Abstract
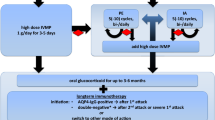
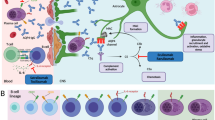
Paraproteinemia is associated with different peripheral neuropathies. The major causes of neuropathy correlated with paraproteinemia are the deposition of immunoglobulin in the myelin, represented by anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) neuropathy; deposition of immunoglobulin or its fragment in the interstitium, represented by immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis (AL amyloidosis); and paraneoplastic mechanisms that cannot be solely attributed to the deposition of immunoglobulin or its fragment, represented by polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy, and skin change (POEMS) syndrome. Patients with anti-MAG neuropathy and POEMS syndrome present with slowing of nerve conduction parameters. This characteristic fulfills the electrodiagnostic criteria for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) defined by the European Academy of Neurology and Peripheral Nerve Society (EAN/PNS). Although direct damage caused by the deposition of amyloid can induce axonal damage in AL amyloidosis, some patients with this condition have features fulfilling the EAN/PNS electrodiagnostic criteria for CIDP. Conventional immunotherapies for CIDP, such as steroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, and plasma exchange, offer no or only minimal-to-modest benefit. Although rituximab can reduce the level of circulating autoantibodies, it may only be effective in some patients with anti-MAG neuropathy. Drugs including melphalan, thalidomide, lenalidomide, and bortezomib for POEMS syndrome and those including melphalan, thalidomide, lenalidomide, pomalidomide, bortezomib, ixazomib, and daratumumab for AL amyloidosis are considered. Since there will be more therapeutic options in the future, thereby enabling appropriate treatments for individual neuropathies, there is an increasing need for early diagnosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Glavey SV, Leung N (2016) Monoclonal gammopathy: the good, the bad and the ugly. Blood Rev 30(3):223–231
Kyle RA, Larson DR, Therneau TM, Dispenzieri A, Kumar S, Cerhan JR, Rajkumar SV (2018) Long-term follow-up of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. N Engl J Med 378(3):241–249
Chaudhry HM, Mauermann ML, Rajkumar SV (2017) Monoclonal gammopathy-associated peripheral neuropathy: diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin Proc 92(5):838–850
Saleun JP, Vicariot M, Deroff P, Morin JF (1982) Monoclonal gammopathies in the adult population of Finistère. France J Clin Pathol 35(1):63–68
Crawford J, Eye MK, Cohen HJ (1987) Evaluation of monoclonal gammopathies in the “well” elderly. Am J Med 82(1):39–45
Kyle RA, Therneau TM, Rajkumar SV, Larson DR, Plevak MF, Offord JR, Dispenzieri A, Katzmann JA, Melton LJ 3rd (2006) Prevalence of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. N Engl J Med 354(13):1362–1369
Vallat JM, Duchesne M, Corcia P, Richard L, Ghorab K, Magy L, Mathis S (2021) The wide spectrum of pathophysiologic mechanisms of paraproteinemic neuropathy. Neurology 96(5):214–225
Kelly JJ Jr, Kyle RA, O’Brien PC, Dyck PJ (1981) Prevalence of monoclonal protein in peripheral neuropathy. Neurology 31(11):1480–1483
Tomita M, Koike H, Kawagashira Y, Iijima M, Adachi H, Taguchi J, Abe T, Sako K, Tsuji Y, Nakagawa M, Kanda F, Takeda F, Sugawara M, Toyoshima I, Asano N, Sobue G (2013) Clinicopathological features of neuropathy associated with lymphoma. Brain 136(Pt 8):2563–2578
Latov N (1995) Pathogenesis and therapy of neuropathies associated with monoclonal gammopathies. Ann Neurol 37(Suppl 1):S32-42
