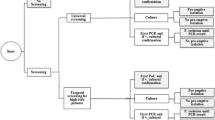
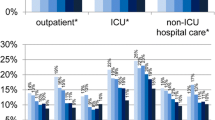
Abstract
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections represent a serious challenge for health care institutions, which is inherent in the combination of prevalence, transmission rates and costs. Furthermore, performing an MRSA screening requires information on the complex system of effectiveness, accuracy and costs of different screening methods. The purpose of this study was to give an overview of parameters with decisive significance for the burden of MRSA and the selection of a specific MRSA screening strategy. A systematic literature search for peer-reviewed health economic studies associated with MRSA was performed (from 1995 to the present). Eighty-seven different studies met all inclusion and exclusion criteria. Primary outcomes included the prevalence of MRSA, MRSA transmission rates, performance characteristics of MRSA screening methods, costs for pre-emptive isolation precautions and costs per MRSA case. The prevalence rates reported for all inpatients (1.2–5.3 %) as well as for inpatients with risk factors or patients in risk areas (3.85–20.6 %) vary greatly. The range of cross-transmission rates per day reported for patients with MRSA in isolation is 0.00081–0.009 and for carriers not in isolation is 0.00137–0.140, respectively. For polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods, the mean sensitivity and specificity were 91.09 and 95.79 %, respectively. Culture methods show an average sensitivity of 89.01 % and an average specificity of 93.21 %. The turn-around time for PCR methods averages 15 h, while for the culture method, it can only be estimated as 48–72 h. This review filtered important parameters and cost drivers, and covered them with literature-based averages. These findings serve as an ideal evidence base for further health economic considerations of the cost-effectiveness of different MRSA screening methods.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vos MC, Verbrugh HA (2005) MRSA: We can overcome, but who will lead the battle? Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 26(2):117–120
Köck R, Becker K, Cookson B, van Gemert-Pijnen JE, Harbarth S, Kluytmans J, Mielke M, Peters G, Skov RL, Struelens MJ, Tacconelli E, Navarro Torné A, Witte W, Friedrich AW (2010) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): burden of disease and control challenges in Europe. Euro Surveill 15(41):19688
Chaberny IF, Ziesing S, Mattner F, Bärwolff S, Brandt C, Eckmanns T, Rüden H, Sohr D, Weist K, Gastmeier P (2005) The burden of MRSA in four German university hospitals. Int J Hyg Environ Health 208(6):447–453
Guleri A, Kehoe A, Hartley J, Lunt B, Harper N, Palmer R, Lickiss J, Mawdsley S, Jones A (2011) The costs and benefits of hospital MRSA screening. Br J Healthc Manag 17(2):64–71
Korczak D, Schöffmann C (2010) Medizinische Wirksamkeit und Kosten-Effektivität von Präventions- und Kontrollmaßnahmen gegen Methicillin-resistente Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)-Infektionen im Krankenhaus. Schriftenreihe Health Technology Assessment (HTA) in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland
Diller R, Sonntag AK, Mellmann A, Grevener K, Senninger N, Kipp F, Friedrich AW (2008) Evidence for cost reduction based on pre-admission MRSA screening in general surgery. Int J Hyg Environ Health 211(1–2):205–212
van Rijen MM, Kluytmans JA (2009) Costs and benefits of the MRSA Search and Destroy policy in a Dutch hospital. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28(10):1245–1252
Karchmer TB, Durbin LJ, Simonton BM, Farr BM (2002) Cost-effectiveness of active surveillance cultures and contact/droplet precautions for control of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Hosp Infect 51(2):126–132
Kramer A, Hübner N-O, Steinmetz I, Ewert R, Bartels C (2009) Infektionsraten mit frühem Screening senken. Berl Med J 6:12–14
Geldner G, Ruoff M, Kiefer P, Georgieff M, Wiedeck H (1999) Kostenanalyse von MRSA-Infektionen auf einer operativen Intensivstation. Anästhesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther 34:409–413
Hübner N-O, Kramer A, Steinmetz I, Bartels C (2009) Das Greifswalder Modell der MRSA-Prävention—Maßnahmen zur Kontrolle multiresistenter Erreger. Klinikarzt 38:192–196
Kramer A, Hübner N, Zygmunt M (2008) Greifswalder Präventionsstrategie greift. Deutsche Hebammen Zeitschrift 3:26–28
Chaberny IF, Bindseil A, Sohr D, Gastmeier P (2008) A point-prevalence study for MRSA in a German university hospital to identify patients at risk and to evaluate an established admission screening procedure. Infection 36(6):526–532
