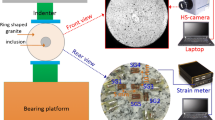
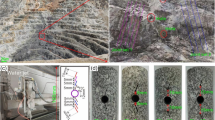
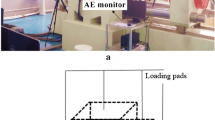
Abstract
In this study, uniaxial compression experiments were conducted of granite specimens containing two preexisting fissures to investigate the effect of bolts on mechanical behaviour, crack arrest, and energy absorption. Different mechanical properties of the granite specimens with and without bolts were analysed according to the axial stress–strain curves. Then the behaviour of the crack evolution during the loading process, as well as the images of granite specimens when they were destroyed, was observed and analysed using the digital image correlation (DIC) method. In addition, various forms of energy at the peak load, including the total strain energy, elastic energy, and dissipative energy, were compared with one another. The experimental results show that (1) bolts have a positive effect on strength enhancement and deformation control, and the effect is related to the joint inclination angle; (2) there are two crack arrest effects: controlling the rate and direction of the propagation of tensile wing crack (type I) and preventing the coalescence of shear crack (type II) from developing through upper and lower preexisting fissures; and (3) the bolt increases the energy absorption but does not change the tendency of the total strain energy with joint inclination angles. These results contribute to the understanding of bolt support in deep-rock engineering.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benmokrane B, Robert M, Mohamed HM (2017) Durability assessment of glass FRP solid and hollow bars (rock bolts) for application in ground control of Jurong Rock Caverns in Singapore. J Compos Constr 21(3):06016002.1–06016002.4. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CC.1943-5614.0000775
Chen L, Li Q, Yang J (2018) Laboratory testing on energy absorption of high-damping rubber in a new bolt for preventing rockburst in deep hard rock mass. Shock Vib 72:14821.1–14821.12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7214821
Chen Y, Li CC (2015) Performance of fully encapsulated rebar bolts and D-bolts under combined pull-and-shear loading. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 45:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2014.09.008
Chen Y, Wen G, Hu J (2020) Analysis of deformation characteristics of fully grouted rock bolts under pull-and-shear loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02108-0
Grasselli G (2005) 3D Behaviour of bolted rock joints: experimental and numerical study. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 42(1):13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.06.003
Gong F, Yan J, Li X (2019) A peak-strength strain energy storage index for rock burst proneness of rock materials. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 117:76–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.03.020
Hadjigeorgiou SY, Thorpe SJ (2020) Impact of steel properties on the corrosion of expandable rock bolts. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(2):705–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01939-w
Hu J, Wen G, Lin Q (2020) Mechanical properties and crack evolution of double-layer composite rock-like specimens with two parallel fissures under uniaxial compression. Theor Appl Fract Mech 108:102610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2020.102610
Jalalifar H, Aziz N (2010) Analytical behaviour of bolt–joint intersection under lateral loading conditions. Rock Mech Rock Eng 43(1):89–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-009-0032-6
Li CC, Stillborg B (1999) Analytical models for rock bolts. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 36(8):1013–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(99)00064-7
Li CC (2012) Performance of D-bolts under static loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45(2):183–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-011-0198-6
Li Y, Zhou H, Zhang L (2016) Experimental and numerical investigations on mechanical property and reinforcement effect of bolted jointed rock mass. Constr Build Mater 126:843–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.09.100
Lin Q, Cao P, Wen G (2021) Crack coalescence in rock-like specimens with two dissimilar layers and pre-existing double parallel joints under uniaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 139:104621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104621
Ma S, Zhao Z, Nie W (2017) An analytical model for fully grouted rockbolts with consideration of the pre- and post-yielding behavior. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(11):3019–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1272-5
Ma S, Zhao Z, Shang J (2019) An analytical model for shear behaviour of bolted rock joints. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci. 121: 104019 https ://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.04.005
Mohammadi M, Hossaini MF, Bagloo H (2017) Rock bolt supporting factor: rock bolting capability of rock mass. B Eng Geol Environ 76(1):231–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-015-0785-y
Nordlund E (2013) Deep hard rock mining and rock mechanics challenges. Seventh International Symposium on Ground Support in Mining and Underground Construction 39–56. https://doi.org/10.36487/ACG_rep/1304_02_Nordlund
Pellet F, Egger P (1993) Analytical model for the mechanical behaviour of bolted rock joints subjected to shearing. Rock Mech Rock Eng 29(2):73–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01079755
