Abstract
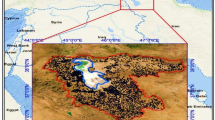
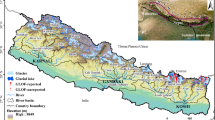
This study assessed changes in the snout, area, and mass of the largest glacier, Zemu, located in Sikkim Himalaya using earth observation data of 87 years from 1931 to 2018. GlabTop model was used to estimate the glacier thickness and potential lakes that could develop in the future. The study assumes importance since massive hydropower infrastructure is being set up without incorporating any knowledge about the retreating glaciers in the region. Between 1931 and 2018, the glacier lost 30.67% (± 2.87%) at a rate of 0.35% per year. The snout of the glacier retreated by ~ 797 m (± 19.7 m) between 1931 and 2018 at a rate of 9.1 m a−1. The rate of retreat increased to ~ 20 m a−1 very recently from 2014 to 2018. The geodetic mass balance estimates suggest that the glacier lost 6.78 Gt (± 2.05 Gt) of mass at a rate of 84.8 Mt a−1 between 1931 and 2012. The mass loss accelerated at 276.5 Mt a−1 between 2000 and 2012. The GlabTop results suggest a mean glacier thickness of 117 m and the formation of a potential future proglacial lake with an area, volume, and peak discharge capacity of 25.3 ha, 3.53 million m3, and 3522 m3s−1, respectively, by the end of this century.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal S, Rai SC, Thakur PK, Emmer A (2017) Inventory and recently increasing GLOF susceptibility of glacial lakes in Sikkim, Eastern Himalaya. Geomorphology 295:39–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.06.014
Albert TH (2002) Evaluation of remote sensing techniques for ice area classification applied to the Tropical Quelccaya Ice Cap, Peru. Polar Geogr 26(3):210–226. https://doi.org/10.1080/789610193
Azam MF, Wagnon P, Berthier E, Vincent C, Fujita K, Kargel JS (2018) Review of the status and mass changes of Himalayan-Karakoram glaciers. J Glaciol 64(243):61–74. https://doi.org/10.1017/jog.2017.86
Bahuguna IM, Rathore BP, Brahmbhatt R, Sharma M, Dhar S, Randhawa SS, Kumar K, Romshoo S, Shah RD, Ganjoo RK, Ajai (2014) Are the Himalayan glaciers retreating? Curr Sci 106(7):1008–1013
Bajracharya SR, Mool PK (2006) Impact of global climate change from 1970’s to 2000’s on the glaciers and glacial lakes in Tamor basin, Eastern Nepal. (Unpublished report for ICIMOD, Kathmandu)
Bajracharya SR, Maharjan SB, Shrestha F, Bajracharya OR, Baidya S (2014) Glacier status in Nepal and decadal change from 1980 to 2010 based on Landsat data. Kathmandu, ICIMOD, ISBN:9789291153114
Bamber JL, Rivera A (2007) A review of remote sensing methods for glacier mass balance determination. Glob Planet Chang 59(1-4):138–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.11.031
Barnett TP, Adam JC, Lettenmaier DP (2005) Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 438(7066):303–309. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04141
Basha G, Kishore P, Ratnam MV, Jayaraman A, Kouchak AA, Ouarda YBMJ, Velicogna I (2017) Historical and projected surface temperature over India during the 20th and 21st century. Sci Rep 7(1):2987. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02130-3
Basnett S, Kulkarni A, Bolch T (2013) The influence of debris cover and glacial lakes on the recession of glaciers in Sikkim Himalaya, India. J Glaciol 59(218):1035–1046. https://doi.org/10.3189/2012JoG11J17510.3189/2013JoG12J184
Bhambri R, Bolch T (2009) Glacier mapping: a review with special reference to the Indian Himalayas. Prog Phys Geogr 33(5):672–704. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309133309348112
Bhutiyani MR, Kale VS, Pawar NJ (2007) Long-term trends in maximum, minimum and mean annual air temperatures across the Northwestern Himalaya during the twentieth century. Climate Change 85:159–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9196-1
Biemans H, Siderius C, Lutz AF, Nepal S, Ahmad B, Hassan T, von Bloh W, Wijngaard RR, Wester P, Shrestha AB, Immerzeel WW (2019) Importance of snow and glacier meltwater for agriculture on the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Nat Sustain 2(7):594–601. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-019-0305-3
