Abstract
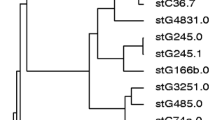
Streptococcal inhibitor of complement (SIC) and distantly related to SIC (DRS) are well-characterized extracellular virulence factors produced by only a few emm types among group A streptococci. The prevalence and sequence variations of the sic-like gene (sicG) in clinical samples of group C and G Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis (SDSE), however, have not been widely investigated. We constructed primers targeting sicG and screened 129 geographically matched and previously emm-typed non-invasive (n = 64) and invasive (n = 65) SDSE isolates for the presence of this gene. sicG was detected in seven non-invasive and eight invasive isolates belonging to eight different emm types. Within five of these emm types, sicG-negative isolates were also detected. All three isolates of stG2078.0 possessed sicG and were associated with severe soft tissue infections. Altogether, six sicG alleles (sicG1–6) were identified, and sequence variations were mainly caused by single nucleotide polymorphisms and deletion/insertion mutations. sicG1–6 were predicted to encode SICG proteins of varying length, composition, and homology with SIC and DRS proteins of group A streptococci. Our findings indicate an unpredictable association between sicG and emm type, a limited distribution and substantial sequence diversity of sicG, and no obvious relation between its presence and disease severity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beres SB, Sesso R, Pinto SW, Hoe NP, Porcella SF, Deleo FR, Musser JM (2008) Genome sequence of a Lancefield group C Streptococcus zooepidemicus strain causing epidemic nephritis: new information about an old disease. PLoS One 3(8):e3026. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003026
Shimomura Y, Okumura K, Murayama SY, Yagi J, Ubukata K, Kirikae T, Miyoshi-Akiyama T (2011) Complete genome sequencing and analysis of a Lancefield group G Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis strain causing streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (STSS). BMC Genomics 12:17. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-17
Takahashi T, Sunaoshi K, Sunakawa K, Fujishima S, Watanabe H, Ubukata K; Invasive Streptococcal Disease Working G (2010) Clinical aspects of invasive infections with Streptococcus dysgalactiae ssp. equisimilis in Japan: differences with respect to Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus agalactiae infections. Clin Microbiol Infect 16(8):1097–1103. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.03047.x
Akesson P, Sjöholm AG, Björck L (1996) Protein SIC, a novel extracellular protein of Streptococcus pyogenes interfering with complement function. J Biol Chem 271(2):1081–1088
Fernie-King BA, Seilly DJ, Lachmann PJ (2006) Inhibition of antimicrobial peptides by group A streptococci: SIC and DRS. Biochem Soc Trans 34(Pt 2):273–275. doi:10.1042/BST20060273
Fernie-King BA, Seilly DJ, Davies A, Lachmann PJ (2002) Streptococcal inhibitor of complement inhibits two additional components of the mucosal innate immune system: secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor and lysozyme. Infect Immun 70(9):4908–4916
Lukomski S, Hoe NP, Abdi I, Rurangirwa J, Kordari P, Liu M, Dou SJ, Adams GG, Musser JM (2000) Nonpolar inactivation of the hypervariable streptococcal inhibitor of complement gene (sic) in serotype M1 Streptococcus pyogenes significantly decreases mouse mucosal colonization. Infect Immun 68(2):535–542
Hartas J, Sriprakash KS (1999) Streptococcus pyogenes strains containing emm12 and emm55 possess a novel gene coding for distantly related SIC protein. Microb Pathog 26(1):25–33. doi:10.1006/mpat.1998.0244
Binks M, Sriprakash KS (2004) Characterization of a complement-binding protein, DRS, from strains of Streptococcus pyogenes containing the emm12 and emm55 genes. Infect Immun 72(7):3981–3986. doi:10.1128/IAI.72.7.3981-3986.2004
Minami M, Ichikawa M, Matsui H, Hata N, Wakiyama N, Matsumoto M, Ohta M, Hasegawa T (2011) Prevalence of a streptococcal inhibitor of a complement-mediated cell lysis-like gene (sicG) in Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis. Curr Microbiol 62(3):884–887. doi:10.1007/s00284-010-9798-8
Kittang BR, Bruun T, Langeland N, Mylvaganam H, Glambek M, Skrede S (2011) Invasive group A, C and G streptococcal disease in western Norway: virulence gene profiles, clinical features and outcomes. Clin Microbiol Infect 17(3):358–364. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03253.x
Kittang BR, Skrede S, Langeland N, Haanshuus CG, Mylvaganam H (2011) emm gene diversity, superantigen gene profiles and presence of SlaA among clinical isolates of group A, C and G streptococci from western Norway. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 30(3):423–433. doi:10.1007/s10096-010-1105-x
Davies MR, McMillan DJ, Beiko RG, Barroso V, Geffers R, Sriprakash KS, Chhatwal GS (2007) Virulence profiling of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis isolated from infected humans reveals 2 distinct genetic lineages that do not segregate with their phenotypes or propensity to cause diseases. Clin Infect Dis 44(11):1442–1454. doi:10.1086/516780
Stockbauer KE, Grigsby D, Pan X, Fu YX, Mejia LM, Cravioto A, Musser JM (1998) Hypervariability generated by natural selection in an extracellular complement-inhibiting protein of serotype M1 strains of group A Streptococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(6):3128–3133
Brandt CM, Haase G, Spellerberg B, Holland R, Lütticken R (2003) drs (Distantly related sic) gene polymorphisms among emm12-type Streptococcus pyogenes isolates. J Clin Microbiol 41(4):1794–1797
Mylvaganam H, Bjorvatn B, Osland A (2001) Polymorphism of the virulence regulon and allelic variations of the sic gene among the emm1 isolates of group A Streptococcus from western Norway. Microb Pathog 30(2):71–79. doi:10.1006/mpat.2000.0408
Ahmad Y, Gertz RE Jr, Li Z, Sakota V, Broyles LN, Van Beneden C, Facklam R, Shewmaker PL, Reingold A, Farley MM, Beall BW (2009) Genetic relationships deduced from emm and multilocus sequence typing of invasive Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis and S. canis recovered from isolates collected in the United States. J Clin Microbiol 47(7):2046–2054. doi:10.1128/JCM.00246-09
Broyles LN, Van Beneden C, Beall B, Facklam R, Shewmaker PL, Malpiedi P, Daily P, Reingold A, Farley MM (2009) Population-based study of invasive disease due to beta-hemolytic streptococci of groups other than A and B. Clin Infect Dis 48(6):706–712. doi:10.1086/597035
Okumura K, Shimomura Y, Murayama SY, Yagi J, Ubukata K, Kirikae T, Miyoshi-Akiyama T (2012) Evolutionary paths of streptococcal and staphylococcal superantigens. BMC Genomics 13:404. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-13-404
Suzuki H, Lefébure T, Hubisz MJ, Pavinski Bitar P, Lang P, Siepel A, Stanhope MJ (2011) Comparative genomic analysis of the Streptococcus dysgalactiae species group: gene content, molecular adaptation, and promoter evolution. Genome Biol Evol 3:168–185. doi:10.1093/gbe/evr006
Acknowledgments
The study has been financed by the University of Bergen and Haraldsplass Deaconal Hospital. The authors wish to thank Trond Bruun for the revision of the manuscript, and Marit Tellevik for the technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oppegaard, O., Mylvaganam, H., Skrede, S. et al. Sequence diversity of sicG among group C and G Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis isolates associated with human infections in western Norway. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 33, 273–277 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-013-1955-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-013-1955-0