Abstract
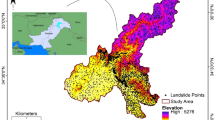
Regional landslide susceptibility map (LSM) is often taken as a significant reference in emergency response and disaster mitigation. In recent years, convolutional neural network (CNN) has been proven to be effective in extracting complex and high-dimension feature information, alleviating the demand for substantial expertise. In this study, convolutional neural network (CNN-3D) with a spatial-channel attention block embedded was applied to generate the LSM for two earthquake-affected regions (Jiuzhaigou, China, and Iburi, Japan). To explore the capability of the proposed model, standard CNN-2D and random forest (RF) were introduced as benchmarks. Besides, receiver operating characteristic (ROC), F1-score, and Kappa index (Kappa) were chosen to quantitatively compare the performance. The results indicated that the CNN-based model possessed more excellent ability than machine learning-based (ML) model in predicting landslides and the proposed model generated the most accurate and smoother LSM. In particular, CNN-3D obtained the highest F1-score and Kappa (0.93 and 0.85 in Jiuzhaigou, 0.96 and 0.92 in Iburi), demonstrating that the proposed model can effectively exploit 3D information of landslides and address non-linear relationship in high dimension. This study confirmed that CNN-3D can serve as an alternative approach to generate LSM rapidly after an earthquake.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achour Y, Boumezbeur A, Hadji R, Chouabbi A, Cavaleiro V, Bendaoud EA (2017) Landslide susceptibility mapping using analytic hierarchy process and information value methods along a highway road section in Constantine, Algeria. Arab J Geosci 10(8). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2980-6
Achour Y, Pourghasemi HR (2020) How do machine learning techniques help in increasing accuracy of landslide susceptibility maps? Geosci Front 11(3):871–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2019.10.001
Achour Y, Saidani Z, Touati R, Pham QB, Pal SC, Mustafa F, Balik Sanli F (2021) Assessing landslide susceptibility using a machine learning-based approach to achieving land degradation neutrality. Environ Earth Sci 80(17). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09889-9
Ai X, Sun B, Chen X (2022) Construction of small sample seismic landslide susceptibility evaluation model based on transfer learning: a case study of Jiuzhaigou earthquake. Bull Eng Geology Environ 81(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02601-6
Alzubaidi L, Zhang J, Humaidi AJ, Al-Dujaili A, Duan Y, Al-Shamma O, Santamaria J, Fadhel MA, Al-Amidie M, Farhan L (2021) Review of deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J Big Data 8(1):53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-021-00444-8
Ayalew L, Kasahara M, Yamagishi H (2011) The spatial correlation between earthquakes and landslides in Hokkaido (Japan), a GIS-based analysis of the past and the future. Landslides 8(4):433–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-011-0262-z
Bai S-B, Wang J, Lü G-N, Zhou P-G, Hou S-S, Xu S-N (2010) GIS-based logistic regression for landslide susceptibility mapping of the Zhongxian segment in the Three Gorges area. China Geomorphology 115(1–2):23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.09.025
Bengio Y, LeCun Y (2007) Scaling learning algorithms toward AI. Large-Scale Kernel Machines 34(5):1–41
Bergstra J, Bengio Y (2012) Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J Mach Learn Res 13(2):281–305
Breiman L, Friedman JH, Olshen RA, Stone CJ (1987) Book review: classification and regression trees. Cytometry 8:534–535
Breiman L (2001) Random Forests Machine Learning 45(1):5–32
Bui DT, Tsangaratos P, Nguyen V-T, Liem NV, Trinh PT (2020) Comparing the prediction performance of a deep learning neural network model with conventional machine learning models in landslide susceptibility assessment. CATENA 188:104426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104426
Chen W, Chai H, Zhao Z, Wang Q, Hong H (2016) Landslide susceptibility mapping based on GIS and support vector machine models for the Qianyang County, China. Environmental Earth Sciences 75(6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5093-0
Chen W, Xie X, Wang J, Pradhan B, Hong H, Bui DT, Duan Z, Ma J (2017) A comparative study of logistic model tree, random forest, and classification and regression tree models for spatial prediction of landslide susceptibility. CATENA 151:147–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.032
