Abstract
Objectives
This study aimed to explore the possible role of plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) circular RNA (circRNA) in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Method
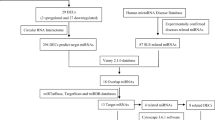
Total RNA was extracted from blood plasma samples obtained from 10 patients with SLE and 10 healthy controls and subjected to microarray analysis to define the profile of circRNA expression. The quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) amplification was conducted. The overlapped circRNA between PBMCs and plasma was performed, the interactions with microRNAs were predicted, the miRNA target mRNA was predicted, and the GEO database was used. The Gene ontology and pathway analysis was performed.
Results
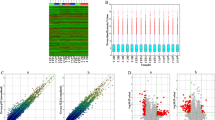
One hundred thirty-one upregulated and 314 significantly downregulated circRNAs were identified in the plasma of patients with SLE by the Fold change criteria (≥ 2.0) and P < 0.05. The qRT-PCR results showed that the expression of has-circRNA-102531, has-circRNA-103984, and has-circRNA-104262 was increased in plasma of SLE, and the expression of has-circRNA-102972, has-circRNA-102006, has-circRNA-104313 was decreased in plasma of SLE. Twenty-eight upregulated circRNAs and 119 downregulated circRNAs were overlapped from PBMCs and plasma, and ubiquitination was enriched. Furthermore, the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network was constructed in SLE after analyzing dataset GSE61635 from GEO. The circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network comprises 54 circRNAs, 41 miRNAs, and 580 mRNAs. In addition, the TNF signaling pathway and the MAPK pathway were enriched from the mRNA of the miRNA target.
Conclusion
We first revealed the differentially expressed circRNAs in plasma and PBMCs, and then the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network was constructed. The network’s circRNAs could be a potential diagnostic biomarker and potentially play an important role in the pathogenesis and development of SLE.
Key Points • This study analyzed the circRNAs expression profiles combined with the plasma and PBMCs, which provided a comprehensive overview of circRNAs expression patterns in SLE. • The network of the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA in SLE was constructed, which contributes to a better understanding of the pathogenesis and development of SLE. |






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Durcan L, O'Dwyer T, Petri M (2019) Management strategies and future directions for systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. The Lancet 393(10188):2332–2343. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(19)30237-5
Dörner T, Furie R (2019) Novel paradigms in systemic lupus erythematosus. The Lancet 393(10188):2344–2358. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(19)30546-x
Andrea Fava MP (2019) Systemic lupus erythematosus: diagnosis and clinical management. J Autoimmun 96:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2018.11.001
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40(9):1725–1725
Yu C, Gershwin ME, Chang C (2014) Diagnostic criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus: a critical review. J Autoimmun 48-49:10–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2014.01.004
Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J (2017) Insights into circular RNA biology. RNA Biol 14(8):1035–1045. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1271524
Wang X, Ma R, Shi W, Wu Z, Shi Y (2021) Emerging roles of circular RNAs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 24:212–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2021.02.028
Zheng F, Yu X, Tang D, Hong X, Zhang X, Liu D, Dai Y (2021) The identification of circular RNAs from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. BMC Med Genom 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-021-00919-w
Zheng F, Yu X, Huang J, Dai Y (2017) Circular RNA expression profiles of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients, based on microarray chip technology. Mol Med Rep 16(6):8029–8036. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7638
Luo Q, Zhang L, Fang L, Fu B, Guo Y, Huang Z, Li J (2020) Circular RNAs hsa_circ_0000479 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity 53(3):167–176. https://doi.org/10.1080/08916934.2020.1728529
Guo G, Wang H, Ye L, Shi X, Yan K, Lin K, Huang Q, Li B, Lin Q, Zhu L, Xue X, Zhang H (2019) Hsa_circ_0000479 as a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front Immunol 10:2281. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02281
Li LJ, Zhu ZW, Zhao W, Tao SS, Li BZ, Xu SZ, Wang JB, Zhang MY, Wu J, Leng RX, Fan YG, Pan HF, Ye DQ (2018) Circular RNA expression profile and potential function of hsa_circ_0045272 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology 155(1):137–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12940
Li H, Li K, Lai W, Li X, Wang H, Yang J, Chu S, Wang H, Kang C, Qiu Y (2018) Comprehensive circular RNA profiles in plasma reveals that circular RNAs can be used as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Chim Acta 480:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2018.01.026
Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL, Brown PO (2013) Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet 9(9):e1003777. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003777
Salzman J (2016) Circular RNA expression: its potential regulation and function. Trends Genet 32(5):309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2016.03.002
