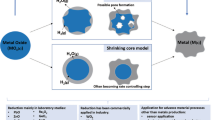
Abstract
Hydrogen (H2) is an energy carrier capable of replacing fossil fuels without the main effect of combustion-based pollutant generation into the atmosphere. Therefore, its sustainable production is of great interest. In this research study, the effect of temperature in the reaction of hydrolysis with recycled aluminum for the H2 production has been evaluated. The reaction was carried by using a concentrated NaOH solution, and different operating temperatures were established. According to the gas chromatography analysis, the produced H2 has a purity of 93.33%. Accumulated H2 production over time at different temperatures was statistically modeled with growth models (Gompertz, Logistic and Asymptotic) which showed a good fit. According to the statistical analysis, it was found that the main effect of temperature on the reaction is the increase in speed, with the highest production (727 mL) in 116 s at 50 °C. Nevertheless, at room temperature, the reaction efficiency was found to be 97%, obtaining 660 mL of H2 in 268 s. The physicochemical characterization of the solid residues obtained in the reaction revealed that these are formed by micrometric agglomerates containing aluminum, sodium, and oxygen. Moreover, the main crystalline phases detected were aluminum hydroxide and sodium aluminum oxide hydrate. It is concluded that the production of H2 from recycled aluminum at room temperature can be a viable option for the generation of clean power with lower energy consumption and financial costs than traditional technologies.
Graphical abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Ajanovic A, Haas R (2021) Prospects and impediments for hydrogen and fuel cell vehicles in the transport sector. Int J Hydrog Energy 46(16):10049–10058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.03.122
Akal D, Öztuna S, Büyükakın MK (2020) A review of hydrogen usage in internal combustion engines (gasoline–Lpg–diesel) from combustion performance aspect. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.02.001
Al-Thubaiti KS, Khan Z (2020) Trimetallic nanocatalysts to enhanced hydrogen production from hydrous hydrazine: the role of metal centers. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.03.093
Ambaryan GN, Vlaskin MS, Dudoladov AO, Meshkov EA, Zhuk AZ, Shkolnikov EI (2016) Hydrogen generation by oxidation of coarse aluminum in low content alkali aqueous solution under intensive mixing. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.08.005
Bolt A, Dincer I, Agelin-Chaab M (2020) Experimental study of hydrogen production process with aluminum and water. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.03.160
Burnham AK (2017) Use and misuse of logistic equations for modeling chemical kinetics. J Therm Anal Calorim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4879-3
Chen X, Zhao Z, Hao M, Wang D (2013) Research of hydrogen generation by the reaction of Al-based materials with water. J Power Sour. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.08.078
Coronel-García MA, Salazar-Barrera JG, Malpica-Maldonado JJ, Martínez-Salazar AL, Melo-Banda JA (2020) Hydrogen production by aluminum corrosion in aqueous hydrochloric acid solution promoted by sodium molybdate dihydrate. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.01.122
Dai HB, Ma GL, Xia HJ, Wang P (2011) Reaction of aluminium with alkaline sodium stannate solution as a controlled source of hydrogen. Energy Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ee00014d
Dawood F, Anda M, Shafiullah GM (2020) Hydrogen production for energy: an overview. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.12.059
Ding C, Gao Z, Wang J, Ma L, Shangguan J, Yuan Q, Zhao M, Zhang K (2021) The coralline cobalt oxides compound of multiple valence states deriving from flower-like layered double hydroxide for efficient hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of NaBH4. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.10.141
Dong L, Wu J, Zhou C, Xu CJ, Liu B, Xing D, Xie G, Wu X, Wang Q, Cao G, Ren N (2020) Low concentration of NaOH/Urea pretreated rice straw at low temperature for enhanced hydrogen production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45(3):1578–1587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.11.037
Dupiano P, Stamatis D, Dreizin EL (2011) Hydrogen production by reacting water with mechanically milled composite aluminum-metal oxide powders. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.01.062