Gastmeier P, Geffers C (2008) Nosocomial infections in Germany. What are the numbers, based on the estimates for 2006? Dtsch Med Wochenschr 133(21):1111–1115
Reich-Schupke S, Geis G, Reising M, Altmeyer P, Stucker M (2010) MRSA in dermatology—Prospective epidemiological study in employees and patients of a dermatological department of a university hospital. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 8(8):607–613
Robert Koch-Institut (2010) Flächendeckendes einmonatiges MRSA-Prävalenzscreening in Akut- und Rehakliniken in Siegen-Wittgenstein. Robert Koch-Institut
Rünz T, Volbracht J, Weiß G, Kellner M (2010) Erfahrungen mit einem neuen MRSA-Management im Klinikverbund Südwest. Hyg Med 35(9):306–314
Woltering R, Hoffmann G, Daniels-Haardt I, Gastmeier P, Chaberny IF (2008) Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in patients in long-term care in hospitals, rehabilitation centers and nursing homes of a rural district in Germany. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 133(19):999–1003
Schulz M, Nonnenmacher C, Mutters R (2009) Cost-effectiveness of rapid MRSA screening in surgical patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28(11):1291–1296
Wernitz MH, Swidsinski S, Weist K, Sohr D, Witte W, Franke KP, Roloff D, Rüden H, Veit SK (2005) Effectiveness of a hospital-wide selective screening programme for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) carriers at hospital admission to prevent hospital-acquired MRSA infections. Clin Microbiol Infect 11(6):457–465
Bracco D, Dubois MJ, Bouali R, Eggimann P (2007) Single rooms may help to prevent nosocomial bloodstream infection and cross-transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in intensive care units. Intensive Care Med 33(5):836–840
Cheng VC, Tai JW, Chan WM, Lau EH, Chan JF, To KK, Li IW, Ho PL, Yuen KY (2010) Sequential introduction of single room isolation and hand hygiene campaign in the control of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in intensive care unit. BMC Infect Dis 10:263
Forrester M, Pettitt AN (2005) Use of stochastic epidemic modeling to quantify transmission rates of colonization with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an intensive care unit. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 26(7):598–606
Jernigan JA, Titus MG, Gröschel DHM, Getchell-White SI, Farr BM (1996) Effectiveness of contact isolation during a hospital outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Epidemiol 143(5):496–504
Jeyaratnam D, Whitty CJM, Phillips K, Liu DM, Orezzi C, Ajoku U, French GL (2008) Impact of rapid screening tests on acquisition of meticillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus: cluster randomised crossover trial. BMJ 336(7650):927–930
Papia G, Louie M, Tralla A, Johnson C, Collins V, Simor AE (1999) Screening high-risk patients for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on admission to the hospital: is it cost effective? Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 20(7):473–477
Raboud J, Saskin R, Simor A, Loeb M, Green K, Low DE, McGeer A (2005) Modeling transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among patients admitted to a hospital. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 26(7):607–615
Akpaka PE, Kissoon S, Rutherford C, Swantson WH, Jayaratne P (2008) Evaluation of methods and costs for detecting methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from clinical specimens at regional hospitals in Trinidad and Tobago. West Indian Med J 57(1):24–27
Bischof LJ, Lapsley L, Fontecchio K, Jacosalem D, Young C, Hankerd R, Newton DW (2009) Comparison of chromogenic media to BD GeneOhm methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) PCR for detection of MRSA in nasal swabs. J Clin Microbiol 47(7):2281–2283
Bishop EJ, Grabsch EA, Ballard SA, Mayall B, Xie S, Martin R, Grayson ML (2006) Concurrent analysis of nose and groin swab specimens by the IDI-MRSA PCR assay is comparable to analysis by individual-specimen PCR and routine culture assays for detection of colonization by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 44(8):2904–2908
Boyce JM, Havill NL (2008) Comparison of BD GeneOhm methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) PCR versus the CHROMagar MRSA assay for screening patients for the presence of MRSA strains. J Clin Microbiol 46(1):350–351
Bühlmann M, Bögli-Stuber K, Droz S, Mühlemann K (2008) Rapid screening for carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by PCR and associated costs. J Clin Microbiol 46(7):2151–2154
Chen WT, Wang JT, Lee WS, Huang CH, Liao CH, Chen YC, Chang SC (2010) Performance of the BD GeneOhm methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) PCR assay for detecting MRSA nasal colonization in Taiwanese adults. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 43(5):372–377
