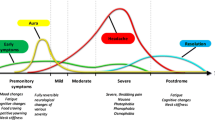
Abstract
Migraine sciences have witnessed tremendous advances in recent years. Pre-clinical and clinical experimental models have contributed significantly to provide useful insights into the brain structures that mediate migraine attacks. These models have contributed to elucidate the role of neurotransmission pathways and to identify the role of important molecules within the complex network involved in migraine pathogenesis. The contribution and efforts of several research groups from all over the world has ultimately lead to the generation of novel therapeutic approaches, specifically targeted for the prevention of migraine attacks, the monoclonal antibodies directed against calcitonin gene-related peptide or its receptor. These drugs have been validated in randomized placebo-controlled trials and are now ready to improve the lives of a large multitude of migraine sufferers. Others are in the pipeline and will soon be available.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreou AP, Edvinsson L (2019) Mechanisms of migraine as a chronic evolutive condition. J Headache Pain 20(1):117
Gormley P, Anttila V, Winsvold BS et al (2016) Meta-analysis of 375,000 individuals identifies 38 susceptibility loci for migraine. Nat Genet 48(8):856–866
de Boer I, van den Maagdenberg AMJM, Terwindt GM (2019) Advance in genetics of migraine. Curr Opin Neurol 32(3):413–421
Mainero C, Boshyan J, Hadjikhani N (2011) Altered functional magnetic resonance imaging resting-state connectivity in periaqueductal gray networks in migraine. Ann Neurol 70(5):838–845
Da Silva AF, Granziera C, Tuch DS, Snyder J, Vincent M, Hadjikhani N (2007) Interictal alterations of the trigeminal somatosensory pathway and periaqueductal gray matter in migraine. Neuroreport. 18(4):301–305
Maleki N, Becerra L, Nutile L, Pendse G, Brawn J, Bigal M, Burstein R, Borsook D (2011) Migraine attacks the basal ganglia. Mol Pain 7:71
Coppola G, Di Lorenzo C, Schoenen J, Pierelli F (2013) Habituation and sensitization in primary headaches. J Headache Pain 14(1):65
Dodick DW (2019) CGRP ligand and receptor monoclonal antibodies for migraine prevention: evidence review and clinical implications. Cephalalgia 2019 39:445–458
Mehrotra S, Gupta S, Garrelds IM, Villalón CM, Saxena PR, Bogers AJ, Maassenvandenbrink A (2006) Effects of current and prospective antimigraine drugs on the porcine isolated meningeal artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 374(3):163–175
Franco-Cereceda A, Rudehill A, Lundberg JM (1987) Calcitonin gene-related peptide but not substance P mimics capsaicin-induced coronary vasodilation in the pig. Eur J Pharmacol 142(2):235–243
Bouchelet I, Case B, Olivier A, Hamel E (2000) No contractile effect for 5-HT1D and 5-HT1F receptor agonists in human and bovine cerebral arteries: similarity with human coronary artery. Br J Pharmacol 129(3):501–508
Sheykhzade M, Amandi N, Pla MV, Abdolalizadeh B, Sams A, Warfvinge K, Edvinsson L, Pickering DS (2017) Binding and functional pharmacological characteristics of gepant-type antagonists in rat brain and mesenteric arteries. Vascul Pharmacol 90:36–43
Maassenvandenbrink A, Chan KY (2008) Neurovascular pharmacology of migraine. Eur J Pharmacol 585(2–3):313–319
De Vries P, Villalón CM, Saxena PR (1999) Pharmacological aspects of experimental models in relation to acute antimigraine therapy. Eur J Pharmacol 375(1–3):61–74
Williamson DJ, Hargreaves RJ, Hill RG, Shepheard SL (1997) Sumatriptan inhibits neurogenic vasodilation of dural blood vessels in the anaesthetized rat—intravital microscope studies. Cephalalgia 17:525–531
