Abstract
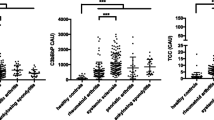
CD147 is a glycosylated membrane protein that belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. This study aimed to determine serum soluble CD147 (sCD147) levels and their clinical associations in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc). Serum sCD147 levels were examined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 61 SSc patients and 24 healthy individuals. Serum sCD147 levels were significantly elevated in SSc patients compared with healthy individuals (P < 0.001). Among patients with SSc, there were no differences in serum sCD147 levels between limited cutaneous (n = 30) and diffuse cutaneous SSc (n = 31). Patients with SSc who had elevated sCD147 levels had renal crisis more often than those with normal sCD147 levels (13% vs 0%; P < 0.05). Serum sCD147 levels were increased in patients with SSc and associated with the presence of renal crisis. These results suggest that sCD147 may have a role in the development of renal crisis in SSc. Measurement of serum sCD147 may be useful for risk stratification for renal crisis in SSc.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
White B (1996) Immunopathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Rheum Dis Clin Nor Am 32:695–708
Toole BP (2003) Emmprin (CD147), a cell surface regulator of matrix metalloproteinase production and function. Curr Top Dev Biol 54:371–389
Biswas C (1982) Tumor cell stimulation of collagenase production by fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 109:1026–1034
Kanekura T, Chen X, Kanzaki T (2002) Basigin (CD147) is expressed on melanoma cells and induces tumor cell invasion by stimulating production of matrix metalloproteinases by fibroblasts. Int J Cancer 99:520–528
Yurchenko V, Constant S, Eisenmesser E, Bukrinsky M (2010) Cyclophilin-CD147 interactions: a new target for anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Clin Exp Immunol 160:305–317
Konttinen YT, Li TF, Mandelin J et al (2000) Increased expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer in rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum 43:275–280
Zhu P, Ding J, Zhou J, Dong WJ, Fan CM, Chen ZN (2005) Expression of CD147 on monocytes/macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis: its potential role in monocyte accumulation and matrix metalloproteinase production. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R1023–R1033
Damsker JM, Okwumabua I, Pushkarsky T, Arora K, Bukrinsky MI, Constant SL (2009) Targeting the chemotactic function of CD147 reduces collagen-induced arthritis. Immunology 126:55–62
Jia J, Wang C, Shi Z et al (2009) Inhibitory effect of CD147/HAb18 monoclonal antibody on cartilage erosion and synovitis in the SCID mouse model for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48:721–726
Pistol G, Matache C, Calugaru A et al (2007) Roles of CD147 on T lymphocytes activation and MMP-9 secretion in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Cell Mol Med 11:339–348
Subcommittee for Scleroderma Criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee (1980) Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum 23:581–590
LeRoy EC, Black C, Fleischmajer R et al (1988) Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol 15:202–205
Steen VD, Powell DL, Medsger TAJ (1988) Clinical correlations and prognosis based on serum autoantibodies in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 31:196–203
Sato S, Ihn H, Kikuchi K, Takehara K (1994) Antihistone antibodies in systemic sclerosis: association with pulmonary fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum 37:391–394
Clements PJ, Lachenbruch PA, Seibold JR et al (1993) Skin thickness score in systemic sclerosis: an assessment of interobeservar variability in 3 independent studies. J Rheumatol 20:1892–1896
Scharffetter K, Lankat-Buttgereit B, Krieg T (1988) Localization of collagen mRNA in normal and scleroderma skin by in-situ hybridization. Eur J Clin Invest 18:9–17
Kato N, Yuzawa Y, Kosugi T et al (2009) The E-selectin ligand basigin/CD147 is responsible for neutrophil recruitment in renal ischemia/reperfusion. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:1565–1576
Gruschwitz MS, Hornstein OP, von den Driesch P (1995) Correlation of soluble adhesion molecules in the peripheral blood of scleroderma patients with their in situ expression and with disease activity. Arthritis Rheum 38:184–189
Steen VD (2003) Scleroderma renal crisis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 29:315–333
Shimada M, Yamabe H, Osawa H et al (2009) Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer is expressed in the proximal tubular epithelial cells of the human kidney. Nephrology (Carlton) 14:171–178
Yang LX, Liu H, Guo RW et al (2010) Angiotensin II induces EMMPRIN expression in THP-1 macrophages via the NF-kappaB pathway. Regul Pept 163:88–95
Penn H, Howie AJ, Kingdon EJ et al (2007) Scleroderma renal crisis: patient characteristics and long-term outcomes. QJM 100:485–494
Bunn CC, Denton CP, Shi-Wen X, Knight C, Black CM (1998) Anti-RNA polymerases and other autoantibody specificities in systemic sclerosis. Br J Rheumatol 37:15–20
Hamaguchi Y, Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M et al (2008) The clinical relevance of serum antinuclear antibodies in Japanese patients with systemic sclerosis. Br J Dermatol 158:487–495
Steen VD, Costantino JP, Shapiro AP, Medsger TA Jr (1990) Outcome of renal crisis in systemic sclerosis: relation to availability of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. Ann Intern Med 113:352–357
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by a grant for Research on Intractable Diseases from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan.
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanaba, K., Asano, Y., Tada, Y. et al. Increased serum soluble CD147 levels in patients with systemic sclerosis: association with scleroderma renal crisis. Clin Rheumatol 31, 835–839 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-1949-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-1949-9