Fasolini A, Cucciniello R, Paone E, Mauriello F, Tabanelli T (2019) A short overview on the hydrogen production via aqueous phase reforming (APR) of cellulose, C6–C5 sugars and polyols. Catalysts 9(11):917. https://doi.org/10.3390/CATAL9110917
Feng Y, Wang H, Chen X, Lv F, Li Y, Zhu Y, Xu C, Zhang X, Liu HR, Li H (2020) Simple synthesis of Cu2O–CoO nanoplates with enhanced catalytic activity for hydrogen production from ammonia borane hydrolysis. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.04.257
Gao Z, Ji F, Cheng D, Yin C, Niu J, Brnic J (2021) Hydrolysis-based hydrogen generation investigation of aluminum system adding low-melting metals. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051433
Hiraki T, Takeuchi M, Hisa M, Akiyama T (2005) Hydrogen production from waste aluminum at different temperatures, with LCA. Mater Trans. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.46.1052
Hiraki T, Yamauchi S, Iida M, Uesugi H, Akiyama T (2007) Process for recycling waste aluminum with generation of high-pressure hydrogen. Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1021/es062883l
Ho CY (2017) Hydrolytic reaction of waste aluminum foils for high efficiency of hydrogen generation. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.06.104
Ilyukhina AV, Kravchenko OV, Bulychev BM (2017) Studies on microstructure of activated aluminum and its hydrogen generation properties in aluminum/water reaction. J Alloy Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.08.151
İzgi MS, Baytar O, Şahin Ö, Kazıcı HÇ (2020) CeO2 supported multimetallic nano materials as an efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of NaBH4. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.04.034
Janssen JLLCC, Weeda M, Detz RJ, van der Zwaan B (2022) Country-specific cost projections for renewable hydrogen production through off-grid electricity systems. Appl Energy 309:118398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.118398
Jiang D, Ge X, Zhang T, Chen Z, Zhang Z, He C, Zhang Q, Li Y (2020) Effect of alkaline pretreatment on photo-fermentative hydrogen production from giant reed: comparison of NaOH and Ca(OH)2. Biores Technol 304:123001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123001
Kumar D, Muthukumar K (2020) An overview on activation of aluminium-water reaction for enhanced hydrogen production. J Alloys Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155189
Lee T, Fu J, Basile V, Corsi JS, Wang Z, Detsi E (2020) Activated alumina as value-added byproduct from the hydrolysis of hierarchical nanoporous aluminum with pure water to generate hydrogen fuel. Renew Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.03.072
Li W, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Sun M, Waterhouse GIN, Huang B, Zhang K, Zhang T, Lu S (2021) Exploiting ru-induced lattice strain in coru nanoalloys for robust bifunctional hydrogen production. Angew Chem Int Edn. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202013985
Ligen Y, Vrubel H, Girault H (2020) Energy efficient hydrogen drying and purification for fuel cell vehicles. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.02.035
Liu M, Zhou L, Luo X, Wan C, Xu L (2020) Recent advances in noble metal catalysts for hydrogen production from ammonia borane. Catalysts. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10070788
Malek A, Ganta A, Divyapriya G, Nambi I, Thomas T (2021) Hydrogen production from human and cow urine using in situ synthesized aluminium nanoparticles. Int J Hyd Energy 46(54):27319–27329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.06.024
Manzotti A, Quattrocchi E, Curcio A, Kwok SCT, Santarelli M, Ciucci F (2022) Membraneless electrolyzers for the production of low-cost, high-purity green hydrogen: a techno-economic analysis. Energy Convers Manage 254:115156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2021.115156
Martino M, Ruocco C, Meloni E, Pullumbi P, Palma V (2021) Main hydrogen production processes: an overview. Catalysts. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11050547
Murugan A, de Huu M, Bacquart T, van Wijk J, Arrhenius K, te Ronde I, Hemfrey D (2019) Measurement challenges for hydrogen vehicles. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.03.190
Ouyang L, Jiang J, Chen K, Zhu M, Liu Z (2021) Hydrogen production via hydrolysis and alcoholysis of light metal-based materials: a review. Nano-Micro Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00657-9