Kawagashira Y, Koike H, Tomita M, Morozumi S, Iijima M, Nakamura T, Katsuno M, Tanaka F, Sobue G (2010) Morphological progression of myelin abnormalities in IgM-monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein neuropathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69(11):1143–1157
Koike H, Mouri N, Fukami Y, Iijima M, Matsuo K, Yagi N, Saito A, Nakamura H, Takahashi K, Nakae Y, Okada Y, Tanaka F, Sobue G, Katsuno M (2021) Two distinct mechanisms of neuropathy in immunoglobulin light chain (AL) amyloidosis. J Neurol Sci 421:117305
Koike H, Iijima M, Mori K, Yamamoto M, Hattori N, Watanabe H, Tanaka F, Doyu M, Sobue G (2008) Neuropathic pain correlates with myelinated fibre loss and cytokine profile in POEMS syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79(10):1171–1179
Ramchandren S, Lewis RA (2009) Monoclonal gammopathy and neuropathy. Curr Opin Neurol 22(5):480–485
Nobile-Orazio E, Manfredini E, Carpo M, Meucci N, Monaco S, Ferrari S, Bonetti B, Cavaletti G, Gemignani F, Durelli L et al (1994) Frequency and clinical correlates of anti-neural IgM antibodies in neuropathy associated with IgM monoclonal gammopathy. Ann Neurol 36(3):416–424
Campagnolo M, Zambello R, Nobile-Orazio E, Benedetti L, Marfia GA, Riva N, Castellani F, Bianco M, Salvalaggio A, Garnero M, Ruiz M, Mataluni G, Fazio R, Ermani M, Briani C (2017) IgM MGUS and Waldenstrom-associated anti-MAG neuropathies display similar response to rituximab therapy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 88(12):1094–1097
Svahn J, Petiot P, Antoine JC, Vial C, Delmont E, Viala K, Steck AJ, Magot A, Cauquil C, Zarea A, Echaniz-Laguna A, Iancu Ferfoglia R, Gueguen A, Magy L, Léger JM, Kuntzer T, Ferraud K, Lacour A, Camdessanché JP (2018) Francophone anti-MAG cohort Group. Anti-MAG antibodies in 202 patients: clinicopathological and therapeutic features. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 89(5):499–505
Steck AJ, Stalder AK, Renaud S (2006) Anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein neuropathy. Curr Opin Neurol 19(5):458–463
Lunn MP, Crawford TO, Hughes RA, Griffin JW, Sheikh KA (2002) Anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein antibodies alter neurofilament spacing. Brain 125(Pt 4):904–911
Trapp BD, Quarles RH (1982) Presence of the myelin-associated glycoprotein correlates with alterations in the periodicity of peripheral myelin. J Cell Biol 92(3):877–882
Lach B, Rippstein P, Atack D, Afar DE, Gregor A (1993) Immunoelectron microscopic localization of monoclonal IgM antibodies in gammopathy associated with peripheral demyelinative neuropathy. Acta Neuropathol 85(3):298–307
Vallat JM, Magy L, Sindou P, Magdelaine C, Cros D (2005) IgG neuropathy: an immunoelectron microscopic study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64(5):386–390
Vallat JM, Tabaraud F, Sindou P, Preux PM, Vandenberghe A, Steck A (2000) Myelin widenings and MGUS-IgA: an immunoelectron microscopic study. Ann Neurol 47(6):808–811
Monaco S, Bonetti B, Ferrari S, Moretto G, Nardelli E, Tedesco F, Mollnes TE, Nobile-Orazio E, Manfredini E, Bonazzi L et al (1990) Complement-mediated demyelination in patients with IgM monoclonal gammopathy and polyneuropathy. N Engl J Med 322(10):649–652
Koike H, Kadoya M, Kaida KI, Ikeda S, Kawagashira Y, Iijima M, Kato D, Ogata H, Yamasaki R, Matsukawa N, Kira JI, Katsuno M, Sobue G (2017) Paranodal dissection in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with anti-neurofascin-155 and anti-contactin-1 antibodies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 88(6):465–473
Koike H, Katsuno M (2020) Pathophysiology of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: insights into classification and therapeutic strategy. Neurol Ther 9(2):213–227