Akerman S, Kaube H, Goadsby PJ (2004) Anandamide acts as a vasodilator of dural blood vessels in vivo by activating TRPV1 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 142:1354–1360
Akerman S, Kaube H, Goadsby PJ (2003) Vanilloid type 1 receptors (VR1) on trigeminal sensory nerve fibres play a minor role in neurogenic dural vasodilatation, and are involved in capsaicin-induced dural dilation. Br J Pharmacol 140:718–724
Haanes KA, Labastida-Ramírez A, Blixt FW, Rubio-Beltrán E, Dirven CM, Danser AH, Edvinsson L, MaassenVanDenBrink A (2019) Exploration of purinergic receptors aspotential anti-migraine targets using established pre-clinical migraine models. Cephalalgia 39(11):1421–1434
Petersen KA, Birk S, Doods H, Edvinsson L, Olesen J (2004) Inhibitory effect of BIBN4096BS on cephalic vasodilatation induced by CGRP or transcranial electrical stimulation in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 43(6):697–704
Connor HE, Stubbs CM, Feniuk W, Humphrey PP (1992) Effect of sumatriptan, a selective 5-HT1-like receptor agonist, on pial vessel diameter in anaesthetized cats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 12(3):514–519
Juhl L, Petersen KA, Larsen EH, Jansen-Olesen I, Olesen J (2006) The in vivo effect of adrenomedullin on rat dural and pial arteries. Eur J Pharmacol 538(1–3):101–107
Wang X, Fang Y, Liang J, Yan M, Hu R, Pan X (2014) 5-HT7 receptors are involved in neurogenic dural vasodilatation in an experimental model of migraine. J Mol Neurosci 54(2):164–170
Malhotra R (2016) Understanding migraine: potential role of neurogenic inflammation. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 19(2):175–182
Zakharov A, Vitale C, Kilinc E, Koroleva K, Fayuk D, Shelukhina I, Naumenko N, Skorinkin A, Khazipov R, Giniatullin R (2015) Hunting for origins of migraine pain: cluster analysis of spontaneous and capsaicin-induced firing in meningeal trigeminal nerve fibers. Front Cell Neurosci 9:287
Knyihar-Csillik E, Tajti J, Mohtasham S, Sari G, Vecsei L (1995) Electrical stimulation of the Gasserian ganglion induces structural alterations of calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive perivascular sensory nerve terminals in the rat cerebral dura mater: a possible model of migraine headache. Neurosci Lett 184(3):189–192
Limmroth V, Katsarava Z, Liedert B, Guehring H, Schmitz K, Diener HC, Michel MC (2001) An in vivo rat model to study calcitonin gene related peptide release following activation of the trigeminal vascular system. Pain 92(1–2):101–106
Markowitz S, Saito K, Moskowitz MA (1987) Neurogenically mediated leakage of plasma protein occurs from blood vessels in dura mater but not brain. J Neurosci 7:4129–4136
Buzzi MG, Moskowitz MA (1990) The antimigraine drug, sumatriptan (GR43175), selectively blocks neurogenic plasma extravasation from blood vessels in dura mater. Br J Pharmacol 99:202–206
Knyihar-Csillik E et al (1997) Effect of a serotonin agonist (sumatriptan) on the peptidergic innervation of the rat cerebral dura mater and on the expression of c-fos in the caudal trigeminal nucleus in an experimental migraine model. J Neurosci Res 48(5):449–464
Bohár Z, Fejes-Szabó A, Tar L, Varga H, Tajti J, Párdutz Á, Vécsei L (2013) Evaluation of c-Fos immunoreactivity in the rat brainstem nuclei relevant in migraine pathogenesis after electrical stimulation of the trigeminal ganglion. Neurol Sci 34(9):1597–1604
Buzzi MG, Carter WB, Shimizu T, Heath H III, Moskowitz MA (1991) Dihydroergotamine and sumatriptan attenuate levels of CGRP in plasma in rat superior sagittal sinus during electrical stimulation of the trigeminal ganglion. Neuropharmacology 30:1193–1200
Zhang Q, Han X, Wu H, Zhang M, Hu G, Dong Z, Yu S (2019) Dynamic changes in CGRP, PACAP, and PACAP receptors in the trigeminovascular system of a novel repetitive electrical stimulation rat model: relevant to migraine. Mol Pain 15:1744806918820452