Saadat M, Taheri A (2020) A numerical study to investigate the influence of surface roughness and boundary condition on the shear behaviour of rock joints. B Eng Geol Environ 79(5):2483–2498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01710-z
Sainsbury BA, Kurucuk N, Bolton J (2020) The mechanical performance of solid reinforcing bar rockbolts. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(10):4599–4608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02187-z
Wagner H (2019) Deep mining: a rock engineering challenge. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(4):1417–1446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01799-4
Wang C, He B, Hou X, Li J, Liu L (2020a) Stress-energy mechanism for rock failure evolution based on damage mechanics in hard rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(3):1021–1037. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01953-y
Wang M, Wan W, Zhao Y (2020b) Experimental study on crack propagation and the coalescence of rock-like materials with two pre-existing fissures under biaxial compression. B Eng Geol Environ 79(6):3121–3144
Wang W, Song Q, Xu C (2018) Mechanical behaviour of fully grouted GFRP rock bolts under the joint action of pre-tension load and blast dynamic load. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 73:82–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2017.12.007
Windsor CR (1996) Rock reinforcement systems. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 34(6):919–951. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(97)80004-4
Wong L, Einstein HH (2009a) Crack coalescence in molded gypsum and carrara marble: Part 1 Macroscopic Observations and Interpretation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 42(3):475–511
Wong L, Einstein HH (2009b) Crack coalescence in molded gypsum and carrara marble: Part 2: microscopic observations and interpretation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 42(3):513–545
Wu X, Jiang Y, Li B (2018) Influence of joint roughness on the shear behaviour of fully encapsulated rock bolt. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:953–959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1365-1
Xue Y, Ma X, Qiu D (2021) Analysis of the factors influencing the nonuniform deformation and a deformation prediction model of soft rock tunnels by data mining. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 109:103769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2020.103769
Yang K, Bai Y, Ding C (2021a) Comparative study on mechanical performance of bolted joints with steel and fibre reinforced polymer bolts. J Build Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102457
Yang S, Chen M, Tao Y (2021b) Experimental study on anchorage mechanical behavior and surface cracking characteristics of a non-persistent jointed rock mass. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54(7):1–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02325-7
Yang S, Dai Y, Han L (2009) Experimental study on mechanical behavior of brittle marble samples containing different flaws under uniaxial compression. Eng Fract Mech 76(12):1833–1845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2009.04.005
Yu W, Pan B, Zhang F (2019) Deformation characteristics and determination of optimum supporting time of alteration rock mass in deep mine. KSCE J Civ Eng 23(11):4921–4932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-019-0365-y
Zhang K, Li N, Liu W (2020a) Experimental study of the mechanical, energy conversion and frictional heating characteristics of locking sections. Eng Fract Mech 228:106905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.106905
Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Wang C (2020b) Shear behavior of bolted non-persistent joints: role of bolting conditions and joint persistency[J]. Geotech Lett 10(4):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgele.20.00030
Zhang X, Lin H, Wang Y (2021) Damage evolution characteristics of saw-tooth joint under shear creep condition. Int J Damage Mech 30:453–480. https://doi.org/10.1177/1056789520974420
Zhao C, Zhou YM, Zhao CF (2018) Cracking processes and coalescence modes in rock-like specimens with two parallel pre-existing cracks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:3377–3393 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1525-y
Zhao K, Yu X, Zhou Y (2020) Energy evolution of brittle granite under different loading rates. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 132(7):104392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104392
Zhao Y, Feng X, Jiang Q (2021) Large deformation control of deep roadways in fractured hard rock based on cracking-restraint method. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54:2559–2580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02384-4
Funding
This paper received funding from projects (41672298, 52274182) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2019-JSKSSYS-01) supported by the State Key Laboratory of Safety and Health for Metal Mines; Project (CSUZC202035) supported by the Open Sharing Fund for the Large-scale Instruments and Equipment of Central South University; Project (CX20220125) supported by Hunan Provincial Postgraduate Scientific Research Innovation Project; and Project (2022zzts033) supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guanping, W., Jianhua, H., Jie, W. et al. Characteristics of stress, crack evolution, and energy conversion of anchored granite containing two preexisting fissures under uniaxial compression. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 5 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-03002-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-03002-5