Abstract
Introduction
Pediatric SAPHO syndrome is regarded as the equivalent of chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis or chronic non-bacterial osteomyelitis. This study aimed to evaluate the clinical features and treatment options for Chinese pediatric patients with SAPHO syndrome.
Method
We conducted a single-center, retrospective study on a sample of 24 pediatric patients with SAPHO syndrome who were diagnosed at Peking Union Medical College Hospital from April 2014 to August 2018. The demographic, clinical, laboratory, imaging, histological, and therapeutic data were collected and analyzed.
Results
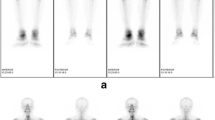
A total of 15 boys and 9 girls were included. The mean age of onset of bone and skin symptoms was 11.7 ± 3.8 and 14.4 ± 2.7 years, respectively. The mean follow-up period was 39.2 months. Seventeen patients had skin manifestations (46% had severe acne, 100% were boys; 21% had palmoplantar pustulosis, 100% were girls). Bone lesions were localized in four of the following major regions: anterior chest wall (42%), mandible (29%), peripheral bones (50%), and spine and sacroiliac joints (21%). Six patients had been treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, 10 with bisphosphonate, 10 with a tumor necrosis factor-α antagonist, and 1 with glucocorticoids, with variable responses. A total of 70% of the patients had complete remission after bisphosphonate or TNF-α antagonist therapy.
Conclusion
Pediatric patients with SAPHO syndrome have different characteristics from other cohorts in the sex ratio, frequency of mandibular involvement, and sex distribution of skin lesions. Bisphosphonate and TNF-α antagonists show a favorable response in pediatric SAPHO syndrome treatment.
Key points •Being the first study that describes an Asian pediatric SAPHO case series. •Chinese pediatric patients with SAPHO syndrome have different characteristics from Chinese adult patients and Caucasian pediatric patients. |



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and material generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article. Detailed data of patients included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
Chamot AM, Benhamou CL, Kahn MF, Beraneck L, Kaplan G, Prost A (1987) Acne-pustulosis-hyperostosis-osteitis syndrome. Results of a national survey. 85 cases. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic 54(3):187–196
Nguyen MT, Borchers A, Selmi C, Naguwa SM, Cheema G, Gershwin ME (2012) The SAPHO syndrome. Semin Arthritis Rheum 42(3):254–265
Li C, Zuo Y, Wu N, Li L, Li F, Zhang W, Xu W, Zhao X, Jing H, Pan Q, Zhou W, Shi X, Fan Y, Wang J, Liu S, Liu Z, Zhang F, Zeng X, Chen H, Zhang S, Liu J, Qiu G, Wu Z, Dong Z, Zhang W (2016) Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis and osteitis syndrome: a single centre study of a cohort of 164 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 55(6):1023–1030
Zemann W, Pau M, Feichtinger M, Ferra-Matschy B, Kaercher H (2011) SAPHO syndrome with affection of the mandible: diagnosis, treatment, and review of literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 111(2):190–195
Wipff J, Adamsbaum C, Kahan A, Job-Deslandre C (2011) Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis. Joint Bone Spine 78(6):555–560
Kahn MF (1995) Current status of the SAPHO syndrome. Presse Med 24(7):338–340
Anderson SE, Heini P, Sauvain MJ, Stauffer E, Geiger L, Johnston JO, Roggo A, Kalbermatten D, Steinbach LS (2003) Imaging of chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis of childhood first presenting with isolated primary spinal involvement. Skelet Radiol 32(6):328–336
Schilling F, Marker-Hermann E: [Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis in association with chronic inflammatory bowel disease: entheropathic CRMO]. Z Rheumatol 2003, 62(6):527–538
Girschick H, Finetti M, Orlando F, Schalm S, Insalaco A, Ganser G, Nielsen S, Herlin T, Kone-Paut I, Martino S et al (2018) The multifaceted presentation of chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis: a series of 486 cases from the Eurofever international registry. Rheumatology (Oxford) 57:1203–1211
