Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study is to assess the impact of interferon (IFN) beta treatment on the development of worsening disability in relapsing-remitting (RR) multiple sclerosis (MS) patients in the single-center observation cohort.
Method
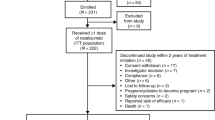
This is a prospective study of 236 IFN-beta-treated and 183 untreated RRMS patients recruited consecutively at the Clinic of Neurology in Belgrade (Serbia). Out of this original cohort, 10-year follow-up data were available for 233 IFN-beta-treated and 131 untreated subjects. The median time since recruitment was 9.7 years.
Results
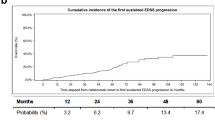
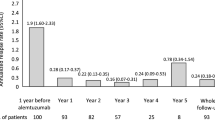
IFN-beta treatment significantly delayed (p < 0.001) the time to reach each of the clinical outcomes (secondary progression-SP, EDSS scores 4 and 6) since recruitment. Time from the first visit to SP was reached after 9.7 years for IFN-beta-treated vs. 7.8 years for untreated patients. The delay for the development of EDSS score ≥ 4 from the first visit was 1.6 years (8.7 years for IFN-beta-treated vs. 7.1 years for untreated patients). Time from the first visit to EDSS score of 6 was reached after 9.8 years for IFN-beta-treated vs. 8.8 years for untreated patients. The IFN-beta-treated group showed significant reduction (p < 0.001) in the risk of conversion to SP when compared with untreated patients (HR = 0.22). There was also a significant difference in reaching EDSS scores 4 and 6 (p < 0.001), in favor of the IFN-beta-treated group (HR = 0.40 and HR = 0.27, respectively).
Conclusion
Comparison of outcomes in our IFN-beta-treated vs. untreated RRMS patients suggests that this treatment may delay development of long-term disability in MS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Confavreux C, Compston A (2006) Natural history of MS. In: Compston A, McDonald I, Noseworthy J, Lassmann H, Miller D, Smith K, Wekerle H, Confavreux C (eds) McAlpine’s multiple sclerosis, 4th edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 183–273
Confavreux C, Vukusic S, Moreau T, Adeleine P (2000) Relapses and progression of disability in multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 343:1430–1438
Confavreux C, Vukusic S, Adeleine P (2003) Early clinical predictors and progression of irreversible disability in multiple sclerosis: an amnesic process. Brain 126:770–782
Noseworthy JH (2000) Multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 343:938–952
Vukusic S, Confavreux C (2003) Prognostic factors for progression of disability in the secondary progressive phase of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 206:135–137
Duddy M, Haghikia A, Cocco E, Eggers C, Drulovic J, Carmona O, Zéphir H, Gold R (2011) Managing MS in a changing treatment landscape. J Neurol 258:728–739
Goodin DS, Frohman EM, Garmany GP Jr, Halper J, Likosky WH, Lublin FD, Silberberg DH, Stuart WH, van den Noort S (2002) Disease modifying therapies in multiple sclerosis: report of the therapeutics and technology assessment subcommittee of the American academy of neurology and the MS council for clinical practice guidelines. Neurology 58:169–178
The IFNB Multiple Sclerosis Study Group (1993) Interferon beta-1b is effective in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. I. Clinical results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Neurology 43:655–661
Jacobs LD, Cookfair DL, Rudick RA, Herndon RM, Richert JR, Salazar AM, Fischer JS, Goodkin DE, Granger CV, Simon JH, Alam JJ, Bartoszak DM, Bourdette DN, Braiman J, Brownscheidle CM, Coats ME, Cohan SL, Dougherty DS, Kinkel RP, Mass MK, Munschauer FE, Priore RL, Pullicino PM, Scherokman BJ, Weinstock-Guttman B, Whitham RH, The Multiple Sclerosis Collaborative Research Group (MSCRG) (1996) Intramuscular interferon beta-1a for disease progression in relapsing multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 39:285–294
