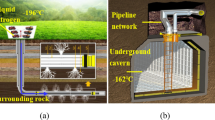
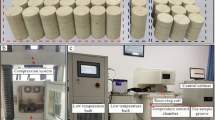
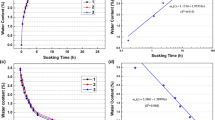
Abstract
To investigate the long-term stability of geotechnical engineering in cold regions, a low-temperature triaxial creep test device was developed for monitoring the rock resistivity during rock creep tests. The creep mechanical properties of red sandstone under different temperature and water content conditions were analyzed. Additionally, the resistivity data were analyzed to determine the state of the internal fractures of the rock. Nuclear magnetic resonance technology was used to analyze the influence mechanism of pore water in frozen red sandstone on the creep characteristics. Finally, with consideration of the resistivity, a mesoscopic analysis of the conductivity of frozen rock at negative temperatures was performed. The results indicated that at room temperature (20 °C), the initial instantaneous elastic strain of the red sandstone samples increased linearly with an increase in the water content, but the failure stress and long-term strength both decreased with the increasing water content. In contrast, at negative temperatures (− 5, − 10, and − 20 °C), the initial instantaneous elastic strains of the samples decreased linearly with the increase in the water content, but the failure stress and long-term strength both increased with the increase in the water content. Thus, water reduces the long-term strength of rocks at room temperature and enhances the long-term strength of rocks at negative temperatures.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almadani S, Ibrahim E, Al-Amri A, Fnais M, Abdelrahman K (2019) Delineation of a fractured granite aquifer in the Alwadeen area, Southwest Saudi Arabia using a geoelectrical resistivity survey. Arab J Geosci 12(15)
Aubertin M, Li L, Simon R (2000) A multiaxial stress criterion for short- and long-term strength of isotropic rock media. Int J Rock Mech Min 37(8)
Barsukov P, Fainberg E (2019) New interpretation of the reduction phenomenon in the electrical resistivity of rock masses before local earthquakes. Phys Earth Planet Inter 294:1–9
Baud P, Meredith PG (1997) Damage accumulation during triaxial creep of darley dale sandstone from pore volumometry and acoustic emission. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 34(3–4):24.e1-24.e10
Behroozmand A, Keating K, Auken E (2015) A review of the principles and applications of the NMR technique for near-surface characterization. Surv Geophys 36(1):27–85
Bray MT (2012) The influence of cryostructure on the creep behavior of ice-rich permafrost. Cold Reg Sci Technol 79–80:43–52
Brotons V, Ivorra S, Martínez-Martínez J et al (2013) Study of creep behavior of a calcarenite: San Julián’s stone Alicante. Mater Constr 63:581–595
Cheng Q, Tao M, Chen X, Binley A (2019) Evaluation of electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) for mapping the soil-rock interface in karstic environments. Environ Earth Sci 78(15)
Cogan J (1976) Triaxial creep tests of Opohonga limestone and Ophir shale. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 13(1)
Cong L, Hu X (2017) Triaxial rheological property of sandstone under low confining pressure. Eng Geol 231:45–55
Cui Z, Sheng Q, Leng X, Ma Y (2019) Investigation of the long-term strength of Jinping marble rocks with experimental and numerical approaches. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78(2)
Damjanac B, Fairhurst C (2010) Evidence for a long-term strength threshold in crystalline rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 43:513–531
Darot M, Gueguen Y (1986) Slow crack growth in minerals and rocks: Theory and experiments. Pure Appl Geophys 124(4):677–692
Falzone S, Robinson J, Slater L (2019) Characterization and monitoring of porous media with electrical imaging: a review. Transp Porous Media 130(1):251–276
Fujii Y (1999) Morphology and propagation of main fracture and echelon cracks in granite. The Geological Society of Japan, The Geological Society of Japan
Geng Z, Bonnelye A, Chen M, Jin Y, Dick P, David C, Fang X, Schubnel A (2018) Time and Temperature Dependent Creep in Tournemire Shale. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 123(11):9658–9675
Géraldine F, Frédéric A, Pellet F (2006) Creep and time-dependent damage in argillaceous rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci
Gold LW (1977) Engineering properties of fresh-water ice. J Glaciol 19(81)
Hamza O, Stace R (2018) Creep properties of intact and fractured muddy siltstone. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 106:109–116
Heap MJ, Baud P, Meredith PG et al (2009) Time-dependent Brittle Deformation in Darley Dale Sandstone. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 114(B7)
Heap MJ, Vinciguerra S, Meredith PG (2009b) The evolution of elastic moduli with increasing crack damage during cyclic stressing of a basalt from Mt. Etna Volcano Tectonophysics 471(1–2):153–160
Heap M, Baud P, Meredith P et al (2011) Brittle creep in basalt and its application to time-dependent volcano deformation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 307(1):71–82
Helal H, Homand-Etienne F, Josien J (1988) Validity of uniaxial compression tests for indirect determination of long term strength of rocks. Int J Min Geo-Eng 6(3)
Hou F, Lai Y, Liu E, Luo H, Liu X (2018) A creep constitutive model for frozen soils with different contents of coarse grains. Cold Reg Sci Technol 145:119–126
Hu Z, Peng K, Li L, Ma Q, Xiao H, Li Z, Ai P (2019) Effect of wetting-drying cycles on mechanical behaviour and electrical resistivity of unsaturated subgrade soil. Adv Civ Eng
ISRM (2007) The complete ISRM suggested methods for rock characterization, testing and-monitoring: 1974–2006. ISRM Turkish National Group, Ankara, Turkey
Jia H, Ding S, Wang Y, Zi F, Sun Q, Yang G (2019) An NMR-based investigation of pore water freezing process in sandstone. Cold Reg Sci Technol 168
Kodama J, Goto T, Fujii Y, Hagan P (2013) The effects of water content, temperature and loading rate on strength and failure process of frozen rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 62:1–13
Lawn B, Wilshaw R (1975) Fracture of Brittle Solids. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, U. K.
