Abstract
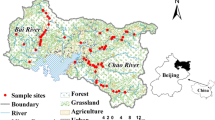
The management of riparian areas in agricultural regions is important for the protection of water quality. In Québec, a buffer strip of at least three meters width is required for riparian buffers adjacent to agricultural areas. However, other qualities of the riparian area and the surrounding landscape may affect the ability of a system to deliver a water purification ecosystem service. This study, located in a tile-drained agroecosystem in the Montérégie (Québec, Canada), aims to unravel the importance of local factors (the environment adjacent to the stream) and landscape factors (the environment in the whole drainage basin) in water purification through sediment and nutrient retention. We assessed riparian and water quality in twenty-one sites distributed among four headwater streams. A regression analysis indicates that both landscape and local variables influence the provision of water purification. We therefore suggest that the effect of riparian buffers might be mediated by other factors such as subsurface drainage or local land management. Landscape configuration (the geometry and location of various land uses) was identified as playing a key role in the level of ecosystem services provided. We suggest that management of water quality in agroecosystems should focus both on buffer strips and on management of larger source areas in the basin. Interventions should not be only limited to recommendations for buffer width, but should also consider interactions between other local and landscape factors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker ME, Weller DE, Jordan TE (2006) Improved methods for quantifying potential nutrient interception by riparian buffers. Landsc Ecol 21:1327–1345. doi:10.1007/s10980-006-0020-0
Balana BB, Lago M, Baggaley N, Castellazzi M, Sample J, Stutter M, Slee B, Vinten A (2012) Integrating economic and biophysical data in assessing cost-effectiveness of buffer strip placement. J Environ Qual 41:380–388. doi:10.2134/jeq2010.0544
Beauchemin S, Simard RR, Cluis D (1998) Forms and concentration of phosphorus in drainage water of twenty-seven tile-drained soils. J Environ Qual 27:721–728. doi:10.2134/jeq1998.00472425002700030033x
Belmar O, Bruno D, Martínez-Capel F, Barquín J, Belasco J (2013) Effects of flow regime alteration on fluvial habitats and riparian quality in a semiarid Mediterranean basin. Ecol Indic 30:52–64. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.01.042
Chapman AS, Foster IDL, Lees JA, Hodgkinson RA, Jackson RH (2001) Particulate phosphorus transport by subsurface drainage from agricultural land in the UK: environmental significance at the catchment and national scale. Sci Total Environ 266:95–102. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00734-8
CRAAQ (2003) Reference fertilization guide. Reference Centre in Agriculture and Agri-Food of Quebec, Québec
Daily G (1997) Nature’s service: societal dependence on natural ecosystems. Island Press, Washington
del Tánago MG, de Jalón DG (2006) Attributes for assessing the environmental quality of riparian zones. Limnetica 25:389–402
del Tánago MG, de Jalón DG (2011) Riparian quality index (RQI): a methodology for characterizing and assessing environmental conditions of riparian zones. Limnetica 30:235–254
del Tánago MG, de Jalón DG, Martínez R (2004) Geomorphological characterization of the stream network of Alto and Medio Guadiana (in Spanish). Technical Report, CEDEX, Madrid
Dormann CF, McPherson JM, Araújo MB, Bivand R, Bolliger J, Carl G, Davies RG, Hirzel A, Jetz W, Kissling D, Kühn I, Ohlemüller R, Peres-Neto PR, Reineking B, Schröder B, Schurr FM, Wilson R (2007) Methods to account for spatial autocorrelation in the analysis of species distributional data: a review. Ecography 30:609–628. doi:10.1111/j.2007.0906-7590.05171.x
Dosskey MG, Vidon P, Gurwick NP, Allan CJ, Duval TP, Lowrance R (2010) The role of riparian vegetation in protecting and improving chemical water quality in streams. J Am Water Resour Assoc 46:261–277. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.2010.00419.x
Farnham IM, Singh AK, Stetzenbach KJ, Johannesson KH (2002) Treatment of nondetects in multivariate analysis of groundwater geochemistry data. Chem Intell Lab Syst 60:265–281. doi:10.1016/S0169-7439(01)00201-5
