Abstract
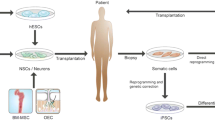
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a gradual neurodegenerative disease. While drug therapy and surgical treatments have been the primary means of addressing PD, they do not offer a cure, and the risks associated with surgical treatment are high. Recent advances in cell reprogramming have given rise to new prospects for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD), with induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), induced dopamine neurons (iDNs), and induced neural stem cells (iNSCs) being created. These cells can potentially be used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. On the other hand, this article emphasizes the limits of iPSCs and iNSCs in the context of Parkinson’s disease treatment, as well as approaches for direct reprogramming of somatic cells into iDNs. The paper will examine the benefits and drawbacks of directly converting somatic cells into iDNs.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- DBS:
-
Deep brain stimulation
- iPSCs:
-
Induced pluripotent stem cells
- iNSCs:
-
Induced neural stem cells
- iDNs:
-
Induced dopamine neurons
- 6-OHDA:
-
6-Hydroxydopamine
- MEFs:
-
Mouse embryonic fibroblasts
- DP:
-
Dopamine precursors
- VPA:
-
Valproic acid
References
Surmeier DJ (2018) Determinants of dopaminergic neuron loss in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS J 285(19):3657–3668
Aquino CC, Fox SH (2015) Clinical spectrum of levodopa-induced complications. Mov Disord 30(1):80–89
Antonini A, Moro E, Godeiro C, Reichmann H (2018) Medical and surgical management of advanced Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 33(6):900–908
Han F, Liu Y, Huang J, Zhang X, Wei C (2021) Current approaches and molecular mechanisms for directly reprogramming fibroblasts into neurons and dopamine neurons. Front Aging Neurosci 13:738529
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126(4):663–676
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S (2007) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131(5):861–872
Han F, Baremberg D, Gao J, Duan J, Lu X, Zhang N, Chen Q (2015) Development of stem cell-based therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Transl Neurodegener 4:16
Yamanaka S (2020) Pluripotent stem cell-based cell therapy-promise and challenges. Cell stem cell 27(4):523–531
Hou S, Lu P (2016) Direct reprogramming of somatic cells into neural stem cells or neurons for neurological disorders. Neural Re-gen Res 11(1):28–31
Ford E, Pearlman J, Ruan T, Manion J, Waller M, Neely GG, Caron L (2020) Human pluripotent stem cells-based therapies for neurodegenerative diseases: current status and challenges. Cells 9(11):2517
Cai CY, Meng FL, Rao L, Liu YY, Zhao XL (2020) Induced pluripotent stem cell technology and its application in disease research. Yi Chuan 42(11):1042–1061
Reddy AP, Ravichandran J (1866) Carkaci-Salli N (2020) Neural regeneration therapies for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease-related disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 4:165506
Hayashi Y, Ohnuma K, Furue MK (2019) Pluripotent stem cell heterogeneity. Adv Exp Med Biol 1123:71–94
Chang CY, Ting HC, Liu CA, Su HL, Chiou TW, Lin SZ, Harn HJ, Ho TJ (2020) Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-based neurodegenerative disease models for phenotype recapitulation and drug screening. Molecules 25(8):2000
Parmar M (2018) Towards stem cell based therapies for Parkinson’s disease. Development 145(1):dev156117
Xu X, Huang J, Li J, Liu L, Han C, Shen Y, Zhang G, Jiang H, Lin Z, Xiong N et al (2016) Induced pluripotent stem cells and Parkinson’s disease: modelling and treatment. Cell Prolif 49(1):14–26
