Abstract
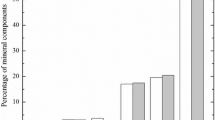
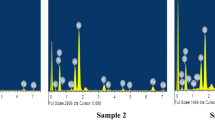
Rocks extracted from deep mining operations often undergo various complex temperature and dynamic load disturbances. In order to investigate the influence of temperature on the mechanical characteristics and fracture mechanisms of sandstone under different loading conditions, thermal treatments were conducted on sandstone samples at temperatures of 25 °C, 200 °C, 400 °C, 600 °C, 800 °C, and 1000 °C. Subsequently, the quasi-static and dynamic mechanical properties of the treated samples were tested and recorded using an electronic universal testing machine and a Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar (SHPB). Simultaneously, detailed analyses and discussions of thermal damage and failure mechanisms of the specimens were carried out using Energy-Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS), X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), and Raman spectroscopy. The results indicate that with increasing temperature, the mass, density, and peak stress of the sandstone specimens decrease, while the porosity and peak strain increase. Transgranular (TG) fracture was identified as the primary failure mode during loading, accompanied by a small amount of intergranular (IG) fracture. Furthermore, high temperatures cause changes in the chemical properties of the sandstone, resulting in thermal decomposition of crystal grains and evaporation of mineral components, which are key factors that weaken the mechanical properties of sandstone. The significance of this study is to provide theoretical and technical support for site selection and safety assessment of underground engineering projects.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai D, Zhao Y, Wang Q, Li C (2019) Experimental and numerical investigation of crack propagation and dynamic properties of rock in SHPB indirect tension test. Int J Impact Eng 126:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.01.001
Behrmann JH, Mainprice D (1987) Deformation mechanisms in a high-temperature quartz-feldspar mylonite: evidence for superplastic flow in the lower continental crust. Tectonophysics 140:297–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(87)90236-8
Chaki S, Takarli M, Agbodjan WP (2008) Influence of thermal damage on physical properties of a granite rock: porosity, permeability and ultrasonic wave evolutions. Constr Build Mater 22:1456–1461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2007.04.002
Chen Y, Yin T, Li X et al (2021) Experimental investigation on dynamic mechanical behavior and fracture evolution of fissure-filled red sandstone after thermal treatment. Eng Geol 295:106433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106433
Cizina MF, Mikesell TD, Kohn MJ (2023) Optimizing Raman spectral collection for quartz and zircon crystals for elastic thermobarometry. Am Mineralogist: J Earth Planet Mater 108:915–927. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2022-8423
Dai F, Huang S, Xia K, Tan Z (2010) Some Fundamental issues in Dynamic Compression and Tension tests of Rocks using Split Hopkinson pressure bar. Rock Mech Rock Eng 43:657–666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-010-0091-8
Dean KJ, Sherman WF, Wilkinson GR (1982) Temperature and pressure dependence of the Raman active modes of vibration of α-quartz. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Mol Spectrosc 38:1105–1108. https://doi.org/10.1016/0584-8539(82)80044-5
Doncieux A, Stagnol D, Huger M et al (2008) Thermo-elastic behaviour of a natural quartzite: itacolumite. J Mater Sci 43:4167–4174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2414-z
Dumańska-Słowik M, Powolny T, Nguyen Khac G (2023) Mineralogy and Geochemistry of Nepheline Syenite from the Bang Phuc Massif of the Alkaline Cho Don Complex in North-Eastern Vietnam—implications for Magma Evolution and fluid–rock interactions. J Petrol 64:egad042. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egad042
Fairhurst CE, Hudson JA (1999) Draft ISRM suggested method for the complete stress-strain curve for intact rock in uniaxial compression. Int j rock mech min sci (1997) 36:279–289
Fan L, Li H, Xi Y (2022) Evaluation of the effects of three different cooling methods on the dynamic mechanical properties of thermal-treated sandstone. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81:154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02630-1
Gautam PK, Dwivedi R, Kumar A et al (2021) Damage characteristics of Jalore Granitic Rocks after Thermal Cycling Effect for Nuclear Waste Repository. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54:235–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02260-7
Gbewade CAF, Grgic D, Giraud A, Schoumacker L (2023) Experimental study of the Effect of temperature on the Mechanical properties of the Callovo-Oxfordian Claystone. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03630-7. Rock Mech Rock Eng
