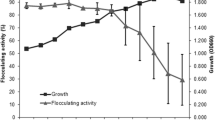
Abstract
Two whey culture supernatants of CJNU 0147 and CJNU 0400 were found to effectively enhance the growth of Bifidobacterium longum FI10564 by 1.58 fold compared to non-fermented whey medium. The 2 isolates were identified to be Leuconostoc mesenteroides (99% identity) by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. To determine whether the whey culture supernatant of CJNU 0147 selectively stimulate the growth of bifidobacteria, the growth rates of Escherichia coli DH5α, Enterococcus faecalis KFRI 675, Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 19111, and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 14458 with the supernatant were measured. In these experiments, the supernatant slightly inhibited the growths of bacteria except for E. coli, indicating that the whey culture supernatant had very little influence on the growth of these bacterial strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
MacConaill LE, Fitzgerald GF, van Sinderen D. Investigation of protein export in Bifidobacterium breve UCC2003. Appl. Environ. Microb. 69: 6994–7001 (2003)
Klijn A, Mercenier A, Arigoni F. Lessons from the genomes of bifidobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 29: 491–509 (2005)
De Dea Lindner J, Canchaya C, Zhang Z, Neviani E, Fitzgerald GF, van Sinderen D, Ventura M. Exploiting Bifidobacterium genomes: The molecular basis of stress response. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 120: 13–24 (2007)
Gueimonde M, Margolles A, de los Reyes-Gavilán CG, Salminen S. Competitive exclusion of enteropathogens from human intestinal mucus by Bifidobacterium strains with acquired resistance to bile -A preliminary study. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 113: 228–232 (2007)
Amenta M, Cascio MT, Di Fiore P, Venturini I. Diet and chronic constipation. Benefits of oral supplementation with symbiotic zir fos (Bifidobacterium longum W11+FOS Actilight). Acta Biomed. 77: 157–162 (2006)
Medina M, Izquierdo E, Ennahar S, Sanz Y. Differential immunomodulatory properties of Bifidobacterium longum strains: Relevance to probiotic selection and clinical applications. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 150: 531–538 (2007)
Sekine K, Ohta J, Onishi M, Tatsuki T, Shimokawa Y, Tomohiro T, Kawashima T, Hashimoto Y. Analysis of antitumor properties of effector cells stimulated with a cell wall preparation (WPG) of Bifidobacterium infantis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 18: 148–153 (1995)
Kouya T, Misawa K, Horiuchi M, Nakayama E, Deguchi H, Tanaka T, Taniguchi M. Production of extracellular bifidogenic growth stimulator by anaerobic and aerobic cultivations of several propionibacterial strains. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 103: 464–471 (2007)
Kouya T, Tobita K, Horiuchi M, Nakayama E, Deguchi H, Tanaka T, Taniguchi M. Production of extracellular bifidogenic growth stimulator (BGS) from Propionibacterium shermanii using a bioreactor system with a microfiltration module and an on-line controller for lactic acid concentration. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 105: 184–191 (2008)
Kelly G. Inulin-type prebiotics-a review: Part 1. Altern. Med. Rev. 13: 316–330 (2008)
Sato Y, Makino S, Yoda N, Isawa K, Kamiyama T, Hojo K, Saito M, Taketomo N, Furuichi K, Ikegami S. Process for producing 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoic acid. U.S. Patent 7,374,915 (2008)
Lee SW. Biological activity of whey proteins and peptides. J. Korean Dairy Technol. Sci. 19: 103–115 (2001)
Marshall K. Therapeutic applications of whey protein. Altern. Med. Rev. 9: 136–156 (2004)
Choi GH, Lee JH, Jo MN, Yoon YC, Paik HD. Growth and antioxidant production of Bacillus polyfermenticus SCD in whey protein concentrate (WPC)-based medium. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 28: 105–108 (2008)
Moon GS, Wegmann U, Gunning AP, Gasson MJ, Narbad A. Isolation and characterization of a theta-type cryptic plasmid from Bifidobacterium longum FI10564. J. Microbiol. Biotechn. 19: 403–408 (2009)
Lee HJ, Joo YJ, Park CH, Lee JS, Park YH, Ahn JS, Mheen TI. Fermentation patterns of green onion kimchi and Chinese cabbage kimchi. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 31: 488–494 (1999)
Cibik R, Lepage E, Talliez P. Molecular diversity of Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Leuconostoc citreum isolated from traditional French cheeses as revealed by RAPD fingerprinting, 16S rDNA sequencing, and 16S rDNA fragment amplification. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 23: 267–278 (2000)
Park SJ, Chang JH, Cha SK, Moon GS. Microbiological analysis of dongchimi, Korean watery radish kimchi, at the early and mid-phase fermentation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 17: 892–894 (2008)
Cho KM, Math RK, Islam SM, Lim WJ, Hong SY, Kim JM, Yun MG, Cho JJ, Yun HD. Novel multiplex PCR for the detection of lactic acid bacteria during kimchi fermentation. Mol. Cell Probes 23: 90–94 (2009)
Cani PD, Delzenne NM. The role of the gut microbiota in energy metabolism and metabolic disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 15: 1546–1558 (2009)
Mitsuoka T. Intestinal flora and aging. Nutr. Rev. 50: 438–446 (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eom, JE., Moon, GS. Leuconostoc mesenteroides producing bifidogenic growth stimulator via whey fermentation. Food Sci Biotechnol 19, 235–238 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-010-0032-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-010-0032-z