Shahbazi E, Mirakhori F, Ezzatizadeh V, Baharvand H (2018) Reprogramming of somatic cells to induced neural stem cells. Methods 133:21–28
Monni E, Cusulin C, Cavallaro M, Lindvall O, Kokaia Z (2014) Human fetal striatum-derived neural stem (NS) cells differentiate to mature neurons in vitro and in vivo. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 9(4):338–346
Choi DH, Kim JH, Kim SM, Kang K, Han DW, Lee J (2017) Therapeutic potential of induced neural stem cells for Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 18(1):224
Xu Z, Su S, Zhou S, Yang W, Deng X, Sun Y, Li L, Li Y (2020) How to reprogram human fibroblasts to neurons. Cell Biosci 10:116
Wang H, Yang Y, Liu J, Qian L (2021) Direct cell reprogramming: approaches, mechanisms and progress. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 22(6):410–424
Pfisterer U, Kirkeby A, Torper O, Wood J, Nelander J, Dufour A, Björklund A, Lindvall O, Jakobsson J, Parmar M (2011) Direct conversion of human fibroblasts to dopaminergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(25):10343–10348
Caiazzo M, Dell'Anno MT, Dvoretskova E, Lazarevic D, Taverna S, Leo D, Sotnikova TD, Menegon A, Roncaglia P, Colciago G et al (2011) Direct generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nature 476(7359):224–227
Kim J, Su SC, Wang H, Cheng AW, Cassady JP, Lodato MA, Lengner CJ, Chung CY, Dawlaty MM, Tsai LH et al (2011) Functional integration of dopaminergic neurons directly converted from mouse fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell 9(5):413–419
Dell'Anno MT, Caiazzo M, Leo D, Dvoretskova E, Medrihan L, Colasante G, Giannelli S, Theka I, Russo G, Mus L et al (2014) Remote control of induced dopaminergic neurons in parkinsonian rats. J Clin Invest 124(7):3215–3229
Oh SI, Park HS, Hwang I, Park HK, Choi KA, Jeong H, Kim SW, Hong S (2014) Efficient reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts to neuronal cells including dopaminergic neurons. Sci World J 2014:957548
Tian C, Li Y, Huang Y, Wang Y, Chen D, Liu J, Deng X, Sun L, Anderson K, Qi X et al (2015) Selective generation of dopaminergic precursors from mouse fibroblasts by direct lineage conversion. Sci Rep 5:12622
Wang Y, Yang H, Yang Q, Yang J, Wang H, Xu H, Gao WQ (2016) Chemical conversion of mouse fibroblasts into functional dopaminergic neurons. Exp Cell Res 347(2):283–292
Qin H, Zhao AD, Sun ML, Ma K, Fu XB (2020) Direct conversion of human fibroblasts into dopaminergic neuron-like cells using small molecules and protein factors. Mil Med Res 7(1):52
Pereira M, Pfisterer U, Rylander D, Torper O, Lau S, Lundblad M, Grealish S, Parmar M (2014) Highly efficient generation of induced neurons from human fibroblasts that survive transplantation into the adult rat brain. Sci Rep 4:6330
Jiang H, Xu Z, Zhong P, Ren Y, Liang G, Schilling HA, Hu Z, Zhang Y, Wang X, Chen S et al (2015) Cell cycle and p53 gate the direct conversion of human fibroblasts to dopaminergic neurons. Nat Commun 6:10100
di Val R, Cervo P, Romanov RA, Spigolon G, Masini D, Martín-Montañez E, Toledo EM, La Manno G, Feyder M, Pifl C, Ng YH et al (2017) Induction of functional dopamine neurons from human astrocytes in vitro and mouse astrocytes in a Parkinson’s disease model. Nat Biotechnolo 35(5):444–452
De Gregorio R, Pulcrano S, De Sanctis C, Volpicelli F, Guatteo E, von Oerthel L, Latagliata EC, Esposito R, Piscitelli RM, Perrone-Capano C et al (2018) miR-34b/c regulates Wnt1 and enhances mesencephalic dopaminergic neuron differentiation. Stem Cell Rep 10(4):1237–1250
Pu J, Gao T, Zheng R, Fang Y, Ruan Y, Jin C, Shen T, Tian J, Zhang B (2020) Parkin mutation decreases neurite complexity and maturation in neurons derived from human fibroblasts. Brain Res Bull 159:9–15