Glover PWJ, Baud P, Darot M et al (1995) α/β phase transition in quartz monitored using acoustic emissions. Geophys J Int 120:775–782. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.1995.tb01852.x
Heuze FE (1983) High-temperature Mechanical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Granitic Rocks. A Review
Homand-Etienne F, Houpert R (1989) Thermally induced microcracking in granites: characterization and analysis. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstracts 26:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(89)90001-6
Hopkinson B (1914) X. A method of measuring the pressure produced in the detonation of high, explosives or by the impact of bullets. Phil Trans R Soc Lond A 213:437–456. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.1914.0010
Jiang Y, Zhu Z, Yu L et al (2022) Investigation of the fracture characteristics of granite and green sandstone under different thermal treatments. Theoret Appl Fract Mech 118:103217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2021.103217
Kranz RL (1983) Microcracks in rocks: a review. Tectonophysics 100:449–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(83)90198-1
Kumar A (1968) The effect of stress rate and temperature on the strength of basalt and granite. Geophysics 33:501–510. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1439947
Kumari WGP, Ranjith PG, Perera MSA et al (2017) Temperature-dependent mechanical behaviour of Australian strathbogie granite with different cooling treatments. Eng Geol 229:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.09.012
Li X, Zhou Z, Lok T-S et al (2008) Innovative testing technique of rock subjected to coupled static and dynamic loads. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 45:739–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2007.08.013
Li M, Wang D, Shao Z (2020a) Experimental study on changes of pore structure and mechanical properties of sandstone after high-temperature treatment using nuclear magnetic resonance. Eng Geol 275:105739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105739
Li Y, Zhai Y, Wang C et al (2020b) Mechanical properties of Beishan granite under complex dynamic loads after thermal treatment. Eng Geol 267:105481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105481
Mahanta B, Vishal V, Sirdesai N et al (2021) Progressive deformation and pore network attributes of sandstone at in-situ stress states using computed tomography. Eng Fract Mech 252:107833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2021.107833
Mardoukhi A, Mardoukhi Y, Hokka M, Kuokkala V-T (2021) Effects of Test temperature and low temperature Thermal Cycling on the dynamic Tensile Strength of Granitic Rocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54:443–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02253-6
Massaro L, Adam J, Yamada Y (2023) Mechanical characterisation of new sand-hemihydrate rock-analogue material: implications for modelling of brittle crust processes. Tectonophysics 855:229828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2023.229828
Mernagh TP (1991) Use of the laser Raman microprobe for discrimination amongst feldspar minerals. J Raman Spectrosc 22:453–457. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.1250220806
Miskovsky K, Seiki T (2011) Effect of heat on the mechanical properties of selected rock types – a laboratory study. In: Zhou Y (ed) Harmonising Rock Engineering and the Environment. CRC, pp 815–820
Narayanaswamy PK (1948) The α-β transformation in quartz. Proc Indian Acad Sci (Math Sci) 28:417. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03170805
Raman CV, Nedungadi TMK (1940) The α-β Transformation of Quartz. Nature 145:147–147. https://doi.org/10.1038/145147a0
Shan R, Jiang Y, Li B (2000) Obtaining dynamic complete stress–strain curves for rock using the Split Hopkinson pressure bar technique. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 37:983–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(00)00031-9
Shapiro SM, O’Shea DC, Cummins HZ (1967) Raman Scattering Study of the Alpha-Beta Phase Transition in Quartz. Phys Rev Lett 19:361–364. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.19.361
Sharma SK, Simons B, Yoder HS (1983) Raman study of anorthite, calcium Tschermak’s pyroxene, and gehlenite in crystalline and glassy states. Am Mineral 68:1113–1125
Sirdesai NN, Singh TN, Pathegama Gamage R (2017) Thermal alterations in the poro-mechanical characteristic of an Indian sandstone – a comparative study. Eng Geol 226:208–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.06.010
Somerton WH (1992) Thermal properties and temperature-related behavior of Rock/Fluid systems. Elsevier
Srinivasan V, Gupta T, Ansari TA, Singh TN (2020a) An experimental study on rock damage and its influence in rock stress memory in a metamorphic rock. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:4335–4348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01813-y
