Abstract
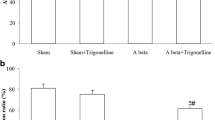
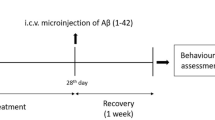
GM-1 ganglioside (GM-1) has been proposed as a new therapeutic agent against Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Therefore, in this study we aimed to investigate the effects of GM1 on memory deficits and oxidative stress in the hippocampus of rat model of AD. Wistar rats were randomly divided into three groups (n = 15): control group, model group, and treatment group, which were injected with vehicle, Aβ1-40, and Aβ1-40 together with GM-1, respectively. Morris water maze test was performed to evaluate spatial learning and memory of the rats. Brain malondialdehyde (MDA) content was detected by biochemical assay, and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) level in the hippocampus was examined by immunohistochemistry. The results showed that learning and memory deficits were improved in treatment group compared to model group. Brain MDA content and 4-HNE level in hippocampus CA1 were much lower in treatment group than in model group. In summary, we demonstrate that GM-1 could improve spatial learning and memory deficits in rat model of AD, and this may be mediated by the inhibition of oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in the neurons. These data suggest that GM-1 is a potential agent for AD treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tedeschi G, Cirillo M, Tessitore A, Cirillo S (2008) Alzheimer’s disease and other dementing conditions. Neurol Sci 29(Suppl 3):301–307
Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev 81:741–766
Cai Z, Zhao B, Ratka A (2011) Oxidative stress and β-amyloid protein in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromolecular Med 13:223–250
Markesbery WR (1997) Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med 23:134–147
Sokolova TV, Zakharova IO, Furaev VV, Rychkova MP, Avrova NF (2007) Neuroprotective effect of ganglioside GM1 on the cytotoxic action of hydrogen peroxide and amyloid beta-peptide in PC12 cells. Neurochem Res 32:1302–1313
Bachis A, Rabin SJ, Del Fiacco M, Mocchetti I (2002) Gangliosides prevent excitotoxicity through activation of TrkB receptor. Neurotox Res 4:225–234
Svennerholm L (1994) Ganglioside-a new therapeutic agent against stroke and Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci 55:2125–2134
Fang C, Zhou H, Li J et al (2008) Effect of high cholesterol diet on spatial learning and memory in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res 3:478–481
HashimotoM Tanabe Y, Fujii Y et al (2005) Chronic administration of docosahexaenoic acid ameliorates the impairment of spatial cognition learning ability in amyloid beta-infused rats. J Nutr 135:549–555
Nunomura A, Aliev G (2001) Oxidative damage is the earliest event in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:759–767
Fighera MR, Royes LF, Furian AF et al (2006) GM1 ganglioside prevents seizures, Na+, K+-ATPase activity inhibition and oxidative stress induced by glutaric acid and pentylenetetrazole. Neurobiol Dis 22:611–623
Tanaka S, Tabuchi K, Hoshino T, Murashita H, Tsuji S, Hara A (2010) Protective effects of exogenous GM-1 ganglioside on acoustic injury of the mouse cochlea. Neurosci Lett 473:237–241
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Youth Fund from the First Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University (No. FY2012-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
R. Yang and Q. Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, R., Wang, Q., Min, L. et al. Monosialoanglioside improves memory deficits and relieves oxidative stress in the hippocampus of rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Sci 34, 1447–1451 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-1263-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-1263-y