Körtési T, Tuka B, Tajti J, Bagoly T, Fülöp F, Helyes Z, Vécsei L (2018) Kynurenic acid inhibits the electrical stimulation induced elevated pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide expression in the TNC. Front Neurol 8:745
Humphrey PP, Feniuk W, Perren MJ, Connor HE, Oxford AW, Coates LH, Butina D (1988) GR43175, a selective agonist for the 5-HT1-like receptor in dog isolated saphenous vein. Br J Pharmacol 94:1123–1132
Zagami AS, Goadsby PJ, Edvinsson L (1990) Stimulation of the superior sagittal sinus in the cat causes release of vasoactive peptides. Neuropeptides 16(2):69–75
Robert C, Bourgeais L, Arreto CD, Condes-Lara M, Noseda R, Jay T, Villanueva L (2013) Paraventricular hypothalamic regulation of trigeminovascular mechanisms involved in headaches. J Neurosci 33(20):8827–8840
Holland PR, Akerman S, Andreou AP, Karsan N, Wemmie JA, Goadsby PJ (2012) Acid-sensing ion channel 1: a novel therapeutic target for migraine with aura. Ann Neurol 72(4):559–563
Kaube H, Keay KA, Hoskin KL, Bandler R, Goadsby PJ (1993) Expression of c-Fos-like immunoreactivity in the caudal medulla and upper cervical spinal cord following stimulation of the superior sagittal sinus in the cat. Brain Res 629(1):95–102
Kaube H, Hoskin KL, Goadsby PJ (1994) Acetylsalicylic acid inhibits cerebral cortical vasodilatation caused by superior sagittal sinus stimulation in the cat. Eur J Neurol 1(2):141–146
Goadsby PJ, Hoskin KL (1999) Differential effects of low dose CP122,288 and eletriptan on fos expression due to stimulation of the superior sagittal sinus in cat. Pain 82:15–22
Hoskin KL, Goadsby PJ (1998) Comparison of a more and less lipophilic serotonin (5HT1B/1D) agonist in a model of trigeminovascular nociception in cat. Exp Neurol 150:45–51
Kurosawa M, Messlinger K, Pawlak M, Schmidt RF (1995) Increase of meningeal blood flow after electrical stimulation of rat dura mater encephali: mediation by calcitonin gene-related peptide. Br J Pharmacol 114:1397–1402
Messlinger K, Hotta H, Pawlak M, Schmidt RF (1997) Effects of the 5-HT1 receptor agonists, sumatriptan and CP 93,129, on dural arterial flow in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 332:173–181
Mitsikostas DD, Sanchez del Rio M, Waeber C, Moskowitz MA, Cutrer FM (1998) The NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 reduces capsaicin-induced c-fos expression within rat trigeminal nucleus caudalis. Pain 76:239–248
Cutrer FM, Mitsikostas DD, Ayata G, Sanchez del Rio M (1999) Attenuation by butalbital of capsaicin-induced c-fos-like immunoreactivity in trigeminal nucleus caudalis. Headache 39:697–704
Mitsikostas DD, Sanchez del Rio M (2001) Receptor systems mediating c-fos expression within trigeminal nucleus caudalis in animal models of migraine. Brain Res Rev 2001(35):20–35
Burstein R (2001) Deconstructing migraine headache into peripheral and central sensitization. Pain 89:107–110
Laborc KF, Spekker E, Bohár Z, Szűcs M, Nagy-Grócz G, Fejes-Szabó A, Vécsei L, Párdutz Á (2020) Trigeminal activation patterns evoked by chemical stimulation of the dura mater in rats. J Headache Pain 21(1):101
Becerra L, Bishop J, Barmettler G, Kainz V, Burstein R, Borsook D (2017) Brain network alterations in the inflammatory soup animal model of migraine. Brain Res 1660:36–46
Edelmayer RM, Vanderah TW, Majuta L, Zhang ET, Fioravanti B, de Felice M, Chichorro JG, Ossipov MH, King T, Lai J, Kori SH, Nelsen AC, Cannon KE, Heinricher MM, Porreca F (2009) Medullary pain facilitating neurons mediate allodynia in headache-related pain. Ann Neurol 2009(65):184–193
