Abstract
Introduction/objectives
Articular cartilage is the target tissue of osteoarthritis (OA), and because it lacks capillary networks, the microenvironment is hypoxic. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) regulates the homeostasis of this tissue. The aim of this study was to investigate whether genetic polymorphisms of the HIF-1α signaling pathway are involved in the development of knee OA.
Method
We performed a case-control association study and genotyped 134 knee OA patients and 267 healthy controls. All participants were genotyped in order to evaluate 42 SNPs from 22 genes involved in the HIF-1α signaling pathway using the OpenArray technology. Gene-gene interactions (epistasis) were analyzed using the multifactor dimensionality reduction (MDR) method.
Results
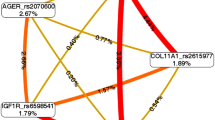
The MDR analysis showed epistasis between AKT2 (rs8100018) and IGF1 (rs2288377), AKT2 (rs8100018) and IGF1 (rs35767), IGF1 (rs35767) and COL2A1 (rs1793953), and between GSK3B (rs6438552) and IGF1 (rs35767) polymorphisms, with information gain values of 21.24%, 8.37%, 9.93%, and 5.73%, respectively. Additionally, our model allowed us to identify high- and low-risk genotypes among COL2A1 rs1793953, GSK3B rs6438552, AKT2 rs8100018, and IGF1 rs35767 polymorphisms.
Conclusions
Knowing the interactions of these polymorphisms involved in HIF-1α signaling pathway could provide a new diagnostic support tool to identify individuals at high risk of developing knee OA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kraus VB, Blanco FJ, Englund M, Karsdal MA, Lohmander LS (2015) Call for standardized definitions of osteoarthritis and risk stratification for clinical trials and clinical use. Osteoarthr Cartil 23(8):1233–1241
Arden N, Nevitt M (2006) Osteoarthritis: epidemiology. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 20(1):3–25
De Filippis L, Gulli S, Caliri A, Romano C, Munaó F, Trimarchi G et al (2004) Epidemiology and risk factors in osteoarthritis: literature review data from "OASIS" study. Reumatismo 56(3):169–164
Woolf AD, Pfleger B (2003) Burden of major musculoskeletal conditions. Bull World Health Organ 81(9):646–656
Peláez-Ballestas I, Sanin LH, Moreno-Montoya J, Alvarez-Nemegyei J, Burgos-Vargas R, Garza-Elizondo M et al (2011) Epidemiology of the rheumatic diseases in Mexico. A study of 5 regions based on the COPCORD methodology. J Rheum Suppl 86:3–8
Sophia Fox AJ, Bedi A, Rodeo SA (2009) The basic science of articular cartilage: structure, composition, and function. Sports Health 1(6):461–468
Pfander D, Swoboda B, Cramer T (2006) The role of HIF-1alpha in maintaining cartilage homeostasis and during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 8(1):104
Ströbel S, Loparic M, Wendt D, Schenk AD, Candrian C, Lindberg RL et al (2010) Anabolic and catabolic responses of human articular chondrocytes to varying oxygen percentages. Arthritis Res Ther 12(2):R34
Fernández-Torres J, Hernández-Díaz C, Espinosa-Morales R, Camacho-Galindo J, Galindo-Sevilla NC, López-Macay A et al (2015) Polymorphic variation of hypoxia inducible factor-1 A (HIF1A) gene might contribute to the development of knee osteoarthritis: a pilot study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 16:218
López-Reyes A, Rodríguez-Pérez JM, Fernández-Torres J, Martínez-Rodríguez N, Pérez-Hernández N, Fuentes-Gómez AJ, Aguilar-González CA, Álvarez-León E, Posadas-Romero C, Villarreal-Molina T, Pineda C, Vargas-Alarcón G (2014) The HIF1A rs2057482 polymorphism is associated with risk of developing premature coronary artery disease and with some metabolic and cardiovascular risk factors. The Genetics of Atherosclerotic Disease (GEA) Mexican Study. Exp Mol Pathol 96(3):405–410
Zhou J, Hara K, Inoue M, Hamada S, Yasuda H, Moriyama H, Endo H, Hirota K, Yonezawa K, Nagata M, Yokono K (2008) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 by glucose availability under hypoxic conditions. Kobe J Med Sci 53(6):283–296
Fan L, Li J, Yu Z, Dang X, Wang K (2014) The hypoxia-inducible factor pathway, prolyl-hydroxylase domain protein inhibitors, and their roles in bone repair and regeneration. Biomed Res Int 2014:239356
Sartori-Cintra AR, Mara CS, Argolo DL, Coimbra IB (2012) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) expression by interleukin-1β (IL-1 β), insulin-like growth factors I (IGF-I) and II (IGF-II) in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Clinics (Säo Paulo, Brazil) 67(1):35–40