Kawagashira Y, Koike H, Takahashi M, Ohyama K, Iijima M, Katsuno M, Niwa JI, Doyu M, Sobue G (2020) Aberrant expression of nodal and paranodal molecules in neuropathy associated with IgM monoclonal gammopathy with anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein antibodies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 79(12):1303–1312
Koike H, Katsuno M (2021) Macrophages and autoantibodies in demyelinating diseases. Cells 10(4):844
Koike H, Nishi R, Ikeda S, Kawagashira Y, Iijima M, Katsuno M, Sobue G (2018) Ultrastructural mechanisms of macrophage-induced demyelination in CIDP. Neurology 91(23):1051–1060
Koike H, Fukami Y, Nishi R, Kawagashira Y, Iijima M, Katsuno M, Sobue G (2020) Ultrastructural mechanisms of macrophage-induced demyelination in Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 91(6):650–659
Kawagashira Y, Kondo N, Atsuta N, Iijima M, Koike H, Katsuno M, Tanaka F, Kusunoki S, Sobue G (2010) IgM MGUS anti-MAG neuropathy with predominant muscle weakness and extensive muscle atrophy. Muscle Nerve 42(3):433–435
Magy L, Kaboré R, Mathis S, Lebeau P, Ghorab K, Caudie C, Vallat JM. 2015 Heterogeneity of polyneuropathy associated with anti-MAG antibodies. J Immunol Res. 2015:450391.
Van den Bergh PYK, van Doorn PA, Hadden RDM, Avau B, Vankrunkelsven P, Allen JA, Attarian S, Blomkwist PH, Cornblath DR, Eftimov F, Goedee HS, Harbo T, Kuwabara S, Lewis RA, Lunn MP, Nobile-Orazio E, Querol L, Rajabally YA, Sommer C, Topaloglu HA. European Academy of Neurology/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on diagnosis and treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint Task Force - Second Revision. J Peripher Nerv Syst. in press.
Kaku DA, England JD, Sumner AJ (1994) Distal accentuation of conduction slowing in polyneuropathy associated with antibodies to myelin-associated glycoprotein and sulphated glucuronyl paragloboside. Brain 117(Pt 5):941–947
Trojaborg W, Hays AP, van den Berg L, Younger DS, Latov N (1995) Motor conduction parameters in neuropathies associated with anti-MAG antibodies and other types of demyelinating and axonal neuropathies. Muscle Nerve 18(7):730–735
Capasso M, Torrieri F, Di Muzio A, De Angelis MV, Lugaresi A, Uncini A (2002) Can electrophysiology differentiate polyneuropathy with anti-MAG/SGPG antibodies from chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy? Clin Neurophysiol 113(3):346–353
Gondim FA, De Sousa EA, Latov N, Sander HW, Chin RL, Brannagan TH (2007) Anti-MAG/SGPG associated neuropathy does not commonly cause distal nerve temporal dispersion. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(8):902–904
Nobile-Orazio E, Bianco M, Nozza A (2017) Advances in the treatment of paraproteinemic neuropathy. Curr Treat Options Neurol 19(12):43
Dalakas MC (2018) Advances in the diagnosis, immunopathogenesis and therapies of IgM-anti-MAG antibody-mediated neuropathies. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 15(11):1756285617746640
Maurer MA, Rakocevic G, Leung CS, Quast I, Lukačišin M, Goebels N, Münz C, Wardemann H, Dalakas M, Lünemann JD (2012) Rituximab induces sustained reduction of pathogenic B cells in patients with peripheral nervous system autoimmunity. J Clin Invest 122(4):1393–1402
Dalakas MC, Rakocevic G, Salajegheh M, Dambrosia JM, Hahn AF, Raju R, McElroy B (2009) Placebo-controlled trial of rituximab in IgM anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein antibody demyelinating neuropathy. Ann Neurol 65(3):286–293