Constantin M, Bednarik M, Jurchescu MC, Vlaicu M (2010) Landslide susceptibility assessment using the bivariate statistical analysis and the index of entropy in the Sibiciu Basin (Romania). Environ Earth Sci 63(2):397–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0724-y
Dao DV, Jaafari A, Bayat M, Mafi-Gholami D, Qi C, Moayedi H, Phong TV, Ly H-B, Le T-T, Trinh PT, Luu C, Quoc NK, Thanh BN, Pham BT (2020) A spatially explicit deep learning neural network model for the prediction of landslide susceptibility. CATENA 188:104451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104451
Dou J, Yunus AP, Merghadi A, Shirzadi A, Nguyen H, Hussain Y, Avtar R, Chen Y, Pham BT, Yamagishi H (2020) Different sampling strategies for predicting landslide susceptibilities are deemed less consequential with deep learning. Sci Total Environ 720:137320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137320
Fan X, Scaringi G, Xu Q, Zhan W, Dai L, Li Y, Pei X, Yang Q, Huang R (2018) Coseismic landslides triggered by the 8th August 2017 Ms 7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake (Sichuan, China): factors controlling their spatial distribution and implications for the seismogenic blind fault identification. Landslides 15(5):967–983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-0960-x
Guzzetti F, Reichenbach P, Ardizzone F, Cardinali M, Galli M (2006) Estimating the quality of landslide susceptibility models. Geomorphology 81(1–2):166–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.04.007
Huang F, Zhang J, Zhou C, Wang Y, Huang J, Zhu L (2019) A deep learning algorithm using a fully connected sparse autoencoder neural network for landslide susceptibility prediction. Landslides 17(1):217–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01274-9
Hu T, Fan X, Wang S, Guo Z, Liu A, Huang F (2020) Landslide susceptibility evaluation of Sinan County using logistics regression model and 3S technology. Bull Geologic Sci Technol 39(2):113–121. https://doi.org/10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0212
Ioffe S, Szegedy C (2015) Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France.
Kamp U, Growley BJ, Khattak GA, Owen LA (2008) GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping for the 2005 Kashmir earthquake region. Geomorphology 101(4):631–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.03.003
Kayalibay B, Jensen G, van der Smagt P (2017) CNN-based segmentation of medical imaging data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.03056v2
Keffer DK (1984) Landslides caused by earthquakes. GSA Bull 95(4):406–421
Lee S, Sambath T (2006) Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Damrei Romel area, Cambodia using frequency ratio and logistic regression models. Environ Geol 50(6):847–855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0256-7
Li Y, Zeng J, Shan S, Chen X (2018) Occlusion aware facial expression recognition using CNN with attention mechanism. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(5):2439–2450. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2886767
Li R, Wang F, Zhang S (2020) Controlling role of Ta-d pumice on the coseismic landslides triggered by 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake. Landslides 17(5):1233–1250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01349-y
Lin L, Lin Q, Wang Y (2017) Landslide susceptibility mapping on a global scale using the method of logistic regression. Nat Hazard 17(8):1411–1424. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-17-1411-2017
Liu Y, Zhang W, Zhang Z, Xu Q, Li W (2021) Risk factor detection and landslide susceptibility mapping using Geo-Detector and random forest models: the 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake. Remote Sensing 13(6):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061157
Liu R, Yang X, Xu C, Wei L, Zeng X (2022) Comparative study of convolutional neural network and conventional machine learning methods for landslide susceptibility mapping. Remote Sens 14(2):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020321
Ma S, Xu C, Tian Y, Xu X (2019) Application of logistic regression model for hazard assessment of earthquake-triggered landslides: a case study of 2017 Jiuzhaigou (China) Ms7. 0 event. Seismol Geo 41(1):162–177. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.01.011
Minato M, Hashimoto S, Fujiwara Y, Kumano S, Okada S (1972) Stratigraphy of the quaternary ash and pumiceous products in southwestern Hokkaido, N. Japan (the pliocene and quaternary geology of Hokkaido, 1st report). J Faculty Sci Hokkaido Univ 15(3–4):679–736.