Bolch T, Menounos B, Wheate R (2010) Landsat-based inventory of glaciers in western Canada, 1985–2005. Remote Sens Environ 114(1):127–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2009.08.015
Bolch T, Kulkarni A, Kaab A, Huggel C, Paul F, Cogley JG, Frey H, Kargel JS, Fujita K, Scheel M, Bajracharya S, Stoffel M (2012) The state and fate of Himalayan glaciers. Science 336(6079):310–314. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1215828
Bose RN, Dutta NP, Lahiri SM (1971) Refraction seismic investigation at Zemu glacier, Sikkim. J Glaciol 10(58):113–119. https://doi.org/10.3189/S0022143000013046
Brun F, Berthier E, Wagnon P, Kääb A, Treichler D (2017) A spatially resolved estimate of high mountain Asia glacier mass balances from 2000 to 2016. Nat Geosci 10:668–673. https://doi.org/10.1038/NGEO2999
Brun F, Wagnon P, Berthier E, Jomelli V, Maharjan SB, Shrestha F, Kraaijenbrink PDA (2019) Heterogeneous influence of glacier morphology on the mass balance variability in High Mountain Asia. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 124(6):1331–1345. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JF004838
Chandy T, Keenan RJ, Petheram RJ, Shepherd P (2012) Impacts of hydropower development on rural livelihood sustainability in Sikkim, India: community perceptions. Mt Res Dev 32(2):117–125. https://doi.org/10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-11-00103.1
Chudley TR, Miles ES, Willis IC (2017) Glacier characteristics and retreat between 1991 and 2014 in the Ladakh Range, Jammu and Kashmir. Remote Sens Lett 8(6):518–527. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2017.1295480
Cogley JG (2009) Geodetic and direct mass-balance measurements: comparison and joint analysis. Ann Glaciol 50(50):96–100. https://doi.org/10.3189/172756409787769744
Dall J, Madsen S, Keller K, Forsberg R (2001) Topography and penetration of the Greenland ice sheet measured with airborne SAR interferometry. Geophys Res Lett 28(9):1703–1706. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GL011787
Debnath M, Syiemlieh JH, Sharma MC, Kumar R, Chowdhury A, Lal U (2019) Glacial lake dynamics and lake surface temperature assessment along the Kangchengayo-Pauhunri Massif, Sikkim Himalaya, 1988-2014. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 9:26–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2017.11.002
Farinotti D, Huss M, Fürst JJ, Landmann J, Machguth H, Maussion F, Pandit A (2019) A consensus estimate for the ice thickness distribution of all glaciers on Earth. Nat Geosci 12(3):168–173. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-019-0300-3
Finsterwalder R (1935) On the map of the Zemu glacier. Himalayan J 7:125–138
Gardelle J, Arnaud Y, Berthier E (2011) Contrasted evolution of glacial lakes along the Hindu Kush Himalaya mountain range between 1990 and 2009. Glob Planet Chang 75(1):47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2010.10.003
Gardelle J, Berthier E, Arnaud Y (2012) Impact of resolution and radar penetration on glacier elevation changes computed from DEM differencing. J Glaciol 58(208):419–422. https://doi.org/10.3189/2012JoG11J175
Garg PK, Shukla A, Jasrotia AS (2017) Influence of topography on glacier changes in the central Himalaya, India. Glob Planet Chang 155:196–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.07.007
Garg PK, Shukla A, Jasrotia AV (2019) On the strongly imbalanced state of glaciers in the Sikkim, eastern Himalaya, India. Sci Total Environ 691:16–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.086
Goyal MK, Goswami UP (2018) Teesta River and Its Ecosystem. In: Singh D (ed) The Indian Rivers. Springer Hydrogeology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2984-4_37
Haeberli W, Hölzle M (1995) Application of inventory data for estimating characteristics of and regional climate-change effects on mountain glaciers: a pilot study with the European Alps. Ann Glaciol 21(1):206–212. https://doi.org/10.3189/S0260305500015834
Hall DK, Bayr KJ, Schöner W, Bindschadler RA, Chien JY (2003) Consideration of the errors inherent in mapping historical glacier positions in Austria from the ground and space (1893–2001). Remote Sens Environ 86(4):566–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(03)00134-2
