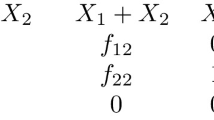Abstract
Modern electricity systems provide a plethora of challenging issues in optimization. The increasing penetration of low carbon renewable sources of energy introduces uncertainty in problems traditionally modeled in a deterministic setting. The liberalization of the electricity sector brought the need of designing sound markets, ensuring capacity investments while properly reflecting strategic interactions. In all these problems, hedging risk, possibly in a dynamic manner, is also a concern. The fact of representing uncertainty and/or competition of different companies in a multi-settlement power market considerably increases the number of variables and constraints. For this reason, usually a trade-off needs to be found between modeling and numerical tractability: the more details are brought into the model, the harder becomes the optimization problem. For structured optimization and generalized equilibrium problems, we explore some variants of solution methods based on Lagrangian relaxation and on Benders decomposition. Throughout we keep as a leading thread the actual practical value of such techniques in terms of their efficiency to solve energy related problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anstreicher K., Wolsey L.: Two “well-known” properties of subgradient optimization. Math. Program. 120, 213–220 (2009)
Bacaud L., Lemaréchal C., Renaud A., Sagastizábal C.: Bundle methods in stochastic optimal power management: a disaggregated approach using preconditioners. Comput. Optim. Appl. 20(3), 227–244 (2001)
Baldick R., Helman U., Hobbs B., O’Neill R.: Design of efficient generation markets. Proc. IEEE 93(11), 1998–2012 (2005)
Barroso L., Carneiro R., Granville S., Pereira M., Fampa M.: Nash equilibrium in strategic bidding: a binary expansion approach. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 21(2), 629–638 (2006)
Batut J., Renaud A.: Daily generation scheduling with transmission constraints: a new class of algorithms. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 7, 982–989 (1992)
Belloni A., Diniz A., Maceira M., Sagastizábal C.: Bundle relaxation and primal recovery in unit commitment problems. The brazilian case. Ann. Oper. Res. 120, 21–44 (2003)
Bertsekas D.P.: Convexification procedures and decomposition methods for nonconvex optimization problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 29, 169–197 (1979)
Bertsekas D.P., Tseng P.: Partial proximal minimization algorithms for convex programming. SIAM J. Optim. 4, 551–572 (1994)
Bienstock D., Shapiro J.: Optimizing resource acquisition decisions by stochastic programming. Manag. Sci. 34(7), 215–229 (1988)
Birge J., Donohue C.J.: The abridged nested decomposition method for multistage stochastic linear programs with relatively complete recourse. Algorithm. Oper. Res. 1, 20–30 (2001)
Bonnans, J.-F., Gilbert, J-Ch., Lemaréchal, C., Sagastizábal, C.: Numerical optimization. Theoretical and Practical Aspects. Universitext, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Borghetti A., D’Ambrosio C., Lodi A., Martello S.: An MILP approach for short-term hydro scheduling and unit commitment with head-dependent reservoir. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 23(3), 1115–1124 (2008)
Bruno S., Sagastizábal C.: Optimization of real asset portfolio using a coherent risk measure: application to oil and energy industries. Optim. Eng. 12, 257–275 (2011)
Carøe C.C., Schultz R.: Dual decomposition in stochastic integer programming. Oper. Res. Lett. 24, 37–45 (1997)
Carpentier P., Cohen G., Culioli J.C., Renaud A.: Stochastic optimization of unit commitment: a new decomposition framework. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 11(2), 1067–1073 (1996)
Chen Z.L., Powell W.: A convergent cutting-plane and partial-sampling algorithm for multistage stochastic linear programs with recourse. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 102, 497–524 (1999)
Chung W., Fuller J.D.: Subproblem approximation in Dantzig–Wolfe decomposition of variational inequality models with an application to a multicommodity economic equilibrium model. Oper. Res. 58, 1318–1327 (2010)