Nam K, Wang F (2019) The performance of using an autoencoder for prediction and susceptibility assessment of landslides: a case study on landslides triggered by the 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi earthquake in Japan. Geoenviron Disasters 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-019-0137-5
Neuhäuser B, Terhorst B (2007) Landslide susceptibility assessment using “weights-of-evidence” applied to a study area at the Jurassic escarpment (SW-Germany). Geomorphology 86(1–2):12–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.08.002
Nhu V-H, Hoang N-D, Nguyen H, Ngo PTT, Thanh Bui T, Hoa PV, Samui P, Tien Bui D (2020) Effectiveness assessment of Keras based deep learning with different robust optimization algorithms for shallow landslide susceptibility mapping at tropical area. CATENA 188:104458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104458
Oh H-J, Lee S, Soedradjat GM (2009) Quantitative landslide susceptibility mapping at Pemalang area. Indonesia Environ Earth Sci 60(6):1317–1328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0272-5
Pham S, Shahabi O, Singh S, Asl A, Quoc L (2019a) Landslide susceptibility assessment by novel hybrid machine learning algorithms. Sustainability 11(16):4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11164386
Pham BT, Prakash I, Dou J, Singh SK, Trinh PT, Tran HT, Le TM, Van Phong T, Khoi DK, Shirzadi A, Bui DT (2019b) A novel hybrid approach of landslide susceptibility modelling using rotation forest ensemble and different base classifiers. Geocarto Int 35(12):1267–1292. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1559885
Pham QB, Achour Y, Ali SA, Parvin F, Vojtek M, Vojteková J, Al-Ansari N, Achu AL, Costache R, Khedher KM, Anh DT (2021) A comparison among fuzzy multi-criteria decision making, bivariate, multivariate and machine learning models in landslide susceptibility mapping. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 12(1):1741–1777. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2021.1944330
Pham VD, Nguyen Q-H, Nguyen H-D, Pham V-M, Vu VM, Bui Q-T (2020) Convolutional neural network–optimized moth flame algorithm for shallow landslide susceptible analysis. IEEE Access 8:32727–32736. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2973415
Pourghasemi HR, Mohammady M, Pradhan B (2012a) Landslide susceptibility mapping using index of entropy and conditional probability models in GIS: Safarood Basin. Iran Catena 97:71–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2012.05.005
Pourghasemi HR, Pradhan B, Gokceoglu C (2012b) Application of fuzzy logic and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) to landslide susceptibility mapping at Haraz watershed. Iran Natural Hazards 63(2):965–996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0217-2
Regmi AD, Devkota KC, Yoshida K, Pradhan B, Pourghasemi HR, Kumamoto T, Akgun A (2013) Application of frequency ratio, statistical index, and weights-of-evidence models and their comparison in landslide susceptibility mapping in Central Nepal Himalaya. Arab J Geosci 7(2):725–742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0807-z
Reichenbach P, Rossi M, Malamud BD, Mihir M, Guzzetti F (2018) A review of statistically-based landslide susceptibility models. Earth Sci Rev 180:60–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.03.001
Saha S, Sarkar R, Roy J, Hembram TK, Acharya S, Thapa G, Drukpa D (2021) Measuring landslide vulnerability status of Chukha, Bhutan using deep learning algorithms. Sci Rep 11(1):16374. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95978-5
Sameen MI, Pradhan B, Lee S (2020) Application of convolutional neural networks featuring Bayesian optimization for landslide susceptibility assessment. CATENA 186:104249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104249
Samia J, Temme A, Bregt A, Wallinga J, Guzzetti F, Ardizzone F, Rossi M (2016) Do landslides follow landslides? Insights in path dependency from a multi-temporal landslide inventory. Landslides 14(2):547–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0739-x
Shao X, Ma S, Xu C, Zhang P, Wen B, Tian Y, Zhou Q, Cui Y (2019) Planet image-based inventorying and machine learning-based susceptibility mapping for the landslides triggered by the 2018 Mw6.6 Tomakomai, Japan Earthquake. Remote Sensing 11(8):978. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080978
Taalab K, Cheng T, Zhang Y (2018) Mapping landslide susceptibility and types using Random Forest. Big Earth Data 2(2):159–178. https://doi.org/10.1080/20964471.2018.1472392
Tharwat A (2020) Classification assessment methods. Applied Computing and Informatics 17(1):168–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aci.2018.08.003
Thi Ngo PT, Panahi M, Khosravi K, Ghorbanzadeh O, Kariminejad N, Cerda A, Lee S (2021) Evaluation of deep learning algorithms for national scale landslide susceptibility mapping of Iran. Geosci Front 12(2):505–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.06.013
Tian Y, Xu C, Hong H, Zhou Q, Wang D (2018) Mapping earthquake-triggered landslide susceptibility by use of artificial neural network (ANN) models: an example of the 2013 Minxian (China) Mw 5.9 event. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk 10(1):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2018.1487471
Tobler WR (1970) A computer movie simulating urban growth in the Detroit region. Econ Geogr 46(1970):234–240. https://doi.org/10.2307/143141
Umar Z, Pradhan B, Ahmad A, Jebur MN, Tehrany MS (2014) Earthquake induced landslide susceptibility mapping using an integrated ensemble frequency ratio and logistic regression models in West Sumatera Province, Indonesia. CATENA 118:124–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.02.005