Burgos-Vega CC, Quigley LD, Trevisan Dos Santos G, Yan F, Asiedu M, Jacobs B, Motina M, Safdar N, Yousuf H, Avona A, Price TJ, Dussor G (2019) Non-invasive dural stimulation in mice: a novel preclinical model of migraine. Cephalalgia. 39(1):123–134
Boyer N, Signoret-Genest J, Artola A, Dallel R, Monconduit L (2017) Propranolol treatment prevents chronic central sensitization induced by repeated dural stimulation. Pain. 158(10):2025–2034
Zhang M, Liu Y, Zhao M, Tang W, Wang X, Dong Z, Yu S (2017) Depression and anxiety behaviour in a rat model of chronic migraine. J Headache Pain 18(1):27
Chen N, Su W, Cui SH, Guo J, Duan JC, Li HX, He L (2019) A novel large animal model of recurrent migraine established by repeated administration of inflammatory soup into the dura mater of the rhesus monkey. Neural Regen Res 14(1):100–106
Ashina M, Hansen JM, Olesen J (2013) Pearls and pitfalls in human pharmacological models of migraine: 30 years’ experience. Cephalalgia 2013 33(8):540–553
Demartini C, Greco R, Zanaboni AM, Sances G, De Icco R, Borsook D, Tassorelli C (2019) Nitroglycerin as a comparative experimental model of migraine pain: from animal to human and back. Prog Neurobiol 177:15–32
Greco R, Mangione AS, Sandrini G, Maccarrone M, Nappi G, Tassorelli C (2011) Effects of anandamide in migraine: data from an animal model. J Headache Pain 12(2):177–183
Pradhan AA, Smith ML, McGuire B, Tarash I, Evans CJ, Charles A (2014) Characterization of a novel model of chronic migraine. Pain 155(2):269–274
Bates EA, Nikai T, Brennan KC, Fu YH, Charles AC, Basbaum AI, Ptácek LJ, Ahn AH (2010) Sumatriptan alleviates nitroglycerin-induced mechanical and thermal allodynia in mice. Cephalalgia 30(2):170–178
Greco R, Bandiera T, Mangione AS, Demartini C, Siani F, Nappi G, Sandrini G, Guijarro A, Armirotti A, Piomelli D, Tassorelli C (2015) Effects of peripheral FAAH blockade on NTG-induced hyperalgesia--evaluation of URB937 in an animal model of migraine. Cephalalgia. 35(12):1065–1076
De Icco R, Fiamingo G, Greco R, Bottiroli S, Demartini C, Zanaboni AM, Allena M, Guaschino E, Martinelli D, Putortì A, Grillo V, Sances G, Tassorelli C (2020) Neurophysiological and biomolecular effects of erenumab in chronic migraine: an open label study. Cephalalgia. 26:333102420942230
Greco R, Demartini C, Zanaboni AM, Tassorelli C (2018) Chronic and intermittent administration of systemic nitroglycerin in the rat induces an increase in the gene expression of CGRP in central areas: potential contribution to pain processing. J Headache Pain 19(1):51
Tassorelli C, Greco R, Cappelletti D, Sandrini G, Nappi G (2005) Comparative analysis of the neuronal activation and cardiovascular effects of nitroglycerin, sodium nitroprusside and L-arginine. Brain Res 1051(1–2):17–24
Koulchitsky S, Fischer MJ, Messlinger K (2009) Calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor inhibition reduces neuronal activity induced by prolonged increase in nitric oxide in the rat spinal trigeminal nucleus. Cephalalgia. 29(4):408–417
Rea BJ, Wattiez AS, Waite JS, Castonguay WC, Schmidt CM, Fairbanks AM, Robertson BR, Brown CJ, Mason BN, Moldovan-Loomis MC, Garcia-Martinez LF, Poolman P, Ledolter J, Kardon RH, Sowers LP, Russo AF (2018) Peripherally administered calcitonin gene-related peptide induces spontaneous pain in mice: implications for migraine. Pain. 159(11):2306–2317
De Logu F, Landini L, Janal MN et al (2019) Migraine-provoking substances evoke periorbital allodynia in mice. J Headache Pain 20(1):18
Mason BN, Kaiser EA, Kuburas A, Loomis MCM, Latham JA, Garcia-Martinez LF, Russo AF (2017) Induction of migraine-like photophobic behavior in mice by both peripheral and central CGRP mechanisms. J Neurosci 37(1):204–216