Cunningham R, Jenks P, Northwood J, Wallis M, Ferguson S, Hunt S (2007) Effect on MRSA transmission of rapid PCR testing of patients admitted to critical care. J Hosp Infect 65(1):24–28
Daeschlein G, Assadian O, Daxboeck F, Kramer A (2006) Multiplex PCR-ELISA for direct detection of MRSA in nasal swabs advantageous for rapid identification of non-MRSA carriers. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 25(5):328–330
Danial J, Noel M, Templeton KE, Cameron F, Mathewson F, Smith M, Cepeda JA (2011) Real-time evaluation of an optimized real-time PCR assay versus Brilliance chromogenic MRSA agar for the detection of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from clinical specimens. J Med Microbiol 60(Pt 3):323–328
Fang H, Hedin G (2003) Rapid screening and identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from clinical samples by selective-broth and real-time PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol 41(7):2894–2899
Farley JE, Stamper PD, Ross T, Cai M, Speser S, Carroll KC (2008) Comparison of the BD GeneOhm methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) PCR assay to culture by use of BBL CHROMagar MRSA for detection of MRSA in nasal surveillance cultures from an at-risk community population. J Clin Microbiol 46(2):743–746
Hagen RM, Seegmüller I, Navai J, Kappstein I, Lehn N, Miethke T (2005) Development of a real-time PCR assay for rapid identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from clinical samples. Int J Med Microbiol 295(2):77–86
Herdman MT, Wyncoll D, Halligan E, Cliff PR, French G, Edgeworth JD (2009) Clinical application of real-time PCR to screening critically ill and emergency-care surgical patients for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a quantitative analytical study. J Clin Microbiol 47(12):4102–4108
Holfelder M, Eigner U, Turnwald AM, Witte W, Weizenegger M, Fahr A (2006) Direct detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in clinical specimens by a nucleic acid-based hybridisation assay. Clin Microbiol Infect 12(12):1163–1167
Hombach M, Pfyffer GE, Roos M, Lucke K (2010) Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in specimens from various body sites: performance characteristics of the BD GeneOhm MRSA assay, the Xpert MRSA Assay, and Broth-Enriched Culture in an Area with a low prevalence of MRSA infections. J Clin Microbiol 48(11):3882–3887
Hope WW, Morton AP, Looke DFM, Schooneveldt JM, Nimmo GR (2004) A PCR method for the identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from screening swabs. Pathology 36(3):265–268
Huletsky A, Lebel P, Picard FJ, Bernier M, Gagnon M, Boucher N, Bergeron MG (2005) Identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carriage in less than 1 hour during a hospital surveillance program. Clin Infect Dis 40(7):976–981
Kelley PG, Grabsch EA, Howden BP, Gao W, Grayson ML (2009) Comparison of the Xpert methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) assay, BD GeneOhm MRSA assay, and culture for detection of nasal and cutaneous groin colonization by MRSA. J Clin Microbiol 47(11):3769–3772
Levi K, Towner KJ (2005) Rapid detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from screening enrichment broths by real-time PCR. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 24(6):423–427
Lucke K, Hombach M, Hug M, Pfyffer GE (2010) Rapid detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in diverse clinical specimens by the BD GeneOhm MRSA assay and comparison with culture. J Clin Microbiol 48(3):981–984
Nulens E, Descheemaeker P, Deurenberg RH, Stobberingh EE, Gordts B (2010) Contribution of two molecular assays as compared to selective culture for MRSA screening in a low MRSA prevalence population. Infection 38(2):98–101
Oberdorfer K, Pohl S, Frey M, Heeg K, Wendt C (2006) Evaluation of a single-locus real-time polymerase chain reaction as a screening test for specific detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in ICU patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 25(10):657–663
Ornskov D, Kolmos B, Bendix Horn P, Nederby Nielsen J, Brandslund I, Schouenborg P (2008) Screening for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in clinical swabs using a high-throughput real-time PCR-based method. Clin Microbiol Infect 14(1):22–28
Patel PA, Ledeboer NA, Ginocchio CC, Condon S, Bouchard S, Qin P, Karchmer T, Peterson LR (2011) Performance of the BD GeneOhm MRSA achromopeptidase assay for real-time PCR detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in nasal specimens. J Clin Microbiol 49(6):2266–2268