Zhou H, Su J, Hu X, Zhou C, Li H, Chen Z, Xiao Q, Wang B, Wu W, Sun Y et al (2020) Glia-to-neuron conversion by CRISPR-CasRx alleviates symptoms of neurological disease in mice. Cell 181(3):590–603.e516
Qian H, Kang X, Hu J, Zhang D, Liang Z, Meng F, Zhang X, Xue Y, Maimon R, Dowdy SF et al (2020) Reversing a model of Parkinson’s disease with in situ converted nigral neurons. Nature 582(7813):550–556
Yoo J, Noh M, Kim H, Jeon NL, Kim BS, Kim J (2015) Nanogrooved substrate promotes direct lineage reprogramming of fibroblasts to functional induced dopaminergic neurons. Biomaterials 45:36–45
Yoo J, Lee E, Kim HY, Youn DH, Jung J, Kim H, Chang Y, Lee W, Shin J, Baek S et al (2017) Electromagnetized gold nanoparticles mediate direct lineage reprogramming into induced dopamine neurons in vivo for Parkinson’s disease therapy. Nat Nanotechnolo 12(10):1006–1014
Chang JH, Tsai PH, Wang KY, Wei YT, Chiou SH, Mou CY (2018) Generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from reprogramming fibroblasts by nonviral-based mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Sci Rep 8(1):11
Chen Y, Pu J, Zhang B (2016) Progress and challenges of cell replacement therapy for neurodegenerative diseases based on direct neural reprogramming. Hum Gene ther 27(12):962–970
Diener C, Keller A, Meese E (2022) Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends Genet 38(6):613–626
Titze-de-Almeida SS, Soto-Sánchez C, Fernandez E, Koprich JB, Brotchie JM, Titze-de-Almeida R (2020) The promise and challenges of developing miRNA-based therapeutics for Parkinson’s disease. Cells 9(4):841
Ambasudhan R, Talantova M, Coleman R, Yuan X, Zhu S, Lipton SA, Ding S (2011) Direct reprogramming of adult human fibroblasts to functional neurons under defined conditions. Cell Stem Cell 9(2):113–118
Grealish S, Drouin-Ouellet J, Parmar M (2016) Brain repair and reprogramming: the route to clinical translation. J Intern Med 280(3):265–275
Wang Q, Liu Y, Han C, Yang M, Huang F, Duan X, Wang S, Yu Y, Liu J, Yang H et al (2021) Efficient RNA virus targeting via CRISPR/CasRx in fish. J Virol 95(19):e0046121
Chuang YF, Wang PY, Kumar S, Lama S, Lin FL, Liu GS (2021) Methods for in vitro CRISPR/CasRx-mediated RNA editing. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:667879
Konermann S, Lotfy P, Brideau NJ, Oki J, Shokhirev MN, Hsu PD (2018) Transcriptome engineering with RNA-targeting type VI-D CRISPR effectors. Cell 173(3):665–676.e614
Wang LL, Serrano C, Zhong X, Ma S, Zou Y, Zhang CL (2021) Revisiting astrocyte to neuron conversion with lineage tracing in vivo. Cell 184(21):5465–5481.e5416
Mertens J, Marchetto MC, Bardy C, Gage FH (2016) Evaluating cell reprogramming, differentiation and conversion technologies in neuroscience. Nat Rev Neurosci 17(7):424–437
Arenas E, Denham M, Villaescusa JC (2015) How to make a midbrain dopaminergic neuron. Development 142(11):1918–1936
Playne R, Connor B (2017) Understanding Parkinson’s disease through the use of cell reprogramming. Stem Cell Rev Rep 13(2):151–169
Funding
This work was supported by the Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation Grants ZR2018LC008 (Y.W.) and Yantai Science and Technology Innovation Development Plan 2020XDRH106 (Y.W.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any study with human subjects performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y.Y., Xu, H. & Wang, Y.S. Progress in direct reprogramming of dopaminergic cell replacement therapy. Neurol Sci 45, 873–881 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-023-07175-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-023-07175-z