interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations. Appl Intell 53(20):23500–23521
Al Salem AA, Awasthi A (2021) Two new methods for decision-making with incomplete reciprocal fuzzy preference relations based on additive consistency. Int J Model Simul 41(1):24–38
Zhang C, Ding J, Zhan J, Sangaiah AK, Li D (2022) Fuzzy intelligence learning based on bounded rationality in IoMT systems: a case study in Parkinson’s disease. IEEE Trans Comput Soc Syst 10(4):1–15
Park D, Kim Y, Um MJ, Choi SU (2015) Robust priority for strategic environmental assessment with incomplete information using multi-criteria decision making analysis. Sustainability 7(8):10233–10249
Kou G, Peng Y, Chao X, Herrera-Viedmade E, Alsaadi FE (2021) A geometrical method for consensus building in GDM with incomplete heterogeneous preference information. Appl Soft Comput 105:107224
Zhang H, Xiao J, Dong Y (2019) Integrating a consensus-reaching mechanism with bounded confidences into failure mode and effect analysis under incomplete context. Knowledge-Based Syst 183:104873
Ye J, Zhan J, Sun B (2021) A three-way decision method based on fuzzy rough set models under incomplete environments. Inform Sci 577:22–48
Xu X, Lin M, Luo X, Xu Z (2023) HRST-LR: A Hessian regularization spatio-temporal low rank algorithm for traffic data imputation. IEEE trans Intell Transp Syst 24(10):11001–11017
Chen H, Lin M, Liu J, Yang H, Zhang C, Xu Z (2024) NT-DPTC: A non-negative temporal dimension preserved tensor completion model for missing traffic data imputation. Inform Sci 653:119797
Ureña R, Chiclana F, Morente-Molinera JA, Herrera-Viedma E (2015) Managing incomplete preference relations in decision making: a review and future trends. Inform Sci 302:14–32
Nan JX, Li DF, Zhang MJ (2010) A lexicographic method for matrix games with payoffs of triangular intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Int J Comput Intell Syst 3(3):280–289
Xu H, Xing QH, Wang W (2017) Method for MADM with incomplete information based on IFS. Proj Sci Technol Eng 17(8):101–105
Tao Y, Luo X, Zhou J, Wu Y, Zhang L, Liu Y (2022) Site selection for underground pumped storage plant using abandoned coal mine through a hybrid multi-criteria decision-making framework under the fuzzy environment: a case in China. J Energy Storage 56:105957
Wan SP, Wang F, Lin LL, Dong JY (2016) Some new generalized aggregation operators for triangular intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and application to multi-criterion group decision making. Comput Ind Eng 93:286–301
Aikhuele DO, Odofin S (2017) A generalized triangular intuitionistic fuzzy geometric averaging operator for decision-making in engineering and management. Information 8(3):78
Li DF (2010) A ratio ranking method of triangular intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and its application to MADM problems. Comput Math with Appl 60(6):1557–1570
Wang CH, Wang JQ (2016) A multi-criteria decision-making method based on triangular intuitionistic fuzzy preference information. Intell Autom Soft Comput 22(3):473–482
Wan SP, Lin LL, Dong JY (2017) MAGDM based on triangular Atanassov’s intuitionistic fuzzy information aggregation. Neural Comput Appl 28(9):2687–2702
Xiang T, Guo HL, Yang FB, Yang GF (2018) Cause analysis of construction platform accidents of super high-rise buildings based on fault tree and fuzzy theory. J Eng Manag 32(5):7–11. https://doi.org/10.13991/j.cnki.jem.2018.05.002
Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F, Chiclana F (2002) A consensus model for multiperson decision making with different preference structures. IEEE Trans Syst Man, Cybern Part A 32(3):394–402
Cabrerizo FJ, Moreno JM, Perez IJ, Herrera-Viedma E (2010) Analyzing consensus approaches in fuzzy group decision making: advantages and drawbacks. Soft Comput 14:451–463
Del Moral MJ, Tapia JM, Chiclana F, Al-Hmouz A, Herrera-Viedma E (2018) An analysis of consensus approaches based on different concepts of coincidence. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 34(4):2247–2259
Yager RR, Filev DP (1994) Parameterized and-uke and or-like owa operators. Int J Gen Syst 22(3):297–316
Chao X, Kou G, Peng Y, Viedma EH (2021) Large-scale group decision-making with non-cooperative behaviors and heterogeneous preferences: an application in financial inclusion. Eur J Oper Res 288(1):271–293
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chao Huang was involved in conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft and editing. Xiaoyue Wu contributed to conceptualization, formal analysis, validation and supervision. Mingwei Lin was involved in investigation and supervision. Zeshui Xu contributed to validation and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, C., Wu, X., Lin, M. et al. An approach for fuzzy group decision making and consensus measure with hesitant judgments of experts. Knowl Inf Syst (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-024-02098-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-024-02098-3