Abstract
GPR137 are ubiquitously expressed in the central nervous system. However, the role o f GPR137 in human malignant glioma is still poorly known. In the present study, we firstly detected the expression of GPR137 in 29 human glioma tissue specimens by immunohistochemistry and in 5 malignant glioma cell lines by quantitative RT-PCR. The expression of GPR137 was much stronger in high-grade gliomas than in low-grade gliomas. Lentivirus-mediated small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) were employed to knock down GPR137 expression in glioma cells. Inhibition of GPR137 expression by RNAi significantly inhibited the proliferation and colony-forming capacity of U251, A172 and U373 cells. Moreover, flow cytometry analysis showed that knockdown of GPR137 led to the cell-cycle arrest at the S phase. Our results indicated that GPR137 is involved in the progression of human glioma, suggesting GPR137 as a potential oncogene of glioma cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359(5):492–507. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0708126359/5/492
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW, Kleihues P (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114(2):97–109. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4
Venkatakrishnan AJ, Deupi X, Lebon G, Tate CG, Schertler GF, Babu MM (2013) Molecular signatures of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 494(7436):185–194. doi:10.1038/nature11896
Yao X-H, Liu Y, Chen K, Gong W, Liu M-Y, Bian X-W, Wang JM (2011) Chemoattractant receptors as pharmacological targets for elimination of glioma stem-like cells. Int Immunopharmacol 11(12):1961–1966. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2011.08.021
Lazarczyk M, Matyja E, Lipkowski A (2007) Substance P and its receptors—a potential target for novel medicines in malignant brain tumour therapies (mini-review). Folia Neuropathol 45(3):99–107
Rosenbaum DM, Rasmussen SGF, Kobilka BK (2009) The structure and function of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 459(7245):356–363. doi:10.1038/nature08144
Dorsam RT, Gutkind JS (2007) G-protein-coupled receptors and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7(2):79–94. doi:10.1038/nrc2069
Lappano R, Maggiolini M (2011) G protein-coupled receptors: novel targets for drug discovery in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10(1):47–60. doi:10.1038/nrd3320
Yoshida M, Miyazato M, Kangawa K (2012) Orphan GPCRs and methods for identifying their ligands. Methods Enzymol 514:33–44. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-381272-8.00002-7
Bohnekamp J, Schoneberg T (2011) Cell adhesion receptor GPR133 couples to Gs protein. J Biol Chem 286(49):41912–41916. doi:10.1074/jbc.C111.265934
Shimizu M, Saitoh Y, Itoh H (1990) Immunohistochemical staining of Ha-ras oncogene product in normal, benign, and malignant human pancreatic tissues. Hum Pathol 21(6):607–612
Vanti WB, Nguyen T, Cheng R, Lynch KR, George SR, O’Dowd BF (2003) Novel human G-protein-coupled receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 305(1):67–71
Regard JB, Sato IT, Coughlin SR (2008) Anatomical profiling of G Protein-coupled receptor expression. Cell 135(3):561–571. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.040
Gong T, Xuan J, Chen L, Riggins RB, Li H, Hoffman EP, Clarke R, Wang Y (2011) Motif-guided sparse decomposition of gene expression data for regulatory module identification. BMC Bioinformatics 12(1):82. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-12-82
Neuhaus EM, Zhang W, Gelis L, Deng Y, Noldus J, Hatt H (2009) Activation of an olfactory receptor inhibits proliferation of prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem 284(24):16218–16225. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.012096M109.012096
Spehr J, Gelis L, Osterloh M, Oberland S, Hatt H, Spehr M, Neuhaus EM (2011) G protein-coupled receptor signaling via Src kinase induces endogenous human transient receptor potential vanilloid type 6 (TRPV6) channel activation. J Biol Chem 286(15):13184–13192. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.183525
Acknowledgments
We thank the great help from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, and supports from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81072066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
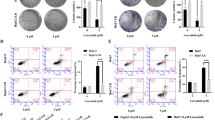
Figure S1. Down-regulation of GPR137 inhibited the colony formation of U373 glioma cells. (A) Expression analyses of GPR137 mRNA levels in U373 cells. (B) Representative images of the size and number of colonies in Con, Lv-shCon and Lv-shGPR137 groups under fluorescent microscopy and light microscopy (4× lens). (C) Statistical analysis of the number of colonies with crystal violet staining. There was a significant difference between Lv-shCon and Lv-shGPR137 (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zong, G., Wang, H., Li, J. et al. Inhibition of GPR137 expression reduces the proliferation and colony formation of malignant glioma cells. Neurol Sci 35, 1707–1714 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-014-1817-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-014-1817-2