Srinivasan V, Tripathy A, Gupta T, Singh TN (2020b) An investigation on the influence of thermal damage on the physical, mechanical and acoustic behavior of Indian Gondwana Shale. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:2865–2885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02087-2
Sun Q, Zhang W, Su T, Zhu S (2016) Variation of Wave Velocity and Porosity of Sandstone after High Temperature Heating. Acta Geophys 64:633–648. https://doi.org/10.1515/acgeo-2016-0021
Thompson AW, Knott JF (1993) Micromechanisms of brittle fracture. Metall Trans A 24:523–534. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02656622
Tian H, Kempka T, Yu S, Ziegler M (2016) Mechanical properties of sandstones exposed to high temperature. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49:321–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0724-z
Tomás R, Cano M, Pulgarín LF et al (2021) Thermal effect of high temperatures on the physical and mechanical properties of a granite used in UNESCO World Heritage sites in north Portugal. J Building Eng 43:102823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102823
Wang P, Yin T, Li X et al (2019) Dynamic properties of thermally treated Granite subjected to cyclic impact loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:991–1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1606-y
Wang F, Liu S, Cao L (2020) Research on dynamic compressive behaviors of marble under high strain rates with split Hopkinson pressure bar. J Struct Geol 138:104095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2020.104095
Winter JK, Okamura FP, Ghose S (1967) A high-temperatursetructuralstudyof highalbite,monalbite. andtheanalbite-+ monalbitephasetransition
Xi Y, Wang H, Zha C et al (2022) Experimental study of the influence of temperature and cooling method on dynamic mechanical properties and damage of granite. Energy Sci Eng 10:3779–3797. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.1249
Xia K, Yao W (2015) Dynamic rock tests using split Hopkinson (Kolsky) bar system – A review. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 7:27–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2014.07.008
Yang S-Q, Ranjith PG, Jing H-W et al (2017) An experimental investigation on thermal damage and failure mechanical behavior of granite after exposure to different high temperature treatments. Geothermics 65:180–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.09.008
Yin T, Li X, Xia K, Huang S (2012) Effect of Thermal Treatment on the dynamic fracture toughness of Laurentian Granite. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45:1087–1094. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0240-3
Yin T, Li X, Cao W, Xia K (2015) Effects of Thermal Treatment on Tensile Strength of Laurentian Granite using Brazilian test. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48:2213–2223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0712-3
Zhang QB, Zhao J (2014) Quasi-static and dynamic fracture behaviour of rock materials: phenomena and mechanisms. Int J Fract 189:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-014-9959-z
Zhang W, Sun Q, Hao S et al (2016) Experimental study on the variation of physical and mechanical properties of rock after high temperature treatment. Appl Therm Eng 98:1297–1304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.01.010
Zhang W, Sun Q, Zhang Y (2019) Effects of pre-existing cracks and temperature on failure mode of granite from Eastern China. J Struct Geol 126:330–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2019.06.018
Zhao Z (2016) Thermal influence on Mechanical properties of Granite: a Microcracking Perspective. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49:747–762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0767-1
Zhou L, Gao W, Yu L et al (2022) Thermal effects on fracture toughness of cracked straight-through Brazilian disk green sandstone and granite. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 14:1447–1460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.02.016
Zwiessler R, Kenkmann T, Poelchau MH et al (2017) On the use of a split Hopkinson pressure bar in structural geology: high strain rate deformation of Seeberger sandstone and Carrara marble under uniaxial compression. J Struct Geol 97:225–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2017.03.007
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51975221, 51705162), Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2022J01319), Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project for High-level talents of Quanzhou City (No. 2023C010R).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Wang, F., Hu, L. et al. Experimental investigation on the mechanical behavior and fracture mechanism of sandstone after heat treatment. Bull Eng Geol Environ 83, 220 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03717-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03717-7