Abstract
Introduction/objectives
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) was an autoimmune disease with a large variety of clinical manifestations and involving many organs. Its exact etiology was unclear, and studies had shown that T cells may play an important role. In this study, we wished to study the regulatory mechanism of circRNA in the T cells from SLE patients.
Method
GSE84655 was retrieved from the GEO database, and the corresponding probe name was converted into an international standard circRNA name by using the practical extraction and report language. The differentially expressed circRNAs (DECs) were analyzed by using R software. Subsequently, we used multiple bioinformatics methods to obtain the target miRNAs of circRNAs and the downstream mRNAs of miRNAs. Finally, a circRNA–miRNA–mRNA regulatory network was constructed and visualized by using Cytoscape 3.6.1 software.
Results
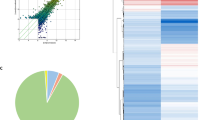
There were a total of 29 DECs that had been identified, including 2 upregulated circRNAs and 27 downregulated circRNAs. After a lot of in-depth analysis, we finally obtained a circRNA–miRNA–mRNA regulatory network consisting of 8 DECs (hsa_circ_0006770, hsa_circ_0002904, hsa_circ_0034044, hsa_circ_0023685, hsa_circ_0049271, hsa_circ_0074491, hsa_circ_0074559, and hsa_circ_0023461), 4 overlap miRNAs (hsa-miR-326, hsa-miR-569, hsa-miR-638, and hsa-miR-1246), and 13 target mRNAs (EPHB3, USH1G,UBE4A, DCAF7, TBL1XR1, SLC27A4, SMO, NAA30, RSBN1, PLAG1, SOX2, GPATCH11, and DYRK1A).
Conclusions
This study could provide a novel insight into the role of circRNA and the circRNA–miRNA–mRNA regulation network in the SLE. However, it also needed to be verified by subsequent experiments and clinical studies.
Key Points • There were 29 DECs (2 up and 27 down) between T cells of SLE and health control. • Hsa-miR-338-3p, hsa-miR-767-3p, and hsa-miR-1827 were the most frequent miRNAs. • We obtained a circRNA–miRNA–mRNA regulatory network for SLE. |





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- DECs:
-
Differentially expressed circRNAs
- circRNA:
-
Circular RNA
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- HMDD:
-
Human microRNA Disease Database
- PBMC:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell
References
Zucchi D, Elefante E, Calabresi E, Signorini V, Bortoluzzi A, Tani C (2019) One year in review 2019: systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol 37(5):715–722
Nusbaum JS, Mirza I, Shum J, Freilich RW, Cohen RE, Pillinger MH, Izmirly PM, Buyon JP (2020) Sex differences in systemic lupus erythematosus: epidemiology, clinical considerations, and disease pathogenesis. Mayo Clin Proc 95(2):384–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.09.012
Li LJ, Zhu ZW, Zhao W, Tao SS, Li BZ, Xu SZ, Wang JB, Zhang MY, Wu J, Leng RX, Fan YG, Pan HF, Ye DQ (2018) Circular RNA expression profile and potential function of hsa_circ_0045272 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology 155(1):137–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12940
Sharabi A, Tsokos GC (2020) T cell metabolism: new insights in systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis and therapy. Nat Rev Rheumatol 16(2):100–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-019-0356-x
Li S, Zhang J, Tan X, Deng J, Li Y, Piao Y, Li C, Yang W, Mo W, Sun J, Sun F, Han T, Wang J, Kuang W, Li C (2019) Microarray expression profile of circular RNAs and mRNAs in children with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 38(5):1339–1350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4392-8
Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross HJ, Kleinschmidt AK (1976) Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 73(11):3852–3856. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.73.11.3852
Li H, Li K, Lai W, Li X, Wang H, Yang J, Chu S, Wang H, Kang C, Qiu Y (2018) Comprehensive circular RNA profiles in plasma reveals that circular RNAs can be used as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Chim Acta 480:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2018.01.026