Gentry LE, David MB, Royer TV, Mitchell CA, Starks KM (2007) Phosphorus transport pathways to streams in tile-drained agricultural watersheds. J Environ Qual 36:408–415. doi:10.2134/jeq2006.0098
Heinen M, Noij IGAM, Heesmans HIM, van Groenigen JW, Groenendijk P, Thissen JTNM (2012) A novel method to determine buffer strip effectiveness on deep soils. J Environ Qual 41:334–347. doi:10.2134/jeq2010.0452
Hunsaker C, Levine D (1995) Hierarchical approaches to the study of water quality in rivers. Bioscience 45:193–203
Johnson L, Richards C, Host G, Arthur J (1997) Landscape influences on water chemistry in Midwestern stream ecosystems. Freshwater Biol 37:193–208. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2427.1997.d01-539.x
Jolliffe IT (2002) Principal component analysis. Springer, New York
Kronvang B, Audet J, Baattrup-Pedersen A, Jensen HS, Larsen SE (2012) Phosphorus load to surface water from bank erosion in a Danish lowland river basin. J Environ Qual 41:304–313. doi:10.2134/jeq2010.0434
Lapp P, Madramootoo CA, Enright P, Papineau F, Perrone J (1998) Water quality of an intensive agricultural watershed in Quebec. J Am Water Resour Assoc 34:427–437. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb04146.x
Liu X, Zhang X, Zhang M (2008) Major factors influencing the efficacy of vegetated buffers on sediment trapping: a review and analysis. J Environ Qual 37:1667–1674. doi:10.2134/jeq2007.0437
Lowrance R, Todd R, Fail JJ, Hendrickson OJ, Leonard R, Asmussen L (1984) Riparian forests as nutrient filters in agricultural watersheds. Bioscience 34:374–377. doi:10.2307/1309729
Martens H, Naes T (1991) Multivariate calibration. Wiley, London
Mayer PM, Reynolds SK, McCutchen MD Jr, Canfield TJ (2007) Meta-analysis of nitrogen removal in riparian buffers. J Environ Qual 36:1172–1180. doi:10.2134/jeq2006.0462
McCracken DI, Cole LJ, Harrison W, Robertson D (2012) Improving the farmland biodiversity value of riparian buffer strips: conflicts and compromises. J Environ Qual 41:355–363. doi:10.2134/jeq2010.0532
MDDEP (2005) Politique de protection des rives, du littoral et des plaines inondables [Law for the protection of shores, litoral and floodplains]. Ministry of Sustainable Development, Environment and Parks, Québec’s Government
Meyer JL, Wallace JB (2001) Lost linkages and lotic ecology: rediscovering small streams. In: Press MC, Huntly NJ, Levin S (eds) Ecology: achievement and challenge. Blackwell Science Ltd., Malden
Mitchell MGE, Bennett EM, Gonzalez A (2013) Linking landscape connectivity and ecosystem service provision: current knowledge and research gaps. Ecosystems 16:894–908. doi:10.1007/s10021-013-9647-2
Mont-Saint-Hilaire Nature Centre (2012) Characterization of riparian zones in Mont-Saint-Hilaire streams (in French)
Munné AN, Prat N, Solà C, Bonada N, Rieradevall M (2003) A simple field method for assessing the ecological quality of riparian habitat in rivers and streams: QBR index. Aquatic Conserv: Mar Freshw Ecosyst 13:147–163. doi:10.1002/aqc.529
Navarro-Llácer C, Baeza D, de las Heras J (2010) Assessment of regulated rivers with índices based on macroinvertebrates, fish and riparian forest in the southeast of Spain. Ecol Indic 10:935–942. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2010.02.003
Noij IGAM, Heinen M, Heesmans HIM, Thissen JTNM, Groenendijk P (2012) Effectiveness of unfertilized buffer strups for reducing nitrogen loads from agricultural lowland to surface waters. J Environ Qual 41:322–333. doi:10.2134/jeq2010.0545
Osborne LL, Kovacic DA (1993) Riparian vegetated buffer strips in water-quality restoration and stream management. Freshwater Biol 29:243–258. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.1993.tb00761.x
Osborne LL, Wiley MJ (1988) Empirical relationships between land use/cover and stream water quality in an agricultural watershed. J Environ Manage 26:9–27
Petersen R (1992) The RCE: a riparian, channel and environmental inventory for small streams in the agricultural landscape. Freshwater Biol 27:295–306. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.1992.tb00541.x
Royer TV, David MB, Gentry LE (2006) Timing of riverine export of nitrate and phosphorus from agricultural watersheds in Illinois: implications for reducing nutrient loading to the Mississippi River. Environ Sci Technol 40:4126–4131. doi:10.1021/es052573n
Saint-Jacques N, Richard Y (1998) Development of a riparian quality index: application to the rivière Chaudière and relation with the biotic integrity of the aquatic environment. Direction of aquatic ecosystems, Quebec