Maxwell PH (2005) Hypoxia-inducible factor as a physiological regulator. Exp Physiol 90(6):791–797
Görlach A (2009) Regulation of HIF-1 alpha at the transcriptional level. Curr Pharm Des 15(33):3844–3852
Semenza GL (2002) Signal transduction to hypoxia-inducible factor. Biochem Pharmacol 64(5–6):993–998
Flügel D, Görlach A, Michiels C, Kietzmann T (2007) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 phosphorylates hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and mediates its destabilization in a VHL-independent manner. Mol Cell Biol 27(9):3253–3265
Chen N, Chen LP, Zhang J, Chen C, Wei XL, Gul Y, Wang WM, Wang HL (2012) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of three hypoxia-inducible factor alpha subunits, HIF-1α/2α/3α of the hypoxia-sensitive freshwater species, Chinese sucker. Gene 498(1):81–90
Patel SA, Simon MC (2008) Biology of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha in development and disease. Cell Death Differ 15(4):628–624
Semenza GL (2000) HIF-1: mediator of physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 88(4):1474–1480
Pfander D, Cramer T, Swoboda B (2005) Hypoxia and HIF-1 alpha in osteoarthritis. Int Orthop 29(1):6–9
Murphy CL, Thoms BL, Vaghjiani RJ, Lafont JE (2009) Hypoxia. HIF-mediated articular chondrocyte function: prospects for cartilage repair. Arthritis Res Ther 11(1):213
Zhang FJ, Luo W, Lei GH (2015) Role of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine 82(3):144–147
Fernández-Moreno M, Rego I, Carreira-García V, Blanco FJ (2008) Genetics in osteoarthritis. Current Genomics 9(8):542–547
van Meurs JB, Uitterlinden AG (2012) Osteoarthritis year 2012 in review: genetics and genomics. Osteoarthr Cartil 20(12):1470–1476
Mechanic LE, Luke BT, Goodman JE, Chanock SJ, Harris CC (2008) Polymorphism interaction analysis (PIA): a method for investigating complex gene-gene interactions. BMC Bioinformatics 9:146
Ritchie MD, Hahn LW, Moore JH (2003) Power of multifactor dimensionality reduction for detecting gene-gene interactions in the presence of genotyping error, missing data, phenocopy, and genetic heterogeneity. Genet Epidemiol 24(2):150–157
Hahn LW, Ritchie MD, Moore JH (2003) Multifactor dimensionality reduction software for detecting gene-gene and gene-environment interactions. Bioinformatics 19(3):376–372
Chen GB, Xu Y, Xu HM, Li MD, Zhu J, Lou XY (2011) Practical and theoretical considerations in study design for detecting gene-gene interactions using MDR and GMDR approaches. PLoS One 6(2):e16981
Altman R, Asch E, Bloch D, Bole G, Borenstein D, Brandt K, Christy W, Cooke TD, Greenwald R, Hochberg M (1986) Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum 29(8):1039–1049
Fernández-Torres J, Martínez-Nava GA, Gutiérrez-Ruíz MA, Gómez-Quiróz LE, Gutiérrez M (2017) Role of hypoxia inducible factor-1α signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Rev Bras Reumatol Engl Ed 57(2):162–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbre.2016.07.008
Choundry S, Coyle NE, Tang H, Salari K, Lind D, Clark SL et al (2006) Population stratification confounds genetic association studies among Latinos. Hum Genet 118(5):652–664
Bonilla C, Parra EJ, Pfaff CL, Dios S, Marshall JA, Hamman RF, Ferrell RE, Hoggart CL, McKeigue PM, Shriver MD (2004) Admixture in the Hispanics of the San Luis Valley, Colorado, and its implications for complex trait gene mapping. Ann Hum Genet 68(Pt 2):139–152
Contreras-Hernández I, Mould-Quevedo JF, Torres-González R, Goycochea-Robles MV, Pacheco-Domínguez RL, Sánchez-García S et al (2008) Cost-effectiveness analysis for joint pain treatment in patients with osteoarthritis treated at the Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social (IMSS): comparison of nonsteroideal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) vs. cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors. Cost Eff Resour Alloc 6:21
Chapman K, Valdes AM (2012) Genetic factors in OA pathogenesis. Bone 51(2):258–254
Dai H, Charnigo RJ, Becker ML, Leeder JS, Motsinger-Reif AA (2013) Risk score modeling of multiple gene to gene interactions using aggregated-multifactor dimensionality reduction. BioData Min 6(1):1