Miao Q, Zhong Z, Jiang Z, Lin Y, Ni B, Yang W, Tang J (2019) RNA-seq of circular RNAs identified circPTPN22 as a potential new activity indicator in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 28(4):520–528. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203319830493
Floris G, Zhang L, Follesa P, Sun T (2017) Regulatory role of circular RNAs and neurological disorders. Mol Neurobiol 54(7):5156–5165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0055-4
Wang L, Shen C, Wang Y, Zou T, Zhu H, Lu X, Li L, Yang B, Chen J, Chen S, Lu X, Gu D (2019) Identification of circular RNA Hsa_circ_0001879 and Hsa_circ_0004104 as novel biomarkers for coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 286:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.05.006
Lei M, Zheng G, Ning Q, Zheng J, Dong D (2020) Translation and functional roles of circular RNAs in human cancer. Mol Cancer 19(1):30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-1135-7
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH, Sherman PM, Holko M, Yefanov A, Lee H, Zhang N, Robertson CL, Serova N, Davis S, Soboleva A (2013) NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res 41(Database issue):D991–D995. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1193
Dudekula DB, Panda AC, Grammatikakis I, De S, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M (2016) CircInteractome: a web tool for exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and microRNAs. RNA Biol 13(1):34–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2015.1128065
Huang Z, Shi J, Gao Y, Cui C, Zhang S, Li J, Zhou Y, Cui Q (2019) HMDD v3.0: a database for experimentally supported human microRNA-disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D1013–D1017. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1010
Huang HY, Lin YC, Li J, Huang KY, Shrestha S, Hong HC, Tang Y, Chen YG, Jin CN, Yu Y, Xu JT, Li YM, Cai XX, Zhou ZY, Chen XH, Pei YY, Hu L, Su JJ, Cui SD, Wang F, Xie YY, Ding SY, Luo MF, Chou CH, Chang NW, Chen KW, Cheng YH, Wan XH, Hsu WL, Lee TY, Wei FX, Huang HD (2020) miRTarBase 2020: updates to the experimentally validated microRNA-target interaction database. Nucleic Acids Res 48(D1):D148–D154. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz896
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW, Bartel DP (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 4. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05005
Chen Y, Wang X (2020) miRDB: an online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res 48(D1):D127–D131. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz757
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Guo G, Wang H, Ye L, Shi X, Yan K, Lin K, Huang Q, Li B, Lin Q, Zhu L, Xue X, Zhang H (2019) Hsa_circ_0000479 as a novel diagnostic biomarker of systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol 10:2281. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02281
Zurawska A, Mycko MP, Selmaj KW (2019) Circular RNAs as a novel layer of regulatory mechanism in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 334:576971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2019.576971
Wang J, Yan S, Yang J, Lu H, Xu D, Wang Z (2019) Non-coding RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: from bench to bedside. Front Immunol 10:3129. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.03129
Luo Q, Zhang L, Li X, Fu B, Guo Y, Huang Z, Li J (2019) Identification of circular RNAs hsa_circ_0044235 and hsa_circ_0068367 as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Mol Med 44(4):1462–1472. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2019.4302
Zhang MY, Wang JB, Zhu ZW, Li LJ, Liu RS, Yang XK, Leng RX, Li XM, Pan HF, Ye DQ (2018) Differentially expressed circular RNAs in systemic lupus erythematosus and their clinical significance. Biomed Pharmacother 107:1720–1727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.161
Xue Q, Sun K, Deng HJ, Lei ST, Dong JQ, Li GX (2014) MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits colorectal carcinoma cell invasion and migration by targeting smoothened. Jpn J Clin Oncol 44(1):13–21. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyt181