Hazra P, Krishna AP (2019) Spatio-temporal and surface elevation change assessment of glaciers of Sikkim Himalaya (India) across different size classes using geospatial techniques. Environ Earth Sci 78:387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8390-1
Hewitt K (2005) The Karakoram anomaly? Glacier expansion and the ‘elevation effect,’Karakoram Himalaya. Mt Resour Dev 25(4):332–340. https://doi.org/10.1659/0276-4741(2005)025[0332:TKAGEA]2.0.CO;2
Hubbard B, Glasser NF (2005) Field techniques in glaciology and glacial geomorphology. Wiley, Ltd, Chichester
Huss M (2013) Density assumptions for converting geodetic glacier volume change to mass change. Cryosphere Discuss 7(1):219–244. https://doi.org/10.5194/tcd-7-219-2013
Immerzeel WW, Beek LPHV, Bierkens MFP (2010) Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 328:1382–1385. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1183188
Jensen JR (2009) Remote sensing of the environment: an earth resource perspective, 2nd edn. Pearson Education India, New Delhi
Joshi D, Platteeuw J, Singh J, Teoh J (2019) Watered down? Civil society organizations and hydropower development in the Darjeeling and Sikkim regions, Eastern Himalaya: A comparative study. Clim Pol 19:S63–S77. https://doi.org/10.1080/14693062.2018.1557035
Kääb A, Berthier E, Nuth C, Gardelle J, Arnaud Y (2012) Contrasting patterns of early twenty-first-century glacier mass change in the Himalayas. Nature 488(7412):495–498. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11324
Kraaijenbrink PDA, Bierkens MFP, Lutz AF, Immerzeel WW (2017) Impact of a global temperature rise of 1.5 degrees Celsius on Asia’s glaciers. Nature 549(7671):257. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23878
Kulkarni AV, Karyakarte Y (2014) Observed changes in Himalayan glaciers. Curr Sci 106(2):237–244
Kulkarni A, Patwardhan SKKK, Kumar KK, Ashok K, Krishnan R (2013) Projected climate change in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan region by using the high-resolution regional climate model PRECIS. Mt Res Dev 33(2):142–151. https://doi.org/10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-11-00131.1
LaTouche THD (1910) Notes on certain glaciers in Sikkim. Rec Geol Surv India 40:52–62
Li Z, Xing Q, Liu S, Zhou J, Huang L (2012) Monitoring volume and thickness changes of the Dongkemadi ice field on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (1969-2000) using Shuttle Radar Topography Mission and map data. Int J Digit Earth 5(6):516–532. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2011.594099
Linsbauer A, Paul F, Haeberli W (2012) Modeling glacier thickness distribution and bed topography over entire mountain ranges with GlabTop: application of a fast and robust approach. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 117(F03007). https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JF002313
Linsbauer A, Frey H, Haeberli W, Machguth H, Azam MF, Allen S (2016) Modelling glacier-bed overdeepenings and possible future lakes for the glaciers in the Himalaya-Karakoram region. Ann Glaciol 57(71):119–130. https://doi.org/10.3189/2016AoG71A
Lutz AF, Immerzeel WW, Shrestha AB, Bierkens MFP (2014) Consistent increase in high Asia’s runoff due to increasing glacier melt and precipitation. Nat Clim Chang 4(7):587–592. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2237
Lutz AF, ter Maat HW, Wijngaard RR, Biemans H, Syed A, Shrestha AB, Wester P, Immerzeel WW (2019) South Asian river basins in a 1.5 C warmer world. Reg Environ Chang 19(3):833–847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-018-1433-4
Maisch M, Haeberli W (1982) Interpretation geometrischer Parameter von Spätglazialgletschern im Gebiet Mittelbünden, Schweizer Alpen, in Beiträge zur Quartärforschung in der Schweiz. Schriftenr. Phys Geogr Univ Zürich, Zurich 1:111–126
Mishra PK, Rai A, Rai SC (2019) Land use and land cover change detection using geospatial techniques in the Sikkim Himalaya, India. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 23(2):133–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2019.02.001