Paule SM, Mehta M, Hacek DM, Gonzalzles TM, Robicsek A, Peterson LR (2009) Chromogenic media vs real-time PCR for nasal surveillance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: impact on detection of MRSA-positive persons. Am J Clin Pathol 131(4):532–539
Rajan L, Smyth E, Humphreys H (2007) Screening for MRSA in ICU patients. How does PCR compare with culture? J Infect 55(4):353–357
Reischl U, Linde HJ, Metz M, Leppmeier B, Lehn N (2000) Rapid identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and simultaneous species confirmation using real-time fluorescence PCR. J Clin Microbiol 38(6):2429–2433
Rossney AS, Herra CM, Brennan GI, Morgan PM, O’Connell B (2008) Evaluation of the Xpert methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) assay using the GeneXpert real-time PCR platform for rapid detection of MRSA from screening specimens. J Clin Microbiol 46(10):3285–3290
Schuenck RP, Lourenco MCS, Iório NLP, Ferreira ALP, Nouér SA, Santos KRN (2006) Improved and rapid detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage using selective broth and multiplex PCR. Res Microbiol 157(10):971–975
Seputienė V, Vilkoicaitė A, Armalytė J, Pavilonis A, Sužiedėlienė E (2010) Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using double duplex real-time PCR and dye Syto 9. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 55(5):502–507
Snyder JW, Munier GK, Johnson CL (2010) Comparison of the BD GeneOhm methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) PCR assay to culture by use of BBL CHROMagar MRSA for detection of MRSA in nasal surveillance cultures from intensive care unit patients. J Clin Microbiol 48(4):1305–1309
van Hal SJ, Jennings Z, Stark D, Marriott D, Harkness J (2009) MRSA detection: comparison of two molecular methods (BD GeneOhm PCR assay and Easy-Plex) with two selective MRSA agars (MRSA-ID and Oxoid MRSA) for nasal swabs. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28(1):47–53
Wagenvoort JHT, van de Cruijs MFHA, Meuwissen CTM, Gronenschild JMH, De Brauwer EIGB (2007) Comparison of an enrichment broth-enhanced commercial PCR procedure versus bacteriological culture for separating non-colonized from suspected or colonized MRSA individuals. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 26:155–160
Warren DK, Liao RS, Merz LR, Eveland M, Dunne WM Jr (2004) Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus directly from nasal swab specimens by a real-time PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol 42(12):5578–5581
Wassenberg MWM, Kluytmans JAJW, Box ATA, Bosboom RW, Buiting AGM, van Elzakker EPM, Melchers WJG, van Rijen MML, Thijsen SFT, Troelstra A, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CMJE, Visser CE, Voss A, Wolffs PFG, Wulf MWH, van Zwet AA, de Wit GA, Bonten MJM (2010) Rapid screening of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using PCR and chromogenic agar: a prospective study to evaluate costs and effects. Clin Microbiol Infect 16(12):1754–1761
Wolk DM, Struelens MJ, Pancholi P, Davis T, Della-Latta P, Fuller D, Picton E, Dickenson R, Denis O, Johnson D, Chapin K (2009) Rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillinresistant S. aureus (MRSA) in wound specimens and blood cultures: multicenter preclinical evaluation of the Cepheid Xpert MRSA/SA skin and soft tissue and blood culture assays. J Clin Microbiol 47(3):823–826
Al-Talib H, Yean CY, Al-Khateeb A, Singh KKB, Hasan H, Al-Jashamy K, Ravichandran M (2010) Comparative evaluation of five culture media with triplex PCR assay for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Curr Microbiol 61(1):1–6
Apfalter P, Assadian O, Kalczyk A, Lindenmann V, Makristathis A, Mustafa S, Rotter M, Hirschl AM (2002) Performance of a new chromogenic oxacillin resistance screen medium (Oxoid) in the detection and presumptive identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 44(2):209–211
Ben Nsira S, Dupuis M, Leclercq R (2006) Evaluation of MRSA Select, a new chromogenic medium for the detection of nasal carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Antimicrob Agents 27(6):561–564
Cherkaoui A, Renzi G, François P, Schrenzel J (2007) Comparison of four chromogenic media for culture-based screening of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol 56(Pt 4):500–503
Colakoglu S, Aliskan H, Senger SS, Turunc T, Demiroglu YZ, Arslan H (2007) Performance of MRSA ID chromogenic medium for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus directly from blood cultures and clinical specimens. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 59(3):319–323