Jelusic M, Cekada N, Frkovic M, Potocki K, Skerlev M, Murat-Susic S, Husar K, Dapic T, Smigovec I, Bajramovic D (2018) Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO) and synovitis acne Pustulosis hyperostosis Osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome—two presentations of the same disease? Acta Dermatovenerol Croat 26(3):212–219
Jansson A, Renner ED, Ramser J, Mayer A, Haban M, Meindl A, Grote V, Diebold J, Jansson V, Schneider K, Belohradsky BH (2007) Classification of non-bacterial osteitis: retrospective study of clinical, immunological and genetic aspects in 89 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46(1):154–160
Roderick MR, Shah R, Rogers V, Finn A, Ramanan AV (2016) Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO)—advancing the diagnosis. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J 14(1):47
Gikas PD, Islam L, Aston W, Tirabosco R, Saifuddin A, Briggs TW, Cannon SR, O'Donnell P, Jacobs B, Flanagan AM (2009) Nonbacterial osteitis: a clinical, histopathological, and imaging study with a proposal for protocol-based management of patients with this diagnosis. J Orthop Sci 14(5):505–516
Pastore S, Ferrara G, Monasta L, Meini A, Cattalini M, Martino S, Alessio M, La Torre F, Teruzzi B, Gerloni V et al (2016) Chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis may be associated with renal disease and bisphosphonates are a good option for the majority of patients. Acta Paediatr 105(7):e328–e333
Hospach T, Langendoerfer M, von Kalle T, Maier J, Dannecker GE (2010) Spinal involvement in chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO) in childhood and effect of pamidronate. Eur J Pediatr 169(9):1105–1111
Jansson AF, Muller TH, Gliera L, Ankerst DP, Wintergerst U, Belohradsky BH, Jansson V (2009) Clinical score for nonbacterial osteitis in children and adults. Arthritis Rheum 60(4):1152–1159
Witt M, Meier J, Hammitzsch A, Proft F, Schulze-Koops H, Grunke M (2014) Disease burden, disease manifestations and current treatment regimen of the SAPHO syndrome in Germany: results from a nationwide patient survey. Semin Arthritis Rheum 43(6):745–750
Colina M, Govoni M, Orzincolo C, Trotta F (2009) Clinical and radiologic evolution of synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis syndrome: a single center study of a cohort of 71 subjects. Arthritis Rheum 61(6):813–821
Hayem G, Bouchaud-Chabot A, Benali K, Roux S, Palazzo E, Silbermann-Hoffman O, Kahn MF, Meyer O (1999) SAPHO syndrome: a long-term follow-up study of 120 cases. Semin Arthritis Rheum 29(3):159–171
Salles M, Olive A, Perez-Andres R, Holgado S, Mateo L, Riera E, Tena X (2011) The SAPHO syndrome: a clinical and imaging study. Clin Rheumatol 30(2):245–249
Cao Y, Li C, Yang Q, Wu N, Xu P, Li Y, Shi X, Pan Q, Wu X, Sun X, Zhao Y, Gu Z, Yuan S, Zuo Y, Li L, Zhang W, Hao W, Liu J, Jing H, Zhang W (2019) Three patterns of osteoarticular involvement in SAPHO syndrome: a cluster analysis based on whole body bone scintigraphy of 157 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 58:1047–1055
Xu W, Li C, Zhao X, Lu J, Li L, Wu N, Zuo Y, Jing H, Dong Z, Zhang W, Zhang W (2017) Whole-spine computed tomography findings in SAPHO syndrome. J Rheumatol 44(5):648–654
Ziobrowska-Bech A, Fiirgaard B, Heuck C, Ramsgaard Hansen O, Herlin T (2013) Ten-year review of Danish children with chronic non-bacterial osteitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 31(6):974–979
Wipff J, Costantino F, Lemelle I, Pajot C, Duquesne A, Lorrot M, Faye A, Bader-Meunier B, Brochard K, Despert V, Jean S, Grall-Lerosey M, Marot Y, Nouar D, Pagnier A, Quartier P, Job-Deslandre C (2015) A large national cohort of French patients with chronic recurrent multifocal osteitis. Arthritis Rheumatol 67(4):1128–1137
Cao Y, Li C, Xu W, Wu X, Sun X, Zhang W, Jing H, Gu Z, Yuan S, Li L et al (2018) Spinal and sacroiliac involvement in SAPHO syndrome: a single center study of a cohort of 354 patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum
Sun X, Li C, Cao Y, Shi X, Li L, Zhang W, Wu X, Wu N, Jing H, Zhang W (2018) F-18 FDG PET/CT in 26 patients with SAPHO syndrome: a new vision of clinical and bone scintigraphy correlation. J Orthop Surg Res 13(1):120
Hayem G (2004) SAPHO syndrome. Rev Prat 54(15):1635–1636
Beck C, Morbach H, Beer M, Stenzel M, Tappe D, Gattenlohner S, Hofmann U, Raab P, Girschick HJ (2010) Chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis in childhood: prospective follow-up during the first year of anti-inflammatory treatment. Arthritis Res Ther 12(2):R74