Su SL, Yang HY, Lee HS, Huang GS, Lee CH, Liu WS, Wang CC, Peng YJ, Lai CH, Chen CY, Lin C, Pan YT, Salter DM, Chen HC (2015) Gene-gene interactions between TGF-β/Smad3 signaling pathway polymorphisms affect susceptibility to knee osteoarthritis. BMJ Open 5(6):e007931
Fernández-Torres J, Martínez-Nava GA, Zamudio-Cuevas Y, Martínez-Flores K, Espinosa-Morales R (2019) Epistasis between ADIPOQ rs1501299 and PON1 rs662 polymorphisms is potentially associated with the development of knee osteoarthritis. Mol Biol Rep 46(2):2049–2058
Semenza GL (2008) Regulation of oxygen homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Physiol (Bethesda) 24:97–106
Du XA, Wang HM, Dai XX, Kou Y, Wu RP, Chen Q et al (2015) Role of selenoprotein S (SEPS1) -105G>A polymorphisms and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in Kashin-Beck disease. Osteoarthr Cartil 23(2):210–216
Peng J, Ma W, Zhou Z, Gu Y, Lu Z, Zhang R, Pan Z (2018) Genetic variations in the PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway predict tumor response and disease-free survival in locally advanced rectal cancer patients receiving preoperative chemoradiotherapy and radical surgery. J Cancer 9(6):1067–1077
Urano T, Narusawa K, Shiraki M, Usui T, Sasaki N, Hosoi T et al (2008) Association of a single nucleotide polymorphism in the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor gene with spinal disc degeneration in postmenopausal Japanese women. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33(11):1256–1261
Claessen KM, Ramautar SR, Pereira AM, Smit JW, Biermasz NR, Kloppenburg M (2012) Relationship between insulin-like growth factor-1 and radiographic disease in patients with primary osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Osteoarthr Cartil 20(2):79–76
Xie Q, Xie J, Zhong J, Cun X, Lin S, Lin Y, Cai X (2016) Hypoxia enhances angiogenesis in an adipose-derived stromal cell/endothelial cell co-culture 3D gel model. Cell Prolif 49(2):236–235
Wei YK, Ma HL, Guo YZ, Yang BH, Pang WX (2015) Association of the IGF-1 rs35767 and rs972936 polymorphisms with the risk of osteoporosis in a Chinese postmenopausal female population. Genet Mol Res 14(4):14325–14330
Chen YC, Zhang L, Li EN, Ding LX, Zhang GA, Hou Y, Yuan W (2017) Association of the insulin-like growth factor-1 single nucleotide polymorphisms rs35767, rs2288377, and rs5742612 with osteoporosis risk: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 96(51):e9231
Snelgrove TA, Peddle LJ, Stone C, Nofball F, Peddle D, Squire D et al (2005) Association of COL1A2, COL2A1 and COL9A1 and primary osteoarthritis in a founder population. Clin Genet 67(4):359–360
Gálvez-Rosas A, González-Huerta C, Borgonio-Cuadra VM, Duarte-Salazár C, Lara-Alvarado L, Soria-Bastida d l A et al (2010) A COL2A1 gene polymorphisms is related with advanced stages of osteoarthritis of the knee in Mexican Mestizo population. Rheumatol Int 30(8):1035–1039
Valdes AM, Loughlin J, Oene MV, Chapman K, Surdulescu GL, Doherty M, Spector TD (2007) Sex and ethnic differences in the association of ASPN, CALM1, COL2A1, COMP, and FRZB with genetic susceptibility to osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum 56(1):137–146
Deng Y, Tan XT, Wu Q, Wang X (2017) Correlations between COL2A and aggrecan genetic polymorphisms and the risk and clinicopathological features of intervertebral disc degeneration in a Chinese Han population: a case-control study. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 21(2):108–115
Litherland GJ, Hui W, Elias MS, Wilkinson DJ, Watson S, Huesa C, Young DA, Rowan AD (2014) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibition stimulates human cartilage destruction and exacerbates murine osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(8):2175–2187
Acknowledgements
We thank the support provided by Dr. Gustavo Reyes Terán in facilitating the laboratory where we genotyped the samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants according to the Declaration of Helsinki and the study protocol was approved by ethics committee of the National Research Centre.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández-Torres, J., Martínez-Nava, G.A., Zamudio-Cuevas, Y. et al. Impact of the gene-gene interactions related to the HIF-1α signaling pathway with the knee osteoarthritis development. Clin Rheumatol 38, 2897–2907 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04635-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04635-w