Cohen, G., Zhu, D.L.: Decomposition coordination methods in large scale optimization problems: the nondifferentiable case and the use of augmented Lagrangians. In: Cruz, J.B. (ed.) Advances in Large Scale Systems, vol. 1, pp. 203–266. JAI, Greenwich, CT (1984)
Conejo A.J., Carrión M., Morales J.M.: Decision Making Under Uncertainty in Electricity Markets. International Series in Operations Research & Management Science. Springer, New York (2010)
Conejo A.J., Redondo N.J.: Short-term hydro-thermal coordination by Lagrangian relaxation: solution of the dual problem. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 14(1), 89–95 (1999)
Culioli J.C., Cohen G.: Decomposition/coordination algorithms in stochastic optimization. SIAM J. Control Optim. 28(6), 1372–1403 (1990)
Daniilidis A., Lemaréchal C.: On a primal-proximal heuristic in discrete optimization. Math. Program. 104, 105–128 (2005)
David, A., Wen, F.: Strategic bidding in competitive electricity markets: a literature survey. In: Power Engineering Society Summer Meeting, 2000. IEEE, vol. 4, pp. 2168–2173 (2000)
Day C., Hobbs B., Pang J.S.: Oligopolistic competition in power networks: a conjectured supply function approach. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 17(3), 597–607 (2002)
Diniz, A., Sagastizábal, C., Maceira, M.: Assessment of Lagrangian relaxation with variable splitting for hydrothermal scheduling. Power Eng. Soc. Gen. Meet. IEEE. (2007). doi:10.1109/PES.2007.386246
Doukopoulos G.H., Charousset S.B., Malick J., Lemaréchal C.: The short-term electricity production management problem at EDF. OPTIMA 84, 2–6 (2010)
Dubost L., Gonzalez R., Lemaréchal C.: A primal-proximal heuristic applied to the French unit-commitment problem. Math. Program. 104, 129–151 (2005)
Ehrenmann A., Neuhoff K.: A comparison of electricity market designs in networks. Oper. Res. 57(2), 274–286 (2009)
Ehrenmann, A., Smeers, Y.: Capacity expansion in non-regulated electricity markets. In: Proceedings of the 39th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS’06) Track 10 (2006). http://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/HICSS.2006.80
Emiel G., Sagastizábal C.: Incremental-like bundle methods with application to energy planning. Comput. Optim. Appl. 46, 305–332 (2010)
Escobar J., Jofré A.: Monopolistic competition in electricity networks with resistance losses. Econ. Theory 44, 101–121 (2010)
Fábián C., Mitra G., Roman D.: Processing second-order stochastic dominance models using cutting-plane representations. Math. Program. 130, 33–57 (2011)
Fábián C.I., Szőke Z.: Solving two-stage stochastic programming problems with level decomposition. Comput. Manag. Sci. 4(4), 313–353 (2007)
Facchinei F., Fischer A., Piccialli V.: On generalized Nash games and variational inequalities. Oper. Res. Lett. 35(2), 159–164 (2007)
Facchinei F., Kanzow C.: Generalized Nash equilibrium problems. Ann. OR 175(1), 177–211 (2010)
Feltenmark S., Kiwiel K.C.: Dual applications of proximal bundle methods, including Lagrangian relaxation of nonconvex problems. SIAM J. Optim. 10(3), 697–721 (2000)
Ferris M.C., Munson T.S.: Interfaces to PATH 3.0: design, implementation and usage. Comput. Optim. Appl. 12, 207–227 (1999)
Finardi E., da Silva E.: Solving the hydro unit commitment problem via dual decomposition and sequential quadratic programming. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 21(2), 835–844 (2006)
Fisher E., O’Neill R., Ferris M.: Optimal transmission switching. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 23(3), 1346–1355 (2008)
Frangioni A.: Unit Commitment problems: a tale in Lagrangian optimization. OPTIMA 84, 6–7 (2010)
Frangioni, A., Gendron, B.: A stabilized structured Dantzig–Wolfe decomposition method. Math. Program. (2011) (accepted for publication)
Frangioni A., Gentile C.: Solving nonlinear single-unit commitment problems with ramping constraints. Oper. Res. 54(4), 767–775 (2006)
Frangioni, A., Gorgone, E.: Generalized bundle methods for sum-functions with “easy” components: applications to multicommodity network design. Tech. rep., Optimization online. http://www.optimization-online.org/DB_HTML/2011/06/3049.html (2011)