Yu Y, Liu L, Hu LL, Yu LL, Li JP, Rao JA, Zhu LJ, Liang Q, Zhang RW, Bao HH, Cheng XS (2021) Potential therapeutic target genes for systemic lupus erythematosus: a bioinformatics analysis. Bioengineered 12(1):2810–2819. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1939637
Postal M, Appenzeller S (2011) The role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cytokine 56(3):537–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2011.08.026
Wong CK, Wong PT, Tam LS, Li EK, Chen DP, Lam CW (2009) Activation profile of intracellular mitogen-activated protein kinases in peripheral lymphocytes of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Immunol 29(6):738–746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-009-9318-4
Meng X, Li X, Zhang P, Wang J, Zhou Y, Chen M (2017) Circular RNA: an emerging key player in RNA world. Brief Bioinform 18(4):547–557. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbw045
Olins AL, Rhodes G, Welch DBM, Zwerger M, Olins DE (2010) Lamin B receptor: multi-tasking at the nuclear envelope. Nucleus 1(1):53–70
Konstantinidou A, Karadimas C, Waterham HR, Superti-Furga A, Kaminopetros P, Grigoriadou M, Kokotas H, Agrogiannis G, Giannoulia-Karantana A, Patsouris E (2008) Pathologic, radiographic and molecular findings in three fetuses diagnosed with HEM/Greenberg skeletal dysplasia. Pren Diag: Pub Affil With the Int Soc Pren Diags 28(4):309–312
Navarro Quiroz E, Chavez-Estrada V, Macias-Ochoa K, Ayala-Navarro MF, Flores-Aguilar AS, Morales-Navarrete F, De la Cruz LF, Gomez Escorcia L, Musso CG, Aroca Martinez G (2019) Epigenetic mechanisms and posttranslational modifications in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Mol Sci 20(22):5679
Doyle HA, Mamula MJ (2005) Posttranslational modifications of self-antigens. Annals New York Acad Sci 1050(1):1–9
Zavala-Cerna MG, Martínez-García EA, Torres-Bugarín O, Rubio-Jurado B, Riebeling C, Nava A (2014) The clinical significance of posttranslational modification of autoantigens. Clin Rev In Allergy Immun 47(1):73–90
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, Kjems J (2013) Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495(7441):384–388
Amarilyo G, La Cava A (2012) miRNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol 144(1):26–31
Singh RP, Hahn BH, Bischoff DS (2022) Identification and contribution of inflammation-induced novel microRNA in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol 13:848149. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.848149
Al-hasso IKQ, Al-Derzi AR, AAH A, Gorial FI, Alnuimi AS (2022) Role of circulating miRNA-130b-3p and TGF-β 1cytokine in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Gene Rep 26:101476
Wang Y, Liang J, Qin H, Ge Y, Du J, Lin J, Zhu X, Wang J, Xu J (2016) Elevated expression of miR-142-3p is related to the pro-inflammatory function of monocyte-derived dendritic cells in SLE. Arthritis Res Ther 18(1):1–11
Zhu L-J, Landolt-Marticorena C, Li T, Yang X, Yu X-Q, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Fortin PR, Wither JE (2010) Altered expression of TNF-α signaling pathway proteins in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 37(8):1658–1666
Kong X, Zhang Z, Fu T, Ji J, Yang J, Gu Z (2019) TNF-α regulates microglial activation via the NF-κB signaling pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus with depression. Int J Biol Macromol 125:892–900
López P, Gutiérrez C, Suárez A (2010) IL-10 and TNFalpha genotypes in SLE. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:838390. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/838390
Aringer M, Smolen JS (2004) Tumour necrosis factor and other proinflammatory cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus: a rationale for therapeutic intervention. Lupus 13(5):344–347. https://doi.org/10.1191/0961203303lu1024oa
Zhu L-J, Yang X, Yu X-Q (2010) Anti-TNF-α therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:465898
Zhang H, Huang X, Ye L, Guo G, Li X, Chen C, Sun L, Li B, Chen N, Xue X (2018) B cell-related circulating microRNAs with the potential value of biomarkers in the differential diagnosis, and distinguishment between the disease activity and lupus nephritis for systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol 9:1473. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01473
Zeng S, Cui J, Zhang Y, Zheng Z, Meng J, Du J (2022) MicroRNA-15b-5p inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced proliferation, migration, and extracellular matrix production of airway smooth muscle cells via targeting yes-associated protein 1. Bioengineered 13(3):5396–5406. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2036890
Funding
This project was supported by Shenzhen science and technology innovation commission (No. JCYJ20200109140412476), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82100726), and the Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission Basic Research Program (JCYJ20210324110403011), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2020A1515110970). “San-ming” Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (no.SZSM201812097).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
Fig. S1 The GO results of these dysregulated mRNAs. Fig. S2 The KEGG pathway results of these dysregulated mRNAs. Fig. S3 A network of overlapped upregulated gene’s interaction
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, F., Tan, L., Zhang, F. et al. The circRNA–miRNA–mRNA regulatory network in plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells and the potential associations with the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 42, 1885–1896 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06560-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06560-5