Compernolle V, Verschraegen G, Claeys G (2007) Combined use of Pastorex Staph-Plus and either of two new chromogenic agars, MRSA ID and CHROMagar MRSA, for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 45(1):154–158
Davies S, McIntyre S, Fowler J, Tovey M (2008) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus detection using chromogenic media: the Sheffield experience. Br J Biomed Sci 65(1):13–17
Diederen BM, van Leest ML, van Duijn I, Willemse P, van Keulen PH, Kluytmans JA (2006) Performance of MRSA ID, a new chromogenic medium for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 44(2):586–588
Flayhart D, Hindler JF, Bruckner DA, Hall G, Shrestha RK, Vogel SA, Richter SS, Howard W, Walther R, Carroll KC (2005) Multicenter evaluation of BBL CHROMagar MRSA medium for direct detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from surveillance cultures of the anterior nares. J Clin Microbiol 43(11):5536–5540
Han Z, Lautenbach E, Fishman N, Nachamkin I (2007) Evaluation of mannitol salt agar, CHROMagar Staph aureus and CHROMagar MRSA for detection of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from nasal swab specimens. J Med Microbiol 56(Pt 1):43–46
Krishna BVS, Smith M, McIndeor A, Gibb AP, Dave J (2008) Evaluation of chromogenic MRSA medium, MRSA select and Oxacillin Resistance Screening Agar for the detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Pathol 61(7):841–843
Lee S, Park YJ, Yoo JH, Kahng J, Jeong IH, Kwon YM, Han K (2008) Comparison of culture screening protocols for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) using a chromogenic agar (MRSA-Select). Ann Clin Lab Sci 38(3):254–257
Louie L, Soares D, Meaney H, Vearncombe M, Simor AE (2006) Evaluation of a new chromogenic medium, MRSA select, for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 44(12):4561–4563
Malhotra-Kumar S, Abrahantes JC, Sabiiti W, Lammens C, Vercauteren G, Ieven M, Molenberghs G, Aerts M, Goossens H; MOSAR WP2 Study (2010) Evaluation of chromogenic media for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 48(4):1040–1046
Nahimana I, Francioli P, Blanc DS (2006) Evaluation of three chromogenic media (MRSA-ID, MRSA-Select and CHROMagar MRSA) and ORSAB for surveillance cultures of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Microbiol Infect 12(12):1168–1174
Nonhoff C, Denis O, Brenner A, Buidin P, Legros N, Thiroux C, Dramaix M, Struelens MJ (2009) Comparison of three chromogenic media and enrichment broth media for the detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from mucocutaneous screening specimens: Comparison of MRSA chromogenic media. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28(4):363–369
Peterson JF, Riebe KM, Hall GS, Wilson D, Whittier S, Palavecino E, Ledeboer NA (2010) Spectra MRSA, a new chromogenic agar medium to screen for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 48(1):215–219
Reyes RC, Stoakes L, Milburn S, Lennox G, Daniel J, Silver SN, Wijnker E, John MA, Hussain Z (2008) Evaluation of a new chromogenic medium for the detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carriage on nasal and perianal specimens. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 60(2):225–227
Safdar N, Narans L, Gordon B, Maki DG (2003) Comparison of culture screening methods for detection of nasal carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a prospective study comparing 32 methods. J Clin Microbiol 41(7):3163–3166
Stoakes L, Reyes R, Daniel J, Lennox G, John MA, Lannigan R, Hussain Z (2006) Prospective comparison of a new chromogenic medium, MRSASelect, to CHROMagar MRSA and mannitol-salt medium supplemented with oxacillin or cefoxitin for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 44(2):637–639
Van Hoecke F, Deloof N, Claeys G (2011) Performance evaluation of a modified chromogenic medium, ChromID MRSA New, for the detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from clinical specimens. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 30:1595–1598
van Loo IH, van Dijk S, Verbakel-Schelle I, Buiting AG (2007) Evaluation of a chromogenic agar (MRSASelect) for the detection of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with clinical samples in The Netherlands. J Med Microbiol 56(Pt 4):491–494
Van Vaerenbergh K, Cartuyvels R, Coppens G, Frans J, Van den Abeele AM, De Beenhouwer H; BILULU Group (2010) Performance of a new chromogenic medium, BBL CHROMagar MRSA II (BD), for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in screening samples. J Clin Microbiol 48(4):1450–1451
Hubben G, Bootsma M, Luteijn M, Glynn D, Bishai D, Bonten M, Postma M (2011) Modelling the costs and effects of selective and universal hospital admission screening for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS One 6(3):e14783