Fuller J.D., Chung W.: Dantzig–Wolfe decomposition of variational inequalities. Comput. Econ. 25, 303–326 (2005)
Gabriel S., Fuller J.: A Benders decomposition method for solving stochastic complementarity problems with an application in energy. Comput. Econ. 35(4), 301–329 (2010)
Gabriel S.A., Zhuang J., Egging R.: Solving stochastic complementarity problems in energy market modeling using scenario reduction. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 197(3), 1028–1040 (2009)
Gollmer R., Nowak M., Römisch W., Schultz R.: Unit commitment in power generation a basic model and some extensions. Ann. Oper. Res. 96, 167–189 (2000)
Gröwe-Kuska, N., Kiwiel, K.C., Nowak, M.P., Römisch, W., Wegner, I.: Decision making under uncertainty: energy and power, IMA volumes in mathematics and its applications, vol. 128, In: Greengard, C., Ruszczynski, A. (eds.) Power Management in a Hydro-thermal System Under Uncertainty by Lagrangian Relaxation, pp. 39–70. Springer, New York (2002)
Guignard M.: Lagrangean decomposition. TOP 11(2), 151–228 (2003)
Guignard M., Kim S.: Lagrangean decomposition: a model yielding stronger Lagrangean bounds. Math. Program. 39(2), 215–228 (1987)
Guigues V., Römisch W.: Sampling-based decomposition methods for multistage stochastic programs based on extended polyhedral risk measures. SIAM J. Optim. 22(2), 286–312 (2012)
Guigues, V., Sagastizábal, C.: Risk averse feasible policies for large-scale multistage stochastic linear programs. Math. Program. (2012) (accepted for publication)
Guigues V., Sagastizábal C.: The value of rolling horizon policies for risk-averse hydro-thermal planning. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 217, 219–240 (2012)
Guigues, V., Sagastizábal, C.: Exploiting structure of autoregressive processes in chance-constrained multistage stochastic linear programs. Oper. Res. Lett. (2012) (accepted for publication)
Guigues, V., Sagastizábal, C., Zubelli, J.: Robust management and pricing of LNG contracts with cancellation options. Tech. rep., IMPA. http://www.preprint.impa.br/Shadows/SERIE_A/2010/687.html (2009)
Heitsch H., Römisch W.: Stability and scenario trees for multistage stochastic programs. In: Infanger, G. (ed) Stochastic Programming, International Series in Operations Research & Management Science, vol. 150, pp. 139–164. Springer, New York (2011)
Higle J.L., Sen S.: Finite master programs in regularized stochastic decomposition. Math. Program. 67(2, Ser. A), 143–168 (1994)
Hinze M., Tröltzsch F.: Discrete concepts versus error analysis in PDE-constrained optimization. GAMM-Mitteilungen 33(2), 148–162 (2010)
Hiriart-Urruty, J.B., Lemaréchal, C.: Convex Analysis and Minimization Algorithms. No. 305-306 in Grund. der math. Wiss. Springer, Berlin (1993) (two volumes)
Hobbs B., Metzler C., Pang J.S.: Strategic gaming analysis for electric power systems: an MPEC approach. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 15(2), 638–645 (2000)
Hobbs B.F., Pang J.S.: Spatial oligopolistic equilibria with arbitrage, shared resources, and price function conjectures. Math. Program. 101, 57–94 (2004)
Hu X., Ralph D.: Using EPECs to model bilevel games in restructured electricity markets with locational prices. Oper. Res. 55(5), 809–827 (2007)
Kannan, A., Shanbhag, U.V., Kim, H.M.: Addressing supply-side risk in uncertain power markets: stochastic generalized Nash models, scalable algorithms and error analysis. Optim. Methods Softw. (2012) (to appear)
Kannan A., Shanbhag U.V., Kim H.M.: Strategic behavior in power markets under uncertainty. Energy Syst. 2(2), 115–141 (2011)
Khodaei A., Shahidehpour M., Kamalinia S.: Transmission switching in expansion planning. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 25(3), 1722–1733 (2010)
Kiwiel K.C.: A proximal bundle method with approximate subgradient linearizations. SIAM J. Optim. 16, 1007–1023 (2006)
Kiwiel, K.C.: Bundle methods for convex minimization with partially inexact oracles. Tech. rep., Optimization online. http://www.optimization-online.org/DB-HTML/2009/03/2257.html (2009)