Cumberbatch MJ, Williamson DJ, Mason GS, Hill RG, Hargreaves RJ (1999) Dural vasodilation causes a sensitization of rat caudal trigeminal neurones in vivo that is blocked by a 5-HT1B/1D agonist. Br J Pharmacol 126:1478–1486
Levy D, Burstein R, Strassman AM (2005) Calcitonin gene-related peptide does not excite or sensitize meningeal nociceptors: implications for the pathophysiology of migraine. Ann Neurol 58:698–705
Bhatt DK, Ramachandran R, Christensen SL, Gupta S, Jansen-Olesen I, Olesen J (2015) CGRP infusion in unanesthetized rats increases expression of c-Fos in the nucleus tractus solitarius and caudal ventrolateral medulla, but not in the trigeminal nucleus caudalis. Cephalalgia 35:220–233
Akerman S, Goadsby PJ (2015) Neuronal PAC1 receptors mediate delayed activation and sensitization of trigeminocervical neurons: relevance to migraine. Sci Transl Med 7(308):308ra157
Pedersen SH, la Cour SH, Calloe K, Hauser F, Olesen J, Klaerke DA, Jansen-Olesen I (2019) PACAP-38 and PACAP (6-38) Degranulate rat meningeal mast cells via the orphan MrgB3-receptor. Front Cell Neurosci 13:114
Costa C, Tozzi A, Rainero I, Cupini LM, Calabresi P, Ayata C, Sarchielli P (2013) Cortical spreading depression as a target for anti-migraine agents. J Headache Pain 14(1):62
Tozzi A, de Iure A, Di Filippo M et al (2012) Critical role of calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors in cortical spreading depression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(46):18985–18990
Jansen-Olesen I, Jorgensen L, Engel U, Edvinsson L (2013) In-depth characterization of CGRP receptors in human intracranial arteries. Eur J Pharmacol 481:206–217
Edvinsson L, Gulbenkian S, Barroso CP, Cunha e Sá M, Polak JM, Mortensen A, Jørgensen L, Jansen-Olesen I (1998) Innervation of the human middle meningeal artery:immunohistochemistry, ultrastructure, and role of endothelium for vasomotility. Peptides 19(7):1213–1225
Tfelt-Hansen P, De Vries P, Saxena PR (2000) Triptans in migraine: a comparative review of pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and efficacy. Drugs 60(6):1259–1287
Edvinsson L, Alm R, Shaw D, Rutledge RZ, Koblan KS, Longmore J, Kane SA (2002) Effect of the CGRP receptor antagonist BIBN4096BS in human cerebral, coronary and omental arteries and in SK-N-MC cells. Eur J Pharmacol 434:49–55
Sicuteri F, Del Bene E, Poggioni M, Bonazzi A (1987) Unmasking latent dysnociception in healthy subjects. Headache 27(4):180–185
Sances G, Tassorelli C, Pucci E, Ghiotto N, Sandrini G, Nappi G (2004) Reliability of the nitroglycerin provocative test in the diagnosis of neurovascular headaches. Cephalalgia 24(2):110–119
Iversen HK, Olesen J, Tfelt-Hansen P (1989) Intravenous nitroglycerin as an experimental model of vascular headache. Basic characteristics. Pain 38(1):17–24
Ashina H, Schytz HW, Ashina M (2019) CGRP in Human Models of Migraine. Handb Exp Pharmacol 255:109–120
Ashina H, Guo S, Vollesen ALH, Ashina M (2017) PACAP38 in human models of primary headaches. J Headache Pain 18(1):110
Falkenberg K, Rønde Bjerg H, Yamani N, Olesen J (2020) Sumatriptan does not antagonize CGRP-induced symptoms in healthy volunteers. Headache 60(4):665–676
Rahmann A, Wienecke T, Hansen JM, Fahrenkrug J, Olesen J, Ashina M (2008) Vasoactive intestinal peptide causes marked cephalic vasodilation, but does not induce migraine. Cephalalgia 28:226–236
Schytz HW, Birk S, Wienecke T, Kruuse C, Olesen J, Ashina M (2009) PACAP38 induces migraine-like attacks in patients with migraine without aura. Brain 132:16–25
Afridi S, Kaube H, Goadsby PJ (2005) Occipital activation in glyceryl trinitrate induced migraine with visual aura. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76(8):1158–1160