Léger JM, Viala K, Nicolas G, Créange A, Vallat JM, Pouget J, Clavelou P, Vial C, Steck A, Musset L, Marin B, RIMAG Study Group (2013) (France and Switzerland). Placebo-controlled trial of rituximab in IgM anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein neuropathy. Neurology 80(24):2217–25
Levine TD, Pestronk A (1999) IgM antibody-related polyneuropathies: B-cell depletion chemotherapy using Rituximab. Neurology 52(8):1701–1704
Kawagashira Y, Koike H, Ohyama K, Hashimoto R, Iijima M, Adachi H, Katsuno M, Chapman M, Lunn M, Sobue G (2015) Axonal loss influences the response to rituximab treatment in neuropathy associated with IgM monoclonal gammopathy with anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein antibody. J Neurol Sci 348(1–2):67–73
Lunn MP, Nobile-Orazio E (2016) Immunotherapy for IgM anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein paraprotein-associated peripheral neuropathies. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 10(10):CD002827
Iancu Ferfoglia R, Guimarães-Costa R, Viala K, Musset L, Neil J, Marin B, Léger JM (2016) Long-term efficacy of rituximab in IgM anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein neuropathy: RIMAG follow-up study. J Peripher Nerv Syst 21(1):10–14
Nakanishi T, Sobue I, Toyokura Y, Nishitani H, Kuroiwa Y, Satoyoshi E, Tsubaki T, Igata A, Ozaki Y (1984) The Crow-Fukase syndrome: a study of 102 cases in Japan. Neurology 34(6):712–720
Dispenzieri A (2019) POEMS Syndrome: 2019 Update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 94(7):812–827
Suichi T, Misawa S, Beppu M, Takahashi S, Sekiguchi Y, Shibuya K, Amino H, Tsuneyama A, Suzuki YI, Nakamura K, Sato Y, Kuwabara S (2019) Prevalence, clinical profiles, and prognosis of POEMS syndrome in Japanese nationwide survey. Neurology 93(10):e975–e983
Suichi T, Misawa S, Sekiguchi Y, Shibuya K, Tsuneyama A, Suzuki YI, Nakamura K, Kano H, Kuwabara S (2020) Treatment response and prognosis of POEMS syndrome coexisting with Castleman disease. J Neurol Sci 413:116771
Adams D, Said G (1998) Ultrastructural characterisation of the M protein in nerve biopsy of patients with POEMS syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64(6):809–812
Watanabe O, Arimura K, Kitajima I, Osame M, Maruyama I (1996) Greatly raised vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in POEMS syndrome. Lancet 347(9002):702
Kanai K, Sawai S, Sogawa K, Mori M, Misawa S, Shibuya K, Isose S, Fujimaki Y, Noto Y, Sekiguchi Y, Nasu S, Nakaseko C, Takano S, Yoshitomi H, Miyazaki M, Nomura F, Kuwabara S (2012) Markedly upregulated serum interleukin-12 as a novel biomarker in POEMS syndrome. Neurology 79(6):575–582
Sobue G, Doyu M, Watanabe M, Hayashi F, Mitsuma T (1992) Extensive demyelinating changes in the peripheral nerves of Crow-Fukase syndrome: a pathological study of one autopsied case. Acta Neuropathol 84(2):171–177
Vital C, Gherardi R, Vital A, Kopp N, Pellissier JF, Soubrier M, Clavelou P, Bellance R, Delisle MB, Ruchoux MM et al (1994) Uncompacted myelin lamellae in polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, M-protein and skin changes syndrome. Ultrastructural study of peripheral nerve biopsy from 22 patients. Acta Neuropathol 87(3):302–7
Ohnishi A, Hirano A (1981) Uncompacted myelin lamellae in dysglobulinemic neuropathy. J Neurol Sci 51(1):131–140
Hashimoto R, Koike H, Takahashi M, Ohyama K, Kawagashira Y, Iijima M, Sobue G (2015) Uncompacted myelin lamellae and nodal ion channel disruption in POEMS syndrome. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 74(12):1127–1136
Yoshikawa H, Dyck PJ (1991) Uncompacted inner myelin lamellae in inherited tendency to pressure palsy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 50(5):649–657