Murthy A, De Angelis G, Pittet D, Schrenzel J, Uckay I, Harbarth S (2010) Cost-effectiveness of universal MRSA screening on admission to surgery. Clin Microbiol Infect 16(12):1747–1753
Uçkay I, Sax H, Iten A, Camus V, Renzi G, Schrenzel J, Perrier A, Pittet D (2008) Effect of screening for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carriage by polymerase chain reaction on the duration of unnecessary preemptive contact isolation. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 29(11):1077–1079
Abramson MA, Sexton DJ (1999) Nosocomial methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus primary bacteremia: at what costs? Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 20(6):408–411
Chaix C, Durand-Zaleski I, Alberti C, Brun-Buisson C (1999) Control of endemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a cost–benefit analysis in an intensive care unit. JAMA 282(18):1745–1751
Gavaldà L, Masuet C, Beltran J, Garcia M, Garcia D, Sirvent JM, Ramon JM (2006) Comparative cost of selective screening to prevent transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), compared with the attributable costs of MRSA infection. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 27(11):1264–1266
Herr CEW, Heckrodt TH, Hofmann FA, Schnettler R, Eikmann TF (2003) Additional costs for preventing the spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and a strategy for reducing these costs on a surgical ward. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 24(9):673–678
Lehnhof T (2009) Attributierbare ökonomische Konsequenzen einer Kolonisation mit Methicillin-resistenten Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Medizinische Fakultät Universität des Saarlandes, Homburg, p 112
Reed SD, Friedman JY, Engemann JJ, Griffiths RI, Anstrom KJ, Kaye KS, Stryjewski ME, Szczech LA, Reller LB, Corey GR, Schulman KA, Fowler VG Jr (2005) Costs and outcomes among hemodialysis-dependent patients with methicillin-resistant or methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 26(2):175–183
Resch A, Wilke M, Fink C (2009) The cost of resistance: incremental cost of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in German hospitals. Eur J Health Econ 10(3):287–297
Rosner AJ, Becker DL, Wong AH, Miller E, Conly JM (2004) The costs and consequences of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection treatments in Canada. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol 15(4):213–220
Wernitz MH (2006) Screening bei stationärer Aufnahme von Risikopatienten für die Kolonisation oder Infektion mit Methicillin-resistentem Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Medizinischen Fakultät Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin, p 102
Kola A, Chaberny I, Mattner F, Reischl U, Vonberg R, Weist K, Wendt C, Witte W, Ziesing S, Gastmeier P (2006) Prävention von Methicillin-resistenten S. aureus durch Screeninguntersuchungen. Der Anaesthesist 55:778–783
Kramer A, Falke D, Miksits K (2009) Epidemiologie der Infektionskrankheiten. In: Hahn H, Schulz TF, Kaufmann SHE, Suerbaum S (eds) Medizinische Mikrobiologie und Infektiologie. Springer Medizin Verlag, Heidelberg
Wertheim HF, Vos MC, Boelens HA, Voss A, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CM, Meester MH, Kluytmans JA, van Keulen PH, Verbrugh HA (2004) Low prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) at hospital admission in the Netherlands: the value of search and destroy and restrictive antibiotic use. J Hosp Infect 56(4):321–325
Geipel U, Herrmann M (2005) Methicillin-resistente Staphylococcus aureus. Resistenztypen und klinische Konsequenzen. Anaesthesist 54(2):155–162
Hornberg C, Knoop D, Kipp F (2006) Bedeutung von MRSA in der Patientenversorgung. Epidemiologie, Prophylaxe und Therapie. Orthopäde 35(11):1159–1168
Robert Koch-Institut (2005) Zum Management des MRSA-Screenings. Epid Bull 42:385–389
Hübner N-O, Tübbicke A, Hübner C, Kramer A, Fleßa St. (2010) Ökonomische Aspekte des Hygienemanagements multiresistenter Erreger in stationären Einrichtungen am Beispiel von MRSA. Umweltmedizin in Forschung und Praxis 15:317–328
Acknowledgements
All authors report no conflict of interest relevant to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Andrea Tübbicke and Claudia Hübner are equally contributing authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tübbicke, A., Hübner, C., Kramer, A. et al. Transmission rates, screening methods and costs of MRSA—a systematic literature review related to the prevalence in Germany. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 31, 2497–2511 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-012-1632-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-012-1632-8