PRISMS (Prevention of Relapses and Disability by Interferon b-1a Sub-cutaneously in Multiple Sclerosis) Study Group (1998) Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study of interferon b-1a in relapsing/remitting multiple sclerosis. Lancet 352:1498–1504
The IFNB Multiple Sclerosis Study Group and the University of British Columbia MS/MRI Analysis Group (1995) Interferon beta-1b in the treatment of multiple sclerosis: final outcome of the randomized controlled trial. Neurology 45:1277–1285
The PRISMS (Prevention of Relapses and Disability by Interferon-b-1a Subcutaneously in Multiple Sclerosis) Study Group, and the University of British Columbia MS/MRI Analysis Group (2001) PRISMS-4: long-term efficacy of interferon-1a in relapsing MS. Neurology 56:1628–1636
Trojano M, Tintore M, Montalban X, Hillert J, Kalincik T, Iaffaldano P, Spelman T, Sormani MP, Butzkueven H (2017) Treatment decisions in multiple sclerosis - insights from real-world observational studies. Nat Rev Neurol 13:105–118
Trojano M, Pellegrini F, Fuiani A, Paolicelli D, Zipoli V, Zimatore GB, Di Monte E, Portaccio E, Lepore V, Livrea P, Amato MP (2007) New natural history of interferon-beta-treated relapsing multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 61:300–306
Shirani A, Zhao Y, Karim ME, Evans C, Kingwell E, van der Kop ML, Oger J, Gustafson P, Petkau J, Tremlett H (2012) Association between use of interferon beta and progression of disability in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. JAMA 308:247–256
Drulovic J, Kostic J, Mesaros S, Dujmovic Basuroski I, Stojsavljevic N, Kisic-Tepavcevic D, Pekmezovic T (2013) Interferon-beta and disability progression in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115(Suppl1):S65–S69
McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G, Goodkin D, Hartung HP, Lublin FD, McFarland HF, Paty DW, Polman CH, Reingold SC, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Sibley W, Thompson A, van den Noort S, Weinshenker BY, Wolinsky JS (2001) Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 50:121–127
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurological impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33:1444–1452
Lublin FD, Reingold SC, Cohen JA, Cutter GR, Sørensen PS, Thompson AJ, Wolinsky JS, Balcer LJ, Banwell B, Barkhof F, Bebo B Jr, Calabresi PA, Clanet M, Comi G, Fox RJ, Freedman MS, Goodman AD, Inglese M, Kappos L, Kieseier BC, Lincoln JA, Lubetzki C, Miller AE, Montalban X, O'Connor PW, Petkau J, Pozzilli C, Rudick RA, Sormani MP, Stüve O, Waubant E, Polman CH (2014) Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: the 2013 revisions. Neurology 83:278–286
Hernan MA, Sauer BC, Hernandez-Diaz S, Platt R, Shrier I (2016) Specifying a target trial prevents immortal time bias and other self-inflicted injuries in observational analyses. J Clin Epidemiol 79:70–75
Normand SL, Sykora K, Li P, Mamdani M, Rochon PA, Anderson GM (2005) Readers guide to critical appraisal of cohort studies: 3. Analytical strategies to reduce confounding. BMJ 330:1021–1023
Filleron T, Kwiatowski F (2016) Propensity score: a credible alternative to randomization? Bull Cancer 103:113–122
Greenberg BM, Balcer L, Calabresi PA, Cree B, Cross A, Frohman T, Gold R, Havrdova E, Hemmer B, Kieseier BC, Lisak R, Miller A, Racke MK, Steinman L, Stuve O, Wiendl H, Frohman E (2013) Interferon beta use and disability prevention in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol 70:248–251
Kappos L, Traboulsee A, Constantinescu C, Erälinna JP, Forrestal F, Jongen P, Pollard J, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Sindic C, Stubinski B, Uitdehaag B, Li D (2006) Long-term subcutaneous interferon beta-1a therapy in patients with relapsing-remitting MS. Neurology 67:944–953