Lagueny A, Latour P, Vital A, Le Masson G, Rouanet M, Ferrer X, Vital C, Vandenberghe A (2001) Mild recurrent neuropathy in CMT1B with a novel nonsense mutation in the extracellular domain of the MPZ gene. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70(2):232–235
Fujinuma Y, Asahina M, Fukushima T, Katagiri A, Yamanaka Y, Misawa S, Kuwabara S (2012) Preserved autonomic function in patients with POEMS syndrome. J Neurol Sci 318(1–2):131–134
Isose S, Misawa S, Kanai K, Shibuya K, Sekiguchi Y, Nasu S, Fujimaki Y, Noto Y, Nakaseko C, Kuwabara S (2011) POEMS syndrome with Guillan-Barre syndrome-like acute onset: a case report and review of neurological progression in 30 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82(6):678–680
Nasu S, Misawa S, Sekiguchi Y, Shibuya K, Kanai K, Fujimaki Y, Ohmori S, Mitsuma S, Koga S, Kuwabara S (2012) Different neurological and physiological profiles in POEMS syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83(5):476–479
Suichi T, Misawa S, Sato Y, Beppu M, Sakaida E, Sekiguchi Y, Shibuya K, Watanabe K, Amino H, Kuwabara S (2019) Proposal of new clinical diagnostic criteria for POEMS syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 90(2):133–137
Mauermann ML, Sorenson EJ, Dispenzieri A, Mandrekar J, Suarez GA, Dyck PJ, Dyck PJ (2012) Uniform demyelination and more severe axonal loss distinguish POEMS syndrome from CIDP. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83(5):480–486
Marsh ES, Keddie S, Terris-Prestholt F, D’Sa S, Lunn MP (2021) Early VEGF testing in inflammatory neuropathy avoids POEMS syndrome misdiagnosis and associated costs. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 92(2):172–176
Sung JY, Kuwabara S, Ogawara K, Kanai K, Hattori T (2002) Patterns of nerve conduction abnormalities in POEMS syndrome. Muscle Nerve 26(2):189–193
Sekiguchi Y, Misawa S, Shibuya K, Nasu S, Mitsuma S, Iwai Y, Beppu M, Sawai S, Ito S, Hirano S, Nakaseko C, Kuwabara S (2013) Ambiguous effects of anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody (bevacizumab) for POEMS syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84(12):1346–1348
Huang CC, Chu CC (1996) Poor response to intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in patients with Castleman’s disease and the POEMS syndrome. J Neurol 243(10):726–727
Brown R, Ginsberg L (2019) POEMS syndrome: clinical update. J Neurol 266(1):268–277
Cerri F, Falzone YM, Riva N, Quattrini A (2019) An update on the diagnosis and management of the polyneuropathy of POEMS syndrome. J Neurol 266(1):258–267
Humeniuk MS, Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Kyle RA, Witzig TE, Kumar SK, Kapoor P, Lust JA, Hayman SR, Buadi FK, Rajkumar SV, Zeldenrust SR, Russell SJ, Dingli D, Lin Y, Leung N, Dispenzieri A (2013) Outcomes of patients with POEMS syndrome treated initially with radiation. Blood 122(1):68–73
Kuwabara S, Hattori T, Shimoe Y, Kamitsukasa I (1997) Long term melphalan-prednisolone chemotherapy for POEMS syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63(3):385–387
Li J, Zhang W, Jiao L, Duan MH, Guan HZ, Zhu WG, Tian Z, Zhou DB (2011) Combination of melphalan and dexamethasone for patients with newly diagnosed POEMS syndrome. Blood 117(24):6445–6449
Ohwada C, Sakaida E, Kawajiri-Manako C, Nagao Y, Oshima-Hasegawa N, Togasaki E, Muto T, Tsukamoto S, Mitsukawa S, Takeda Y, Mimura N, Takeuchi M, Shimizu N, Misawa S, Iseki T, Kuwabara S, Nakaseko C (2018) Long-term evaluation of physical improvement and survival of autologous stem cell transplantation in POEMS syndrome. Blood 131(19):2173–2176