Wang F, Fan X, Yunus AP, Siva Subramanian S, Alonso-Rodriguez A, Dai L, Xu Q, Huang R (2019a) Coseismic landslides triggered by the 2018 Hokkaido, Japan (Mw 6.6), earthquake: spatial distribution, controlling factors, and possible failure mechanism. Landslides 16(8):1551–1566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01187-7
Wang J, Jin W, Cui Y-F, Zhang W-F, Wu C-H, Alessandro P (2019b) Earthquake-triggered landslides affecting a UNESCO Natural Site: the 2017 Jiuzhaigou Earthquake in the World National Park. China J Mount Sci 15(7):1412–1428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-4823-7
Wang Q, Li W, Wu Y, Pei Y, Xie P (2016) Application of statistical index and index of entropy methods to landslide susceptibility assessment in Gongliu (Xinjiang, China). Environ Earth Sci 75(7):599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5400-4
Wang Y, Fang Z, Hong H (2019c) Comparison of convolutional neural networks for landslide susceptibility mapping in Yanshan County, China. Sci Total Environ 666:975–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.263
Wang Y, Fang Z, Niu R, Peng L (2021) Landslide susceptibility analysis based on deep learning. J Geo-Inform Sci 23(12):2244–2260. https://doi.org/10.12082/dqxxkx.2021.210057
Woo S, Park J, Lee J, Kweon I (2018) Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. Proceed European Conf Comp Vis (ECCV): 3–19
Xu C, Xu X, Dai F, Wu Z, He H, Shi F, Wu X, Xu S (2013a) Application of an incomplete landslide inventory, logistic regression model and its validation for landslide susceptibility mapping related to the May 12, 2008. Wenchuan Earthquake of China Natural Hazards 68(2):883–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0661-7
Xu C, Xu X, Yao X, Dai F (2013b) Three (nearly) complete inventories of landslides triggered by the May 12, 2008, Wenchuan Mw 7.9 earthquake of China and their spatial distribution statistical analysis. Landslides 11(3):441–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0404-6
Yalcin A (2008) GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping using analytical hierarchy process and bivariate statistics in Ardesen (Turkey): Comparisons of results and confirmations. CATENA 72(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2007.01.003
Yamagishi H, Ito Y, Kawamura M (2002) Characteristics of deep-seated landslides of Hokkaido: analyses of a database of landslides of Hokkaido. Japan Environ Eng Geosci 8(1):35–46
Yang X, Liu R, Yang M, Chen J, Liu T, Yang Y, Chen W, Wang Y (2021) Incorporating landslide spatial information and correlated features among conditioning factors for landslide susceptibility mapping. Remote Sensing 13(11):2166. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13112166
Yao J, Qin S, Qiao S, Liu X, Zhang L, Chen J (2022) Application of a two-step sampling strategy based on deep neural network for landslide susceptibility mapping. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81(4). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02615-0
Yi Y, Zhang Z, Zhang W, Xu Q, Deng C, Li Q (2019) GIS-based earthquake-triggered-landslide susceptibility mapping with an integrated weighted index model in Jiuzhaigou region of Sichuan Province, China. Nat Hazard 19(9):1973–1988. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-19-1973-2019
Yi Y, Zhang Z, Zhang W, Jia H, Zhang J (2020) Landslide susceptibility mapping using multiscale sampling strategy and convolutional neural network: a case study in Jiuzhaigou region. CATENA 195:104851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104851
Yin Y, Wang F, Sun P (2009) Landslide hazards triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan. China Landslides 6(2):139–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-009-0148-5
Youssef AM, Pradhan B, Dikshit A, Al-Katheri MM, Matar SS, Mahdi AM (2022) Landslide susceptibility mapping using CNN-1D and 2D deep learning algorithms: comparison of their performance at Asir Region, KSA. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81(4). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02657-4
Zhang Y, Chan W, Jaitly N (2017) Very deep convolutional networks for end-to-end speech recognition. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) 4845–4849. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2017.7953077.
Zhao B, Wang YS, Luo YH, Li J, Zhang X, Shen T (2018) Landslides and dam damage resulting from the Jiuzhaigou earthquake (8 August 2017), Sichuan. China R Soc Open Sci 5(3):171418. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.171418
Funding
This study was supported by the National Institute of Natural Hazards, Ministry of Emergency Management of China (ZDJ2021-14) and the Lhasa National Geophysical Observation and Research Station (NORSLS20-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.X. proposed the research concept and offered the remote sensing data; X.S provided the related controlling factors in the Iburi region; S.M provided the landslide dataset and controlling factors in the Jiuzhaigou region. L.L reformatted the manuscript and participated in the interpretation work in Jiuzhaigou region; Z.Y. designed the framework of the research, conducted the experiment, and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Xu, C., Shao, X. et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping based on CNN-3D algorithm with attention module embedded. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81, 412 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02889-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02889-4