Gao L, Xiong DD, He RQ, Lai ZF, Liu LM, Huang ZG, Yang X, Wu HY, Yang LH, Ma J, Li SH, Lin P, Yang H, Luo DZ, Chen G, Dang YW (2019) Identifying TF-miRNA-mRNA regulatory modules in nitidine chloride treated HCC xenograft of nude mice. Am J Transl Res 11(12):7503–7522
Fasihi A, Bahram MS, Atashi A, Nasiri S (2018) Introduction of hsa-miR-103a and hsa-miR-1827 and hsa-miR-137 as new regulators of Wnt signaling pathway and their relation to colorectal carcinoma. J Cell Biochem 119(7):5104–5117. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26357
Alexandri C, Daniel A, Bruylants G, Demeestere I (2020) The role of microRNAs in ovarian function and the transition toward novel therapeutic strategies in fertility preservation: from bench to future clinical application. Hum Reprod Update 26:174–196. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmz039
Jimenez-Lucena R, Camargo A, Alcala-Diaz JF, Romero-Baldonado C, Luque RM, van Ommen B, Delgado-Lista J, Ordovas JM, Perez-Martinez P, Rangel-Zuniga OA, Lopez-Miranda J (2018) A plasma circulating miRNAs profile predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus and prediabetes: from the CORDIOPREV study. Exp Mol Med 50(12):168–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0194-y
Foinquinos A, Batkai S, Genschel C, Viereck J, Rump S, Gyongyosi M, Traxler D, Riesenhuber M, Spannbauer A, Lukovic D, Weber N, Zlabinger K, Hasimbegovic E, Winkler J, Fiedler J, Dangwal S, Fischer M, de la Roche J, Wojciechowski D, Kraft T, Garamvolgyi R, Neitzel S, Chatterjee S, Yin X, Bar C, Mayr M, Xiao K, Thum T (2020) Preclinical development of a miR-132 inhibitor for heart failure treatment. Nat Commun 11(1):633. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14349-2
Salvi V, Gianello V, Tiberio L, Sozzani S, Bosisio D (2019) Cytokine targeting by miRNAs in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol 10:15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00015
Sharaf-Eldin WE, Kishk NA, Gad YZ, Hassan H, Ali MAM, Zaki MS, Mohamed MR, Essawi ML (2017) Extracellular miR-145, miR-223 and miR-326 expression signature allow for differential diagnosis of immune-mediated neuroinflammatory diseases. J Neurol Sci 383:188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2017.11.014
Chen JQ, Papp G, Poliska S, Szabo K, Tarr T, Balint BL, Szodoray P, Zeher M (2017) MicroRNA expression profiles identify disease-specific alterations in systemic lupus erythematosus and primary Sjogren’s syndrome. PLoS One 12(3):e0174585. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174585
Hikami K, Kawasaki A, Ito I, Koga M, Ito S, Hayashi T, Matsumoto I, Tsutsumi A, Kusaoi M, Takasaki Y, Hashimoto H, Arinami T, Sumida T, Tsuchiya N (2011) Association of a functional polymorphism in the 3′-untranslated region of SPI1 with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 63(3):755–763. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.30188
Steen SO, Iversen LV, Carlsen AL, Burton M, Nielsen CT, Jacobsen S, Heegaard NH (2015) The circulating cell-free microRNA profile in systemic sclerosis is distinct from both healthy controls and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 42(2):214–221. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.140502
Ishibe Y, Kusaoi M, Murayama G, Nemoto T, Kon T, Ogasawara M, Kempe K, Yamaji K, Tamura N (2018) Changes in the expression of circulating microRNAs in systemic lupus erythematosus patient blood plasma after passing through a plasma adsorption membrane. Ther Apher Dial 22(3):278–289. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-9987.12695
Funding
The work was supported by NSFC (Natural Science Foundation of China) Grant U1605223 to Dr. Guixiu Shi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Junhui Zhang: analyze the data and write a first draft; Liu Yuan, revised paper; Shi Guixiu, overall guidance and revised paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Liu, Y. & Shi, G. The circRNA–miRNA–mRNA regulatory network in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 40, 331–339 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05212-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05212-2