Misawa S, Sato Y, Katayama K, Nagashima K, Aoyagi R, Sekiguchi Y, Sobue G, Koike H, Yabe I, Sasaki H, Watanabe O, Takashima H, Nishizawa M, Kawachi I, Kusunoki S, Mitsui Y, Kikuchi S, Nakashima I, Ikeda S, Kohara N, Kanda T, Kira J, Hanaoka H, Kuwabara S, Japanese POEMS Syndrome for Thalidomide (J-POST) Trial Study Group (2016) Safety and efficacy of thalidomide in patients with POEMS syndrome: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 15(11):1129–37
Delforge M, Bladé J, Dimopoulos MA, Facon T, Kropff M, Ludwig H, Palumbo A, Van Damme P, San-Miguel JF, Sonneveld P (2010) Treatment-related peripheral neuropathy in multiple myeloma: the challenge continues. Lancet Oncol 11(11):1086–1095
Suichi T, Misawa S, Nagashima K, Sato Y, Iwai Y, Katayama K, Sekiguchi Y, Shibuya K, Amino H, Suzuki YI, Tsuneyama A, Nakamura K, Kuwabara S (2020) Lenalidomide treatment for thalidomide-refractory POEMS syndrome: a prospective single-arm clinical trial. Intern Med 59(9):1149–1153
Gertz MA, Comenzo R, Falk RH, Fermand JP, Hazenberg BP, Hawkins PN, Merlini G, Moreau P, Ronco P, Sanchorawala V, Sezer O, Solomon A, Grateau G (2005) Definition of organ involvement and treatment response in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis (AL): a consensus opinion from the 10th International Symposium on Amyloid and Amyloidosis, Tours, France, 18–22 April 2004. Am J Hematol 79(4):319–328
Adams D (2001) Hereditary and acquired amyloid neuropathies. J Neurol 248(8):647–657
Adams D, Koike H, Slama M, Coelho T (2019) Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis: a model of medical progress for a fatal disease. Nat Rev Neurol 15(7):387–404
Vital C, Vallat JM, Deminiere C, Loubet A, Leboutet MJ (1982) Peripheral nerve damage during multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia: an ultrastructural and immunopathologic study. Cancer 50(8):1491–1497
Sommer C, Schröder JM (1989) Amyloid neuropathy: immunocytochemical localization of intra- and extracellular immunoglobulin light chains. Acta Neuropathol 79(2):190–199
Koike H, Katsuno M (2019) Ultrastructure in transthyretin amyloidosis: from pathophysiology to therapeutic insights. Biomedicines 7(1):11
Mathis S, Magy L, Diallo L, Boukhris S, Vallat JM (2012) Amyloid neuropathy mimicking chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 45(1):26–31
Hamidi Asl K, Liepnieks JJ, Nakamura M, Benson MD (1999) Organ-specific (localized) synthesis of Ig light chain amyloid. J Immunol 162(9):5556–5560
Kyle RA, Greipp PR (1983) Amyloidosis (AL). Clinical and laboratory features in 229 cases. Mayo Clin Proc 58(10):665–83
Shimazaki C, Hata H, Iida S, Ueda M, Katoh N, Sekijima Y, Ikeda S, Yazaki M, Fukushima W, Ando Y (2018) Nationwide survey of 741 patients with systemic amyloid light-chain amyloidosis in Japan. Intern Med 57(2):181–187
Koike H, Misu K, Sugiura M, Iijima M, Mori K, Yamamoto M, Hattori N, Mukai E, Ando Y, Ikeda S, Sobue G (2004) Pathology of early- vs late-onset TTR Met30 familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Neurology 63(1):129–138
Koike H, Katsuno M (2020) Transthyretin amyloidosis: update on the clinical spectrum, pathogenesis, and disease-modifying therapies. Neurol Ther 9(2):317–333
Koike H, Tanaka F, Hashimoto R, Tomita M, Kawagashira Y, Iijima M, Fujitake J, Kawanami T, Kato T, Yamamoto M, Sobue G (2012) Natural history of transthyretin Val30Met familial amyloid polyneuropathy: analysis of late-onset cases from non-endemic areas. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83(2):152–158
Gertz MA (2020) Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis: 2020 update on diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Am J Hematol 95(7):848–860
Koike H, Okumura T, Murohara T, Katsuno, M. Multidisciplinary approaches for transthyretin amyloidosis. Cardiol Ther., in press.
