Abstract
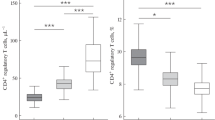
The aim of this work was to analyze the effects of highly active antiretroviral therapy on the chronically activated immune system of 26 antiretroviral-naive HIV-1-infected patients. Samples from baseline to week 24 or 36 of treatment were tested for serum levels of β2-microglobulin, tumor necrosis factor α and soluble tumor necrosis factor α receptor type II, as well as for human leukocyte antigen-DR expression on T cells. After starting therapy, the mean HIV-1 RNA serum levels decreased and the mean CD4+ cell counts increased from baseline to week 36 (P<0.001). Mean levels of tumor necrosis factor α receptor type II, tumor necrosis factor α and β2-microglobulin as well as expression of human leukocyte antigen-DR were significantly reduced at the end of follow-up (P<0.01). Deactivation kinetics of these parameters was similar in patients with CD4+ counts>200 cells/μl at baseline versus those with CD4+ counts <200 cells/μl at baseline, despite higher activation at baseline in the group with <200 cells/μl. In summary, this study shows that highly active antiretroviral therapy is able to induce a strong deactivation of the immune system of HIV-1-infected patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franco, J., Rubio, A., Rey, C. et al. Reduction of Immune System Activation in HIV-1-Infected Patients Undergoing Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy. EJCMID 18, 733–736 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100960050388
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100960050388