Pighin SA, Urretavizcaya G, Bobet JL, Castro FJ (2020) Nanostructured Mg for hydrogen production by hydrolysis obtained by MgH2 milling and dehydriding. J Alloy Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154000
Pinheiro J, Bates D (2021) Self-Starting Nls Asymptotic Regression Model. ETH Zürich. http://stat.ethz.ch/R-manual/R-patched/library/stats/html/SSasymp.html. Accessed 26 October 26 2021
Prasad D, Patil KN, Sandhya N, Chaitra CR, Bhanushali JT, Samal AK, Keri RS, Jadhav AH, Nagaraja BM (2019) Highly efficient hydrogen production by hydrolysis of NaBH4 using eminently competent recyclable Fe2O3 decorated oxidized MWCNTs robust catalyst. Appl Surf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.06.041
Razi F, Dincer I, Gabriel K (2022) Assessment study of a four-step copper-chlorine cycle modified with flash vaporization process for hydrogen production. Int J Hyd Energy 47(4):2164–2177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.10.198
Sørensen B (2005) Hydrogen and fuel cells. Hyd Fuel Cells. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-655281-2.X5000-8
Streicher MA (1949) The Dissolution of aluminum in sodium hydroxide solutions II. J Electrochem Soc 96(3):170. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2776781
Tjørve KMC, Tjørve E (2017) The use of Gompertz models in growth analyses, and new Gompertz-model approach: an addition to the Unified-Richards family. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178691
Wang HZ, Leung DYC, Leung MKH, Ni M (2009) A review on hydrogen production using aluminum and aluminum alloys. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2008.02.009
Wu T, Xu F, Sun LX, Cao Z, Chu HL, Sun YJ, Wang L, Chen PH, Chen J, Pang Y, Zou YJ, Qiu SJ, Xiang CL, Zhang HZ (2014) Al-Li3AlH6: a novel composite with high activity for hydrogen generation. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.04.159
Xiao F, Guo Y, Li J, Yang R (2018) Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of activated aluminum composites in tap water. Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.05.201
Xu S, Yang XH, Tang SS, Liu J (2019) Liquid metal activated hydrogen production from waste aluminum for power supply and its life cycle assessment. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.05.176
Yavor Y, Goroshin S, Bergthorson JM, Frost DL, Stowe R, Ringuette S (2013) Enhanced hydrogen generation from aluminum–water reactions. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.09.070
Yavor Y, Goroshin S, Bergthorson JM, Frost DL (2015) Comparative reactivity of industrial metal powders with water for hydrogen production. Int J Hyd Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.11.075
Zhang H, Xu G, Zhang L, Wang W, Miao W, Chen K, Cheng L, Li Y, Han S (2020a) Ultrafine cobalt nanoparticles supported on carbon nanospheres for hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Renew Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.08.031
Zhang J, Lin F, Yang L, He Z, Huang X, Zhang D, Dong H (2020) Ultrasmall Ru nanoparticles supported on chitin nanofibers for hydrogen production from NaBH4 hydrolysis. Chin Chem Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.11.042
Zou H, Chen S, Zhao Z, Lin W (2013) Hydrogen production by hydrolysis of aluminum. J Alloys Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.06.016
Acknowledgements
The collaboration of the Environmental Engineering laboratories of the Faculty of Engineering of the Autonomous University of Yucatan, Mexico, and the use and facilities of LANNBIO, Cinvestav-Merida are gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
This research received support of: CONACYT Project CB-2015-255109, CONACYT (CB-2015-01) Project 254321 and Project CONACYT-SENER 254667.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization was contributed by M.R-G. and L.S-P.; methodology was contributed by R.Q. and J.M.; C.V-P. and J.M. contributed to software; M.F-B. and R.Q. contributed to validation; C.V-P. and M.F-B. contributed to formal analysis; M.A.E-S. and E.H-N. contributed to research; writing—original draft preparation, was contributed by L.S-P. and E.H-N.; writing—review and editing, was contributed by M.R-G. and M.A.E-S.; M.R-G. and L.S-P contributed to project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Soberanis, M.A.E., Vales-Pinzón, C., Hernández-Núñez, E. et al. Temperature dependence on hydrogen production from hydrolysis reaction of recycled aluminum. Clean Techn Environ Policy 25, 35–49 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-022-02386-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-022-02386-y