Hansen JM, Thomsen LL, Olesen J, Ashina M (2010) Coexisting typical migraine in familial hemiplegic migraine. Neurology 74(7):594–600
Asghar MS, Hansen AE, Amin FM, van der Geest RJ, Koning Pv, Larsson HB, Olesen J, Ashina M (2011) Evidence for a vascular factor in migraine. Ann Neurol 69(4):635–645
Christiansen I, Daugaard D, Lykke Thomsen L, Olesen J (2000) Glyceryl trinitrate induced headache in migraineurs - relation to attack frequency. Eur J Neurol 7(4):405–411
Afridi SK, Kaube H, Goadsby PJ (2004) Glyceryl trinitrate triggers premonitory symptoms in migraineurs. Pain 110(3):675–680
Maniyar FH, Sprenger T, Schankin C, Goadsby PJ (2014) The origin of nausea in migraine-a PET study. J Headache Pain 15(1):84
Guo S, Vollesen AL, Olesen J, Ashina M (2016) Premonitory and nonheadache symptoms induced by CGRP and PACAP38 in patients with migraine. Pain 157(12):2773–2781
de Hoon JN, Willigers JM, Troost J, Struijker-Boudier HA, van Bortel LM (2003) Cranial and peripheral interictal vascular changes in migraine patients. Cephalalgia 23(2):96–104
Di Clemente L, Coppola G, Magis D, Gérardy PY, Fumal A, De Pasqua V, Di Piero V, Schoenen J (2009) Nitroglycerin sensitises in healthy subjects CNS structures involved in migraine pathophysiology: evidence from a study of nociceptive blink reflexes and visual evoked potentials. Pain 144(1–2):156–161
Perrotta A, Serrao M, Tassorelli C, Arce-Leal N, Guaschino E, Sances G, Rossi P, Bartolo M, Pierelli F, Sandrini G, Nappi G (2011) Oral nitric-oxide donor glyceryl-trinitrate induces sensitization in spinal cord pain processing in migraineurs: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study. Eur J Pain 15(5):482–490
Asghar MS, Becerra L, Larsson HB, Borsook D, Ashina M (2016) Calcitonin gene- related peptide modulates heat nociception in the human brain - an fmri study in healthy volunteers. PLoS One 11(3):e0150334
Tvedskov JF, Thomsen LL, Iversen HK, Gibson A, Wiliams P, Olesen J (2004) The prophylactic effect of valproate on glyceryltrinitrate induced migraine. Cephalalgia 24(7):576–585
Fullerton T, Komorowski-Swiatek D, Forrest A, Gengo FM (1999) The pharmacodynamics of sumatriptan in nitroglycerin-induced headache. J Clin Pharmacol 39(1):17–29
Van der Schueren BJ, Blanchard R, Murphy MG, Palcza J, De Lepeleire I, Van Hecken A, Depré M, de Hoon JN (2011) The potent calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist, telcagepant, does not affect nitroglycerin-induced vasodilation in healthy men. Br J Clin Pharmacol 71(5):708–717
Petersen KA, Birk S, Lassen LH, Kruuse C, Jonassen O, Lesko L, Olesen J (2005) The CGRP-antagonist, BIBN4096BS does not affect cerebral or systemic haemodynamics in healthy volunteers. Cephalalgia 25(2):139–147
Greco R, Demartini C, Zanaboni AM, Tumelero E, Reggiani A, Misto A, Piomelli D, Tassorelli C (2020) FAAH inhibition as a preventive treatment for migraine: A pre-clinical study. Neurobiol Dis 134:104624
Mogil JS, Miermeister F, Seifert F, Strasburg K, Zimmermann K, Reinold H, Austin JS, Bernardini N, Chesler EJ, Hofmann HA, Hordo C, Messlinger K, Nemmani KV, Rankin AL, Ritchie J, Siegling A, Smith SB, Sotocinal S, Vater A, Lehto SG, Klussmann S, Quirion R, Michaelis M, Devor M, Reeh PW (2005) Variable sensitivity to noxious heat is mediated by differential expression of the CGRP gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(36):12938–12943
Chu DQ, Choy M, Foster P, Cao T, Brain SD (2000) A comparative study of the ability of calcitonin generelated peptide and adrenomedullin (13–52) to modulate microvascular but not thermal hyperalgesia responses. Br J Pharmacol 130(7):1589–1596
Marquez de Prado B, Hammond DL, Russo AF (2009) Genetic enhancement of calcitonin gene-related Peptide-induced central sensitization to mechanical stimuli in mice. J Pain 10(9):992–1000