Borzutzky A, Stern S, Reiff A, Zurakowski D, Steinberg EA, Dedeoglu F, Sundel RP (2012) Pediatric chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis. Pediatrics 130(5):e1190–e1197
Huber AM, Lam PY, Duffy CM, Yeung RS, Ditchfield M, Laxer D, Cole WG, Kerr Graham H, Allen RC, Laxer RM (2002) Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis: clinical outcomes after more than five years of follow-up. J Pediatr 141(2):198–203
Skrabl-Baumgartner A, Singer P, Greimel T, Gorkiewicz G, Hermann J (2019) Chronic non-bacterial osteomyelitis: a comparative study between children and adults. Pediatr Rheumatol 17:49
Costa-Reis P, Sullivan KE (2013) Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis. J Clin Immunol 33(6):1043–1056
Catalano-Pons C, Comte A, Wipff J, Quartier P, Faye A, Gendrel D, Duquesne A, Cimaz R, Job-Deslandre C (2008) Clinical outcome in children with chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47(9):1397–1399
Ishikawa-Nakayama K, Sugiyama E, Sawazaki S, Taki H, Kobayashi M, Koizumi F, Furuta I (2000) Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis showing marked improvement with corticosteroid treatment. J Rheumatol 27(5):1318–1319
Kerrison C, Davidson JE, Cleary AG, Beresford MW (2004) Pamidronate in the treatment of childhood SAPHO syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43(10):1246–1251
Deutschmann A, Mache CJ, Bodo K, Zebedin D, Ring E (2005) Successful treatment of chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis with tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockage. Pediatrics 116(5):1231–1233
Taylor JB, Young WO, Rutar T (2010) Posterior subcapsular cataracts in children receiving adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) for infantile spasms. J Child Neurol 25(8):1017–1019
Allen DB, Julius JR, Breen TJ, Attie KM (1998) Treatment of glucocorticoid-induced growth suppression with growth hormone. National Cooperative Growth Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83(8):2824–2829
Li C, Zhao Y, Zuo Y, Zhou Y, Zhang F, Liu S, Zhu Q, Chen J, Zhang W, Xu W et al (2019) Efficacy of bisphosphonates in patients with synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis syndrome: a prospective open study. Clin Exp Rheumatol 37:663
Acknowledgments
We thank Ellen Knapp, PhD, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81822030 to W.N.), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7172175 to W.N.), the Central Level Public Interest Program for Scientific Research Institute (2018RC31003 to W.N.), CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (2017-I2M-3-001 to L.C.), and Capital Medical Research and Development Fund (2016-4-40112 to L.C.). The role of the funding body was in the design and collection of data of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Nan Wu, Yuming Shao, and Jianwei Huo contributed equally this study and should be regarded as co-first authors. Chen Li, Nan Wu, and Jianwei Huo designed the manuscript. Yuming Shao, Yanying Yu, and Chenyang Yu carried out the literature search. Yuming Shao, Nan Wu, Yanan Zhang, Yihan Cao, Hongli Jing, Fa Zhang, Hongmei Song, and Wen Zhang contributed to data extraction, and data analysis. Nan Wu, Jianwei Huo, and Yihan Cao supports for data interpretation. Yuming Shao drafted the manuscript. All authors approved the final version to be published after critically revising the manuscript for important intellectual content.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures None.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Peking Union Medical College Hospital (approval number: ZS-944).
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from each patient.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
We used SPSS 22.0 for data analysis and no code were generated or used during the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, N., Shao, Y., Huo, J. et al. Clinical characteristics of pediatric synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome: the first Chinese case series from a single center. Clin Rheumatol 40, 1487–1495 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05393-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05393-w