Momblanch A, Papadimitriou L, Jain SK, Kulkarni A, Ojha CSP, Adeloye AJ, Holman IP (2019) Untangling the water-food-energy-environment nexus for global change adaptation in a complex Himalayan water resource system. Sci Total Environ 655:35–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.045
Muhammad S, Tian L, Nüsser M (2019) No significant mass loss in the glaciers of Astore basin (North-Western Himalaya), between 1999 and 2016. J Glaciol 65(250):270–278. https://doi.org/10.1017/jog.2019.5
Mukherji A, Sinisalo A, Nüsser M, Garrard R, Eriksson M (2019) Contributions of the cryosphere to mountain communities in the Hindu Kush Himalaya: a review. Reg Environ Chang 19:1311–1326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-019-01484-w
Neckel N, David L, Melanie R (2017) Recent slowdown and thinning of debris-covered glaciers in south-eastern Tibet. Earth Planet Sci Lett 464:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2017.02.008
Nie Y, Liu Q, Liu S (2013) Glacial lake expansion in the Central Himalayas by Landsat images, 1990–2010. PLoS One 8(12):e83973. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0083973
Nüsser M, Schmidt S (2017) Nanga Parbat revisited: evolution and dynamics of sociohydrological interactions in the Northwestern Himalaya. Ann Am Assoc Geogr 107(2):403–415. https://doi.org/10.1080/24694452.2016.1235495
Nüsser M, Dame J, Kraus B, Baghel R, Schmidt S (2019) Socio-hydrology of “artificial glaciers” in Ladakh, India: assessing adaptive strategies in a changing cryosphere. Reg Environ Chang 19(5):1327–1337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-1372-0
Palazzi E, Von Hardenberg J, Provenzale A (2013) Precipitation in the Hindu-Kush Karakoram Himalaya: observations and future scenarios. J Geophys Res-Atmos 118(1):85–100. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JD018697
Paul F, Huggel C, Kääb A (2004) Combining satellite multispectral image data and a digital elevation model for mapping debris-covered glaciers. Remote Sens Environ 89(4):510–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2003.11.007
Pepin N, Deng H, Zhang H, Zhang F, Kang S, Yao T (2015) An examination of temperature trends at high elevations across the Tibetan Plateau: the use of MODIS LST to understand patterns of elevation-dependent warming. Nat Clim Chang 5(5):424–430. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD029798
Pradhan KC, Sharma E, Pradhan G, Chhetri AB (2004) Sikkim study series: geography and environment. Department of Information and Public Relations, Government of Sikkim, Sikkim, p. 366
Pratap B, Dobhal DP, Bhambri R, Mehta M, Tewari VC (2016) Four decades of glacier mass balance observations in the Indian Himalaya. Reg Environ Chang 16(3):643–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s1011
Racoviteanu AE, Arnaud Y, Willaims MW, Manley WF (2015) Spatial patterns in glacier characteristics and area changes from 1962 to 2006 in the Kanchenjunga–Sikkim area, eastern Himalaya. Cryosphere 9:505–523. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-9-505-2015
Rahaman MM, Mamun AA (2020) Hydropower development along Teesta river basin: opportunities for cooperation. Water Policy 22(4):641–657. https://doi.org/10.2166/wp.2020.136
Raina VK (2009) Himalayan glaciers. A state-of-art review of glacial studies, glacial retreat and climate change. Ministry of Environment and Forests, India. http://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/files/MoEDiscussionPaper.pdf. Accessed 28 Sept 2020
Ramsankaran RAAJ, Pandit A, Azam MF (2018) Spatially distributed ice thickness modeling for Chota Shigri Glacier in western Himalayas, India. Int J Remote Sens 39(10):3320–3343. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1441563
Ramsankaran RAAJ, Pandit A, Parla A (2019) Decadal estimates of surface mass balance for glaciers in Chandra basin, Western Himalayas, India-A Geodetic Approach. In: Climate Change Signals and Response. Springer, Singapore, pp 109–125
Rashid I, Abdullah T (2016) Investigation of temporal change in glacial extent of Chitral watershed using Landsat data: a critique. Environ Monit Assess 188(10):546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5565-z