Klein CJ, Vrana JA, Theis JD, Dyck PJ, Dyck PJ, Spinner RJ, Mauermann ML, Bergen HR 3rd, Zeldenrust SR, Dogan A (2011) Mass spectrometric-based proteomic analysis of amyloid neuropathy type in nerve tissue. Arch Neurol 68(2):195–199
Matsuda M, Gono T, Morita H, Katoh N, Kodaira M, Ikeda S (2011) Peripheral nerve involvement in primary systemic AL amyloidosis: a clinical and electrophysiological study. Eur J Neurol 18(4):604–610
Jones NF, Hilton PJ, Tighe JR, Hobbs JR (1972) Treatment of “primary” renal amyloidosis with melphalan. Lancet 2(7778):616–619
Kyle RA, Gertz MA, Greipp PR, Witzig TE, Lust JA, Lacy MQ, Therneau TM (1997) A trial of three regimens for primary amyloidosis: colchicine alone, melphalan and prednisone, and melphalan, prednisone, and colchicine. N Engl J Med 336(17):1202–1207
Comenzo RL, Vosburgh E, Simms RW, Bergethon P, Sarnacki D, Finn K, Dubrey S, Faller DV, Wright DG, Falk RH, Skinner M (1996) Dose-intensive melphalan with blood stem cell support for the treatment of AL amyloidosis: one-year follow-up in five patients. Blood 88(7):2801–2806
Jaccard A, Moreau P, Leblond V, Leleu X, Benboubker L, Hermine O, Recher C, Asli B, Lioure B, Royer B, Jardin F, Bridoux F, Grosbois B, Jaubert J, Piette JC, Ronco P, Quet F, Cogne M, Fermand JP (2007) Myélome Autogreffe (MAG) and Intergroupe Francophone du Myélome (IFM) Intergroup. High-dose melphalan versus melphalan plus dexamethasone for AL amyloidosis. N Engl J Med 357(11):1083 93
Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, Buadi FK, Dingli D, Hayman SR, Kumar SK, Leung N, Lust J, Rajkumar SV, Russell SJ, Suman VJ, Le-Rademacher JG, Hogan WJ (2016) Stem cell transplantation compared with melphalan plus dexamethasone in the treatment of immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis. Cancer 122(14):2197–2205
Obici L, Adams D (2020) Acquired and inherited amyloidosis: knowledge driving patients’ care. J Peripher Nerv Syst 25(2):85–101
Biolo A, Ramamurthy S, Connors LH, O’Hara CJ, Meier-Ewert HK, Soo Hoo PT, Sawyer DB, Seldin DC, Sam F (2008) Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in cardiac amyloidosis: relationship to structural, functional myocardial changes and to light chain amyloid deposition. Circ Heart Fail 1(4):249–257
Ward JE, Ren R, Toraldo G, Soohoo P, Guan J, O’Hara C, Jasuja R, Trinkaus-Randall V, Liao R, Connors LH, Seldin DC (2011) Doxycycline reduces fibril formation in a transgenic mouse model of AL amyloidosis. Blood 118(25):6610–6617
D’Souza A, Flynn K, Chhabra S, Dhakal B, Hamadani M, Jacobsen K, Pasquini M, Weihrauch D, Hari P (2017) Rationale and design of DUAL study: doxycycline to upgrade response in light chain (AL) amyloidosis (DUAL): a phase 2 pilot study of a two-pronged approach of prolonged doxycycline with plasma cell-directed therapy in the treatment of AL amyloidosis. Contemp Clin Trials Commun 24(8):33–38
Griffin JM, Rosenblum H, Maurer MS (2021) Pathophysiology and therapeutic approaches to cardiac amyloidosis. Circ Res 128(10):1554–1575