Stutter MI, Chardon WJ, Kronvang B (2012) Riparian buffer strips as a multifunctional management tool in agricultural landscapes: introduction. J Environ Qual 41:297–303. doi:10.2134/jeq2011.0439
Terrado M, Acuña V, Ennaanay D, Tallis H, Sabater S (2014) Impact of climate extremes on hydrological ecosystem services in a heavily humanized Mediterranean basin. Ecol Indic 37:199–209. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.01.016
Tran CP, Bode RW, Smith AJ, Kleppel GS (2010) Land-use proximity as a basis for assessing stream water quality in New York State (USA). Ecol Indic 10:727–733. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2009.12.002
Uriarte M, Yackulic CB, Lim Y, Arce-Nazario JA (2011) Influence of land use on water quality in a tropical landscape: a multi-scale analysis. Landsc Ecol 26:1151–1164. doi:10.1007/s10980-011-9642-y
Verstraeten G, Poesen J, Gillijns K, Govers G (2006) The use of riparian vegetated filter strips to reduce river sediments loads: an overestimated control measure? Hydrol Process 20:4259–4267. doi:10.1002/hyp.6155
Vidon P, Allan C, Burns D, Duval TP, Gurwick N, Inamdar S, Lowrance R, Okay J, Scott D, Sebestyen S (2010) Hot spots and hot moments in riparian zones: potential for improved water quality management. J Am Water Resour Assoc 46:278–298. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.2010.00420.x
Villamagna AM, Angermeier PL, Bennett EM (2013) Capacity, demand, pressure and flow: a conceptual framework for analyzing ecosystem service provision and delivery. Ecol Complex 15:114–121. doi:10.1016/j.ecocom.2013.07.004
Wall GJ, Coote DR, Pringle EA, Shelton IJ (2002) RUSLEFAC. Revised universal soil loss equation for application in Canada. A handbook for estimating soil loss from water erosion in Canada. Cereal and Oilseed Research Centre, Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Ottawa, Ontario
Ward TA, Tate KW, Atwill ER (2003) Visual assessment of riparian health. Rangeland Monitoring Series. University of California, Davis, CA
Weller DE, Jordan TE, Correll DL (1998) Heuristic models for material discharge from landscapes with riparian buffers. Ecol Appl 8:1156–1169. doi:10.1890/1051-0761
Winward AH (2000) Monitoring the vegetation resources in riparian areas. USDA Forest Service, Ogden
Wold S, Sjöström M, Eriksson L (2001) PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics. Chemometr Intell Lab 58:109–130. doi:10.1016/S0169-7439(01)00155-1
Woodcock T, Mihuc T, Romanowicz E, Allen E (2004) Land-use effects on catchment and patch: scale habitat and macroinvertebrate response in the Adirondack Uplands. Landscape Influences on Stream Habitats and Biological Assemblages 48:395–411
Zaimes GN, Schultz RC, Isenhart TM (2004) Stream bank erosion adjacent to riparian forest buffers, row-crop fields, and continuously-grazed pastures along Bear Creek in central Iowa. J Soil Water Conserv 59:19–27
Zedler JB (2003) Wetlands at your service: reducing impacts of agriculture at the watershed scale. Front Ecol Environ 1:65–72. doi:10.1890/1540-9295
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Education through the National Program for the Mobility of Human Resources from the National Plan I-D + I 2008–2011 and by an NSERC Strategic Projects grant. The authors would like to thank people in E. Bennett’s laboratory for their assistance in sampling, and A. Gonzalez for help with study design. We thank H. Lalande for allowing us to use the laboratory facilities and the people from the Gault Nature Reserve for caring so much about our work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Wolfgang Cramer.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10113_2014_733_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Composition (loading plots) and spatial distribution (score plots) of the four principal components identified in the PCA of physicochemical data in the studied streams (see Table 2 for variable identification) (TIFF 13,466 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terrado, M., Tauler, R. & Bennett, E.M. Landscape and local factors influence water purification in the Monteregian agroecosystem in Québec, Canada. Reg Environ Change 15, 1743–1755 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-014-0733-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-014-0733-6