Kleywegt, A.J., Shapiro, A., Homem-de Mello, T.: The sample average approximation method for stochastic discrete optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 12(2), 479–502 (2001/02)
Kulkarni A.A., Shanbhag U.V.: On the variational equilibrium as a refinement of the generalized Nash equilibrium. Automatica 48, 45–55 (2012)
Lemaréchal C.: Lagrangian relaxation. In: Jünger, M., Naddef, D. (eds) Computational Combinatorial Optimization, pp. 112–156. Springer, Berlin (2001)
Lemaréchal C., Pellegrino F., Renaud A., Sagastizábal C.: Bundle methods applied to the unit-commitment problem. In: Dolezal, J., Fidler, J. (eds) System Modelling and Optimization., pp. 395–402. Chapman and Hall, London (1996)
Lemaréchal C., Renaud A.: A geometric study of duality gaps, with applications. Math. Program. 90, 399–427 (2001)
Lemaréchal C., Sagastizábal C.: Variable metric bundle methods: from conceptual to implementable forms. Math. Program. A 76, 393–410 (1997)
Luna, J.P., Sagastizábal, C., Solodov, M.: A class of Dantzig–Wolfe type decomposition methods for variational inequality problems. Tech. rep., Optimization online. http://www.optimization-online.org/DB_HTML/2011/11/3256.html (2011)
Marcato R., Sagastizábal C.: Introducing environmental constraints in generation expansion problems. Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 14, 351–368 (2007)
Martinez M.G., Diniz A., Sagastizábal C.: A comparative study of two forward dynamic programming techniques for solving local thermal unit commitment problem. In: Proceedings of the 16th Power Systems Computation Conference. http://www.pscc-central.org/uploads/tx_ethpublications/pscc2008_323.pdf (2008)
Motto A., Galiana F.: Coordination in markets with nonconvexities as a mathematical program with equilibrium constraints-part I: a solution procedure. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 19(1), 308–316 (2004)
Moulin L., Poss M., Sagastizábal C.: Transmission expansion planning with re-design. Energy Syst. 1, 113–139 (2010)
Nedič A., Ozdaglar A.E.: A geometric framework for nonconvex optimization duality using augmented Lagrangian functions. J. Glob. Optim. 40(4), 545–573 (2008)
Nowak M.P., Römisch W.: Stochastic Lagrangian relaxation applied to power scheduling in a hydro-thermal system under uncertainty. Ann. Oper. Res. 100, 251–272 (2000)
Nowak M.P., Schultz R., Westphalen M.: A stochastic integer programming model for incorporating day-ahead trading of electricity into hydro-thermal unit commitment. Optim. Eng. 6, 163–176 (2005)
Nurnberg R., Römisch W.: A two-stage planning model for power scheduling in a hydro-thermal system under uncertainty. Optim. Eng. 3, 355–378 (2002)
Oliveira, W.L., Sagastizábal, C.: Level bundle methods for oracles with on-demand accuracy. Tech. rep., Optimization online. http://www.optimization-online.org/DB_HTML/2012/03/3390.html (2012)
Oliveira, W.L., Sagastizábal, C., Lemaréchal, C.: Inaccurate bundle methods in depth: a unified convergence framework (2012) (in preparation)
Oliveira W.L., Sagastizábal C., Penna D., Maceira M., Damázio J.: Optimal scenario tree reduction for stochastic streamflows in power generation planning problems. Optim. Methods Softw. 25, 917–936 (2010)
Oliveira W.L., Sagastizábal C., Scheimberg S.: Inexact bundle methods for two-stage stochastic programming. SIAM J. Optim. 21, 517–544 (2011)
Pereira M., Pinto L.: Multi-stage stochastic optimization applied to energy planning. Math. Program. 52(2), 359–375 (1991)
Philpott A., Guan Z.: On the convergence of stochastic dual dynamic programming and related methods. Oper. Res. Lett. 36(4), 450–455 (2008)
Philpott A., de Matos V.: Dynamic sampling algorithms for multi-stage stochastic programs with risk aversion. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 218, 470–483 (2012)
Philpott A., Schultz R.: Unit commitment in electricity pool markets. Math. Program. 108, 313–337 (2006)
Ralph, D., Smeers, Y.: EPECs as models for electricity markets. In: Power Systems Conference and Exposition, 2006. PSCE ’06. 2006 IEEE PES, pp. 74–80 (2006). doi:10.1109/PSCE.2006.296252
