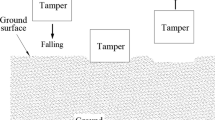
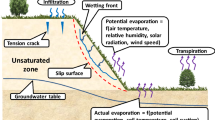
Abstract
Under the influence of rainfall, the failure mechanism and stability of layered slopes is one of the current hot topics. This paper aims to examine the influence of rainstorm conditions on the stability of layered soil slopes and analyze the inter infiltration rule and water-holding response characteristics through physical model tests and numerical simulation. The results demonstrate that the layered structure and inclination can affect the rainwater infiltration and stability of layered soil slopes under rainstorm conditions. Different inclinations greatly influence the safety factors of the layered soil slopes and the downdip slopes are more susceptible to landslides due to heavy rainfall. Meanwhile, the pore water pressure of the sand layer dissipates 90.95% and 70.45% under the horizontal layer and downdip layer, respectively. In addition, settlement occurs on the surface of the slope at the initial stage of rainfall. As rainwater continuously infiltrates, the slope’s surface expands unevenly. The expansion amplitudes of the shoulder and toe of the slope have a more extensive expansion range, which is crucial in landslide prevention and control. The results of the model test are consistent with the numerical simulation analysis. The results provide a theoretical basis for designing a stratified soil slope management plan.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Abancó C, Bennett GL, Matthews AJ, Matera MAM, Tan FJ (2021) The role of geomorphology, rainfall and soil moisture in the occurrence of landslides triggered by 2018 Typhoon Mangkhut in the Philippines. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 21(5):1531–1550. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-21-1531-2021
Ali A, Huang J, Lyamin AV, Sloan SW, Cassidy MJ (2014) Boundary effects of rainfall-induced landslides. Comput Geotech 61:341–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.05.019
Almedeij J, Esen II (2014) Modified Green-Ampt infiltration model for steady rainfall. J Hydrol Eng 19(9):4014011. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001111
Anagnostopoulos GG, Fatichi S, Burlando P (2015) An advanced process-based distributed model for the investigation of rainfall-induced landslides: The effect of process representation and boundary conditions. Water Resour Res 51(9):7501–7523. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015WR016909
Augusto Filho O, Fernandes MA (2019) Landslide analysis of unsaturated soil slopes based on rainfall and matric suction data. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78(6):4167–4185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1392-5
Cao L, Zhang YG, Lu HZ, Yuan JQ, Zhu YY, Liang Y (2015) Grass hedge effects on controlling soil loss from concentrated flow: a case study in the red soil region of China. Soil Tillage Res 148:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2014.12.009
Chaharsooghi SK, Honarvar M, Modarres M (2011) A multi-stage stochastic programming model for dynamic pricing and lead time decisions in multi-class make-to-order firm. Sci Iran 18(3):711–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scient.2011.05.018
Chelli A, Francese R, Petrella E, Carri A, Quagliarini A, Segalini A, Caporicci MP, Diena M, Giorgi M, Celico F (2020) A multi-parameter field monitoring system to investigate the dynamics of large earth slides–earth flows in the Northern Apennines, Italy. Eng. Geol. 275:105780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105780
Chen X (2020) Modelling rainfall-induced landslides from initiation of instability to post-failure. Comput Geotech 129(3):103877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103877
Cheng Q, Tang CS, Zeng H, Zhu C, An N, Shi B (2020) Effects of microstructure on desiccation cracking of a compacted soil. Eng Geol 265:105418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105418
Chua LHC, Wong TSW, Sriramula LK (2008) Comparison between kinematic wave and artificial neural network models in event-based runoff simulation for an overland plane. J Hydrol 357(3–4):337–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.05.015
Crawford MM, Bryson LS, Woolery EW, Wang Z (2019) Long-term landslide monitoring using soil-water relationships and electrical data to estimate suction stress. Eng Geol 251:146–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.02.015