Kappos L, Kuhle J, Multanen J, Kremenchutzky M, Verdun di Cantogno E, Cornelisse P, Lehr L, Casset-Semanaz F, Issard D, Uitdehaag BM (2015) Factors influencing long-term outcomes in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: PRISMS-15. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 86:1202–1207
Traboulsee A et al (2011) Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging predictors of long-term outcomes in patients with relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis: additional analyses. Neurology 76(Suppl 4):A389
Goodin DS, Traboulsee A, Knappertz V, Reder AT, Li D, Langdon D, Wolf C, Beckmann K, Konieczny A, Ebers GC (2012) Relationship between early clinical characteristics and long term disability outcomes: 16 year cohort study (follow-up) of the pivotal interferon β-1b trial in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:282–287
Ebers GC, Traboulsee A, Li D, Langdon D, Reder AT, Goodin DS, Bogumil T, Beckmann K, Wolf C, Konieczny A (2010) Analysis of clinical outcomes according to original treatment groups 16 years after the pivotal IFNB-1b trial. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81:907–912
Cree BA, Gourraud PA, Oksenberg JR, Bevan C, Crabtree-Hartman E, Gelfand JM, Goodin DS, Graves J, Green AJ, Mowry E, Okuda DT, Pelletier D, von Büdingen HC, Zamvil SS, Agrawal A, Caillier S, Ciocca C, Gomez R, Kanner R, Lincoln R, Lizee A, Qualley P, Santaniello A, Suleiman L, Bucci M, Panara V, Papinutto N, Stern WA, Zhu AH, Cutter GR, Baranzini S, Henry RG, Hauser SL (2016) Long-term evolution of multiple sclerosis disability in the treatment era. Ann Neurol 80:499–510
Rudick RA, Stuart WH, Calabresi PA, Confavreux C, Galetta SL, Radue EW, Lublin FD, Weinstock-Guttman B, Wynn DR, Lynn F, Panzara MA, Sandrock AW, Investigators SENTINEL (2006) Natalizumab plus interferon beta-1a for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 354:911–923
Hauser SL, Bar-Or A, Comi G, Giovannoni G, Hartung HP, Hemmer B, Lublin F, Montalban X, Rammohan KW, Selmaj K, Traboulsee A, Wolinsky JS, Arnold DL, Klingelschmitt G, Masterman D, Fontoura P, Belachew S, Chin P, Mairon N, Garren H, Kappos L, OPERA I, OPERA II Clinical Investigators (2017) Ocrelizumab versus interferon beta-1a in relapsing multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 376:221–234
Leray E, Yaouanq J, Le Page E, Coustans M, Laplaud D, Oger J, Edan G (2010) Evidence for a two-stage disability progression in multiple sclerosis. Brain 133:1900–1913
Rio J, Rovira A, Tintore M, Otero-Romero S, Comabella M, Vidal-Jordana A, Galan I, Castillo J, Arrambide G, Nos C, Tur C, Pujal B, Auger C, Sastre-Garriga J, Montalban X (2018) Disability progression markers over 6-12 years in interferon-β-treated multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler 24:322–330
Tommasin S, De Giglio L, Ruggieri S, Petsas N, Giannì C, Pozzilli C, Pantano P (2019) Relation between functional connectivity and disability in multiple sclerosis: a non-linear model. In: J Neurol doi.org/10.1007/s00415-018-9075-5
Sormani MP, De Stefano N (2013) Defining and scoring response to IFN-β in multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Neurol 9:504–512
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (grant nos. 175031 and 175087).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine University of Belgrade. Participants provided informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drulovic, J., Ivanovic, J., Mesaros, S. et al. Long-term disability outcomes in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a 10-year follow-up study. Neurol Sci 40, 1627–1636 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03878-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03878-4