Rashid I, Majeed U (2018) Recent recession and potential future lake formation on Drang Drung glacier, Zanskar Himalaya, as assessed with earth observation data and glacier modeling. Environ Earth Sci 77:429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7601-5
Rashid I, Romshoo SA, Abdullah T (2017) The recent deglaciation of Kolahoi valley in Kashmir Himalaya, India in response to the changing climate. J Asian Earth Sci 138:38–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.02.002
Rashid I, Majeed U, Jan A, Glasser NF (2019) The January 2018 to September 2019 surge of Shisper Glacier, Pakistan, detected from remote sensing observations. Geomorphology 51(2020):106957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.106957
Rashid I, Majeed U, Jan A, Glasser NF (2020a) The January 2018 to September 2019 surge of Shisper Glacier, Pakistan, detected from remote sensing observations. Geomorphology 351:106957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.106957
Rashid I, Majeed U, Aneaus S, Pelto M (2020b) Linking the recent glacier retreat and depleting streamflow patterns with land system changes in Kashmir Himalaya, India. Water 12(4):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041168
Rignot E, Echelmeyer K, Krabill W (2001) Penetration depth of interferometric synthetic-aperture radar signals in snow and ice. Geophys Res Lett 28(18):3501–3504. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GL012484
Romshoo SA, Dar RA, Rashid I, Marazi A, Ali N, Zaz SN (2015) Implications of shrinking cryosphere under changing climate on the streamflows in the Lidder catchment in the Upper Indus Basin, India. Arct Antarct Alp Res 47(4):627–644. https://doi.org/10.1657/AAAR0014-008
Scherler D, Bookhagen B, Strecker MR (2011) Spatially variable response of Himalayan glaciers to climate change affected by debris cover. Nat Geosci 4(3):156–159. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1068
Schmidt S, Nüsser M (2009) Fluctuations of Raikot Glacier during the past 70 years: a case study from the Nanga Parbat massif, northern Pakistan. J Glaciol 55(194):949–959. https://doi.org/10.3189/002214309790794878
Schmidt S, Nüsser M (2012) Changes of high altitude glaciers from 1969 to 2010 in the Trans-Himalayan Kang Yatze Massif, Ladakh, northwest India. Arct Antarct Alp Res 44(1):107–121. https://doi.org/10.1657/1938-4246-44.1.107
Schmidt S, Nüsser M (2017) Changes of high altitude glaciers in the Trans-Himalaya of Ladakh over the past five decades (1969–2016). Geosciences 7(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7020027
Shah SK, Bhattacharyya A, Chaudhary V (2014) Streamflow reconstruction of Eastern Himalaya River, Lachen ‘Chhu’, North Sikkim, based on tree-ring data of Larix griffithiana from Zemu Glacier basin. Dendrochronologia 32(2):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dendro.2014.01.005
Sharma RK, Shrestha DG (2016) Climate perceptions of local communities validated through scientific signals in Sikkim Himalaya, India. Environ Monit Assess 188(10):578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5582-y
Sharma E, Molden D, Rahman A, Khatiwada YR, Zhang L, Singh SP, Yao T, Wester P (2019) Introduction to the Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment. In: The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment. Springer, Cham, pp 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-92288-1_1
Shrestha AB, Wake CP, Mayewski PA, Dibb JE (1999) Maximum temperature trends in the Himalaya and its vicinity : an analysis based on Temperature records from Nepal for the period 1971-94. J Clim 12(9):2775–2786. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1999)012<2775:MTTITH>2.0.CO;2
Shukla A, Gupta RP, Arora MK (2009) Estimation of debris cover and its temporal variation using optical satellite sensor data- a case study in Chenab basin, Himalayas. Ann Glaciol 55(191):444–451. https://doi.org/10.3189/002214309788816632
Shukla A, Garg PK, Srivastava S (2018) Evolution of glacial and high-altitude lakes in the Sikkim, Eastern Himalaya over the past four decades (1975–2017). Front Environ Sci:6(81). https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2018.00081