Crosta GB, Frattini P (2010) Rainfall-induced landslides and debris flows. Hydrol Process 22(4):473–477. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6885
Dai FC, Lee CF (2002) Landslide characteristics and slope instability modeling using GIS, Lantau Island. Hong Kong Geomorphology 42(3–4):213–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-555X(01)00087-3
Damiano E, Greco R, Guida A, Olivares L, Picarelli L (2017) Investigation on rainwater infiltration into layered shallow covers in pyroclastic soils and its effect on slope stability. Eng Geol 220:208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.02.006
Egbueri JC, Igwe O, Unigwe CO (2021) Gully slope distribution characteristics and stability analysis for soil erosion risk ranking in parts of southeastern Nigeria: a case study. Environ Earth Sci 80(7):208–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09605-7
Fredlund DG, Rahardjo H (1993) Soil mechanics for unsaturated soils. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Fredlund DG, Xing A (1994) Equations for the soil-water characteristic curve. NRC Res Press Ottawa, Canada 31(4):512–532. https://doi.org/10.1139/t94-120
Fredlund DG, Morgenstern NR, Widger RA (1978) The shear strength of unsaturated soils. Can Geotech J 15(3):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1139/t78-029
Guo L, Chen G, Gong S, Sun H, Chantat K (2021) Analysis of rainfall-induced landslide using the extended DDA by incorporating matric suction. Comput Geotech 135:104145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2021.104145
Hong HY, Tsangaratos P, Ilia I, Liu JZ, Zhu AX, Xu C (2018) Applying genetic algorithms to set the optimal combination of forest fire related variables and model forest fire susceptibility based on data mining models. The case of Dayu County. China Sci Total Environ 630:1044–1056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.278
Horn R, Fleige H (2003) A method for assessing the impact of load on mechanical stability and on physical properties of soils. Soil Tillage Res 73(1–2):89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(03)00102-8
Hou TS, Xu GL, Shen YJ, Wu ZZ, Zhang NN, Wang R (2013) Formation mechanism and stability analysis of the Houba expansive soil landslide. Eng Geol 161:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.04.010
Hu C, Zhang Y, Jiang Z, Wang M, Han C (2021) Development of large-scale sand bodies fault-bounded lake basin: Pleistocene-Holocene Poyang Lake, Southern China. J Paleolimnol 65(4):407–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-021-00179-9
Ishii Y, Ota K, Kuraoka S, Tsunaki R (2012) Evaluation of slope stability by finite element method using observed displacement of landslide. Landslides 9(3):335–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-011-0303-7
Jaworski D, Linkov A, Rybarska-Rusinek L (2016) On solving 3D elasticity problems for inhomogeneous region with cracks, pores and inclusions. Comput Geotech 71:295–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2015.04.017
Jiang SY, Zhang Q, Werner AD, Wellen C, Hu P, Sun JH, Deng YQ, Rode M (2020) Modelling the impact of runoff generation on agricultural and urban phosphorus loading of the subtropical Poyang Lake (China). J Hydrol 590:125490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125490
Kampf SK, Brogan DJ, Schmeer S, MacDonald LH, Nelson PA (2016) How do geomorphic effects of rainfall vary with storm type and spatial scale in a post-fire landscape? Geomorphology 273:39–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.08.001
Kumar N, Verma AK, Sardana S, Sarkar K, Singh TN (2018) Correction to: Comparative analysis of limit equilibrium and numerical methods for prediction of a landslide. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77(2):609–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1247-0
Li GR, Li XL, Chen WT, Li JF, Zhu HL, Hu XS, Zhou HK, Sun HQ (2020) Effects of degradation severity on the physical, chemical and mechanical properties of topsoil in alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, west China. Catena 187:104370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104370
Liu X, Wang Y (2021) Probabilistic simulation of entire process of rainfall-induced landslides using random finite element and material point methods with hydro-mechanical coupling. Comput Geotech 132:103989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103989