Rebennack, S., Pardalos, P., Pereira, M., Iliadis, N. (eds): Handbook of Power Systems, Energy Systems, vol. I and II. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Rockafellar R., Uryasev S.: Conditional value-at-risk for general loss distributions. J. Bank. Finance 26(7), 1443–1471 (2002)
Rubinov A.M., Huang X.X., Yang X.Q.: The zero duality gap property and lower semicontinuity of the perturbation function. Math. Oper. Res. 27(4), 775–791 (2002)
Ruszczyński A.: On convergence of an augmented Lagrangian decomposition method for sparse convex optimization. Math. Oper. Res. 20(3), 634–656 (1995)
Ruszczyński A.: Decomposition methods. In: Ruszczynski, A., Shapiro, A. (eds) Stochastic Programming, Handbooks in Operations Research and Management Science, vol. 10, pp. 141–211. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2003)
Sen S.: Algorithms for stochastic mixed-integer programming models. In: Aardal, G.N.K., Weismantel, R. (eds) Discrete Optimization, Handbooks in Operations Research and Management Science, vol. 12, pp. 515–558. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2005)
Sen S., Yu L., Genc T.: A stochastic programming approach to power portfolio optimization. Oper. Res. 54(1), 55–72 (2006)
Shapiro A.: Analysis of stochastic dual dynamic programming method. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 209(1), 63–72 (2011)
Shapiro, A., Dentcheva, D., Ruszczyński, A.: Lectures on Stochastic Programming: Modeling and Theory. MPS/SIAM Series on Optimization, vol. 9, pp. xvi+436 (2009)
Shapiro, A., Tekaya, W.: Report for technical cooperation between Georgia Institute of Technology and ONS—Operador Nacional do Sistema Elétrico. Report 2: risk averse approach. http://www.isye.gatech.edu/people/faculty/Alex_Shapiro/Report-4.pdf (2011)
Takriti S., Birge J., Long E.: A stochastic model for the unit commitment problem. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 11, 1497–1508 (1996)
Van Ackooij W., Henrion R., Möller A., Zorgati R.: On probabilistic constraints induced by rectangular sets and multivariate normal distributions. Math. Methods Oper. Res. 71, 535–549 (2010)
Van Ackooij W., Henrion R., Möller A., Zorgati R.: On joint probabilistic constraints with gaussian coefficient matrix. Oper. Res. Lett. 39(2), 99–102 (2011)
Van Ackooij, W., Zorgati, R., Henrion, R., Möller, A.: Chance constrained programming and its applications to energy management. In: Dritsas, I. (ed.) Stochastic Optimization—Seeing the Optimal for the Uncertain, pp. 291–320. InTech. http://www.intechopen.com/books/show/title/stochastic-optimization-seeing-the-optimal-for-the-uncertain (2011)
Van Slyke R., Wets R.: L-shaped linear programs with applications to control and stochastic programming. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 17, 638–663 (1969)
Wallace S.W., Fleten S.E.: Stochastic programming models in energy. In: Ruszczynski, A., Shapiro, A. (eds) Stochastic Programming, Handbooks in Operations Research and Management Science, vol. 10, pp. 637–677. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2003)
Yakowitz D.: A regularized stochastic decomposition algorithm for two-stage stochastic linear programs. Comput. Optim. Appl. 3(1), 59–81 (1994)
Yao J., Oren S.S., Adler I.: Two-settlement electricity markets with price caps and Cournot generation firms. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 181(3), 1279–1296 (2007)
Yin H., Shanbhag U., Mehta P.: Nash equilibrium problems with scaled congestion costs and shared constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 56(7), 1702–1708 (2011)
Zakeri G., Philpott A.B., Ryan D.M.: Inexact cuts in Benders decomposition. SIAM J. Optim. 10(3), 643–657 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research partially supported by Grants CNPq 303840/2011-0, AFOSR FA9550-08-1-0370, NSF DMS 0707205, as well as by PRONEX-Optimization and FAPERJ.
C. Sagastizábal: on leave from INRIA, France.
C. Sagastizábal is a visiting researcher at IMPA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sagastizábal, C. Divide to conquer: decomposition methods for energy optimization. Math. Program. 134, 187–222 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-012-0570-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-012-0570-7