Hrncic R, Wall J, Wolfenbarger DA, Murphy CL, Schell M, Weiss DT, Solomon A (2000) Antibody-mediated resolution of light chain-associated amyloid deposits. Am J Pathol 157(4):1239–1246
Nardelli E, Steck AJ, Barkas T, Schluep M, Jerusalem F (1988) Motor neuron syndrome and monoclonal IgM with antibody activity against gangliosides GM1 and GD1b. Ann Neurol 23(5):524–528
Eurelings M, Ang CW, Notermans NC, Van Doorn PA, Jacobs BC, Van den Berg LH (2001) Antiganglioside antibodies in polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy. Neurology 57(10):1909–1912
Vlam L, Piepers S, Sutedja NA, Jacobs BC, Tio-Gillen AP, Stam M, Franssen H, Veldink JH, Cats EA, Notermans NC, Bloem AC, Wadman RI, van der Pol WL, van den Berg LH (2015) Association of IgM monoclonal gammopathy with progressive muscular atrophy and multifocal motor neuropathy: a case-control study. J Neurol 262(3):666–673
Carpo M, Meucci N, Allaria S, Marmiroli P, Monaco S, Toscano A, Simonetti S, Scarlato G, Nobile-Orazio E (2000) Anti-sulfatide IgM antibodies in peripheral neuropathy. J Neurol Sci 176(2):144–150
Dabby R, Weimer LH, Hays AP, Olarte M, Latov N (2000) Antisulfatide antibodies in neuropathy: clinical and electrophysiologic correlates. Neurology 54(7):1448–1452
Matà S, Borsini W, Ambrosini S, Toscani L, Barilaro A, Piacentini S, Sorbi S, Lolli F (2011) IgM monoclonal gammopathy-associated neuropathies with different IgM specificity. Eur J Neurol 18(8):1067–1073
Campagnolo M, Ferrari S, Dalla Torre C, Cabrini I, Cacciavillani M, Lucchetta M, Ruggero S, Toffanin E, Cavallaro T, Briani C (2015) Polyneuropathy with anti-sulfatide and anti-MAG antibodies: clinical, neurophysiological, pathological features and response to treatment. J Neuroimmunol 15(281):1–4
Boso F, Ruggero S, Giannotta C, Benedetti L, Marfia GA, Ermani M, Campagnolo M, Salvalaggio A, Gallia F, De Michelis C, Visentin A, Bianco M, Ruiz M, Mataluni G, Nobile-Orazio E, Briani C (2017) Anti-sulfatide/galactocerebroside antibodies in immunoglobulin M paraproteinemic neuropathies. Eur J Neurol 24(11):1334–1340
Willison HJ, O’Leary CP, Veitch J, Blumhardt LD, Busby M, Donaghy M, Fuhr P, Ford H, Hahn A, Renaud S, Katifi HA, Ponsford S, Reuber M, Steck A, Sutton I, Schady W, Thomas PK, Thompson AJ, Vallat JM, Winer J (2001) The clinical and laboratory features of chronic sensory ataxic neuropathy with anti-disialosyl IgM antibodies. Brain 124(Pt 10):1968–1977
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Health and Labour Sciences Research Grant on Intractable Diseases (Neuroimmunological Diseases) from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (20FC1030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Haruki Koike conceived and wrote the first draft and Masahisa Katsuno revised it for intellectual content. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This is a review article and ethical approval is not required.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koike, H., Katsuno, M. Paraproteinemia and neuropathy. Neurol Sci 42, 4489–4501 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05583-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05583-7