Singh V, Goyal MK (2017) Spatio-temporal heterogeneity and changes in extreme precipitation over eastern Himalayan catchments India. Stoch Env Res Risk A 31(10):2527–2546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-016-1350-3
Smith T, Bookhagen B, Cannon F (2015) Improving semi-automated glacier mapping with a multi-method approach: applications in central Asia. Cryosphere 9(5):1747–1459. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-0-1747-2015
Soheb M, Ramanathan A, Angchuk T, Mandal A, Kumar N, Lotus S (2020) Mass-balance observation, reconstruction and sensitivity of Stok glacier, Ladakh region, India, between 1978 and 2019. J Glaciol 66:627–642. https://doi.org/10.1017/jog.2020.34
Song C, Sheng Y, Wang J, Ke L, Madson A, Nie Y (2017) Heterogeneous glacial lake changes and links of lake expansions to the rapid thinning of adjacent glacier termini in the Himalayas. Geomorphology 280:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.12.002
Vijay S, Braun M (2018) Early 21st century spatially detailed elevation changes of Jammu and Kashmir glaciers (Karakoram–Himalaya). Glob Planet Chang 165:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.03.014
Vikhamar D, Solberg R (2003) Snow-cover mapping in forests by constrained linear spectral unmixing of MODIS data. Remote Sens Environ 88(3):309–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2003.06.004
Wada Y, Vinca A, Parkinson S, Willarts BA, Magnuszweski P et al (2019) Co-designing Indus water-energy-land futures. One Earth 1(2):185–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oneear.2019.10.006
Wang W, Xiang Y, Gao Y, Lu A, Yao T (2015) Rapid expansion of glacial lakes caused by climate and glacier retreat in the Central Himalayas. Hydrol Process 29(6):859–874. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10199
Wiltshire AJ (2014) Climate change implications for the glaciers of the Hindu Kush, Karakoram and Himalayan region. Cryosphere 8(3):941–958. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-8-941-2014
Yadava AK, Yadav RR, Misra KG, Singh J, Singh D (2015) Tree ring evidence of late summer warming in Sikkim, northeast India. Quat Int 371:175–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2014.12.067
Yao T, Thompson LG, Mosbrugger V, Zhang F, Ma Y, Luo T, Xu B, Yang X, Joswiak DR, Wang W, Joswiak ME, Devkota LP, Tayal S, Jilani R, Fayziev R (2012) Third pole environment (TPE). Environ Dev 3:52–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envdev.2012.04.002
Ye Q, Zhong Z, Kang S, Stein A, Wei Q, Jingshi L (2009) Monitoring glacial and supra-glacier lakes from space in Mt. Qomolangma Region of the Himalayas on the Tibetan Plateau in China. J Mt Sci 6:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-009-1016-4
Zhou Y, Hu J, Li Z, Li J, Zhao R, Ding X (2018) Quantifying glacier mass change and its contribution to lake growths in central Kunlun during 2000-2015 from multi-source remote sensing data. J Hydrol 570:38–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydrol.2019.01.007
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to USGS for making the Landsat data freely available to users. The authors also express gratitude to Dr. Andreas Linsbauer, University of Zurich, for providing the GlabTop model. The suggestions from the two anonymous reviewers, Editor-in-Chief (Prof. Wolfgang Cramer), and Associate Editor (Prof. Juan I. Lopez Moreno) helped in improving the manuscript content and structure. The second author also acknowledges the support of the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India (DST, GoI) for INSPIRE fellowship (Grant Number: IF180682) for pursuing Ph.D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Juan Ignacio Lopez Moreno
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOC 3212 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rashid, I., Majeed, U. Retreat and geodetic mass changes of Zemu Glacier, Sikkim Himalaya, India, between 1931 and 2018. Reg Environ Change 20, 125 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-020-01717-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-020-01717-3