Huang Y, Brodda-Jansen G, Lundeberg T, Yu LC (2004) Anti-nociceptive effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide in nucleus raphe magnus of rats: an effect attenuated by naloxone. Brain Res 873(1):54–59
Yao G, Huang Q, Wang M, Yang CL, Liu CF, Yu TM (2017) Behavioral study of a rat model of migraine induced by CGRP. Neurosci Lett 651:134–139
Christensen SL, Petersen S, Kristensen DM, Olesen J, Munro G (2019) Targeting CGRP via receptor antagonism and antibody neutralisation in two distinct rodent models of migraine-like pain. Cephalalgia 39(14):1827–1837
Greco R, Mangione AS, Siani F, Blandini F, Vairetti M, Nappi G, Sandrini G, Buzzi MG, Tassorelli C (2014) Effects of CGRP receptor antagonism in nitroglycerin-induced hyperalgesia. Cephalalgia 34(8):594–604
Sundrum T, Walker CS (2018) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide receptors in the trigeminovascular system: implications for migraine. Br J Pharmacol 175(21):4109–4120
Moldovan Loomis C, Dutzar B, Ojala EW, Hendrix L, Karasek C, Scalley-Kim M, Mulligan J, Fan P, Billgren J, Rubin V, Boshaw H, Kwon G, Marzolf S, Stewart E, Jurchen D, Pederson SM, Perrino McCulloch L, Baker B, Cady RK, Latham JA, Allison D, Garcia-Martinez LF (2019) Pharmacologic Characterization of ALD1910, a Potent Humanized Monoclonal Antibody against the Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase- Activating Peptide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 369(1):26–36
Demartini C, Tassorelli C, Zanaboni AM, Tonsi G, Francesconi O, Nativi C, Greco R (2017) The role of the transient receptor potential ankyrin type-1 (TRPA1) channel in migraine pain: evaluation in an animal model. J Headache Pain 18(1):94
Mirrasekhian E, Nilsson JLÅ, Shionoya K, Blomgren A, Zygmunt PM, Engblom D, Högestätt ED, Blomqvist A (2018) The antipyretic effect of paracetamol occurs independent of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1-mediated hypothermia and is associated with prostaglandin inhibition in the brain. FASEB J 32(10):5751–5759
Vila-Pueyo M (2018) Targeted 5-HT1F Therapies for Migraine. Neurotherapeutics 15(2):291–303
Pertwee RG (2001) Cannabinoid receptors and pain. Prog Neurobiol 63(5):569–611
Navratilova E, Behravesh S, Oyarzo J, Dodick DW, Banerjee P, Porreca F (2020) Ubrogepant does not induce latent sensitization in a preclinical model of medication overuse headache. Cephalalgia 40(9):892–902
Saengjaroentham C, Strother LC, Dripps I, Sultan Jabir MR, Pradhan A, Goadsby PJ, Holland PR (2020) Differential medication overuse risk of novel anti-migraine therapeutics. Brain 143(9):2681–2688
Funding
This manuscript was partly supported by grants from the Italian Ministry of Health to IRCCS Mondino 432 Foundation, Pavia, Italy (GR-2016-02363848, and RC2017-2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
CT received honoraria for the participation to advisory boards or for oral presentations from 424 Allergan, ElectroCore, Eli-Lilly, Novartis, and Teva. CT has no ownership interest and does not 425 own stocks of any pharmaceutical company. CT serves as Chief Section Editor of Frontiers in 426 Neurology—Section Headache Medicine and Facial Pain and on the editorial board of The Journal of Headache and Pain.
The other authors have no potential conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any study with human subjects.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greco, R., Demartini, C., De Icco, R. et al. Migraine neuroscience: from experimental models to target therapy. Neurol Sci 41 (Suppl 2), 351–361 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04808-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04808-5