Lizárraga JJ, Buscarnera G (2018) Spatially distributed modeling of rainfall-induced landslides in shallow layered slopes. Landslides 16(4):253–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1088-8
Nuth M, Laloui L (2008) Advances in modelling hysteretic water retention curve in deformable soils. Comput Geotech 35(6):835–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2008.08.001
Premathilake R (2006) Relationship of environmental changes in central Sri Lanka to possible prehistoric land-use and climate changes. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 240(3–4):468–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.03.001
Shankman D, Keim BD, Song J (2006) Flood frequency in China’s Poyang Lake region: Trends and teleconnections. Int J Climatol 26(9):1255–1266. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1307
Sun G, Lin S, Cheng S, Sui T, Li C, Zheng H (2017) Mechanisms of interaction between an arch dam and abutment slope using physical model tests. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(8):2483–2504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04353-6
Sun D, Wen H, Zhang Y, Zhang YL, Xue MM (2020) An optimal sample selection-based logistic regression model of slope physical resistance against rainfall-induced landslide. Nat Hazards 105:1255–1279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04353-6
Sun S, Wang WC, Wei JH, Song JL, Yu YX, He W, Zhang JX (2021) The physical–mechanical properties degradation mechanism and microstructure response of acid–alkali-contaminated Xiashu loess. Nat Hazards 106(3):2845–2861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04570-7
Tanyaş H, Kirschbaum D, Lombardo L (2021) Capturing the toeprints of ground motion in the spatial distribution of rainfall-induced landslides. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80(6):4323–4345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02238-x
Vanapalli SK, Fredlund DG, Pufahl DE, Clifton AW (1996) Model for the prediction of shear strength with respect to soil suction. Can Geotech J 33:379–392. https://doi.org/10.1139/t96-060
Wang B, Cui B, Li H, Du P, Jia B (2011a) Wood-Rotting fungi in eastern China. 5. Polypore diversity in jiangxi province. Ann Bot Fenn 48(3):237–246. https://doi.org/10.5735/085.048.0304
Wang Y, Zhang B, Lin L, Zepp H (2011b) Agroforestry system reduces subsurface lateral flow and nitrate loss in Jiangxi Province, China. Agr Ecosyst Environ 140(3–4):441–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.01.007
Zhang J, Zhu D, Zhang SH (2020) Shallow slope stability evolution during rainwater infiltration considering soil cracking state. Comput Geotech 117:103285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.103285
Zhang YF, Long AF, Zhao Y, Zang AN, Wang CL (2023) Mutual impact of true triaxial stress, borehole orientation and bedding inclination on laboratory hydraulic fracturing of Lushan shale. J Rock Mech Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.02.015
Zhao Y, Zhang YF, Tian G, Wang CL, Bi J (2020) A new model for predicting hydraulic fracture penetration or termination at an orthogonal interface between dissimilar formations. Petrol Sci 19:2810–2829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petsci.2022.08.002
Zhao Y, Zhang YF, Yang HQ, Liu Q, Tian GD (2022) Experimental study on relationship between fracture propagation and pumping parameters under constant pressure injection conditions. Fuel 307:121789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121789
Zhuang J, Peng J, Zhu Y, Leng Y, Huang W (2020) The internal erosion process and effects of undisturbed loess due to water infiltration. Landslides 18(1):629–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01518-z
Zou Z, Lei D, Jiang GL, Luo B, Chang SZ, Hou CP (2020) Experimental study of bridge foundation reinforced with front and back rows of Anti-Slide piles on gravel soil slope under EI centro waves. Appl Sci 10(9):3108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093108
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42167024, No. 52064006, No. 52004072, and No. 52164001) and the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Foundation (No. [2020]4Y044) and No. [2021]292).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Xue, K., Zhao, Y. et al. Study on the stability and disaster mechanism of layered soil slopes under heavy rain. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 272 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03277-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03277-2