Legchenko A, Baltassat JM, Duwig C, Boucher M, Girard JF, Soruco A, Beauce A, Mathieu F, Legout C, Descloitres M, Patricia FA (2020) Time-lapse magnetic resonance sounding measurements for numerical modeling of water flow in variably saturated media. J Appl Geophys 175:103984
Li D-W, Fan J-H, Wang R-H (2011) Research on visco-elastic-plastic creep model of artificially frozen soil under high confining pressures. Cold Reg Sci Technol 65(2):219–225
Liu T, Zhang C, Cao P, Zhou K (2020) Freeze-thaw damage evolution of fractured rock mass using nuclear magnetic resonance technology. Cold Reg Sci Technol 170
Liu Y, Liu C, Kang Y, Wang D, Ye D (2015) Experimental research on creep properties of limestone under fluid-solid coupling. Environ Earth Sci 73(11):7011–7018
Lockner DA, Walsh JB, Byerlee JD (1977) Changes in seismic velocity and attenuation during deformation of granite. J Geophys Res 82(33):5374–5378
Lockner DA (1993) Room temperature creep in saturated granite. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 98(B1):475–487
Lockner DA (1998) A generalized law for brittle deformation of Westerly granite. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 103(B3):5107–5123
Lu Y, Wang L (2017) Effect of water and temperature on short-term and creep mechanical behaviors of coal measures mudstone. Environ Earth Sci 76(17)
Mallet C, Fortin J, Guéguen Y, Bouyer F (2015) Brittle creep and subcritical crack propagation in glass submitted to triaxial conditions. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 120(2):879–893
Mallet C, Fortin J, Guéguen Y, Bouyer F (2015b) Role of the pore fluid in crack propagation in glass. Mechanics of Time-Dependent Materials 19(2):117–133
Nara Y, Hiroyoshi N, Yoneda T et al (2010) Effects of relative humidity and temperature on subcritical crack growth in igneous rock. Int J Rock Mech Min 47(4):640–646
Okubo S, Fukui K, Hashiba K (2010) Long-term creep of water-saturated tuff under uniaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47(5):839–844
Tang L, Wang K, Jin L, Yang G, Jia H, Taoum A (2018) A resistivity model for testing unfrozen water content of frozen soil. Cold Reg Sci Technol 153:55–63
Urai JL, Spiers CJ, Zwart HJ, Lister GS (1986) Weakening of rock salt by water during long-term creep. Nature 324(6097):554–557
Wang D, Chen G, Jian D, Zhu J, Lin Z (2021) Shear creep behavior of red sandstone after freeze-thaw cycles considering different temperature ranges. Bull Eng Geol Environ (prepublish)
Wang S, Qi J, Yin Z, Zhang J, Ma W (2014) A simple rheological element based creep model for frozen soils. Cold Reg Sci Technol 106:47–54
Watanabe K, Wake T (2009) Measurement of unfrozen water content and relative permittivity of frozen unsaturated soil using NMR and TDR. Cold Reg Sci Technol 59(1):34–41
Wu FT, Thomsen L (1975) Microfracturing and deformation of westerly granite under creep condition. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 12(5–6):167–173
Xiong L, Li T, Yang L (2014) Biaxial compression creep test on green-schist considering the effects of water content and anisotropy. KSCE J Civ Eng 18(1):103–112
Xu LY, Song CX, Chen WY (2021) Liquefaction-induced settlement of the pile group under vertical and horizontal ground motions. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 144:106709
Yang C, Daemen JJK (1997) Temperature effects on creep of tuff and its time—Dependent damage analysis. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 34(3–4):383–384
Yang Y, Lai Y, Chang X (2010) Experimental and theoretical studies on the creep behavior of warm ice-rich frozen sand. Cold Reg Sci Technol 63(1–2):61–67
Yao Q, Zheng D, Wang Y et al (2020) Genetic mechanism of cataclastic loose rock mass in the Alpine mountain regions and deep valley. Disaster Prev Manag 40(05):706–713
Yao Y, Liu D, Che Y, Tang D, Tang S, Huang W (2010) Petrophysical characterization of coals by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Fuel 89(7):1371–1380
Yu C, Tang S, Tang, CA, Duan D, Zhang Y, Liang Z, Ma K, Ma T (2019) The effect of water on the creep behavior of red sandstone. Eng Geol 253:64–74
Zhang G, Liu E, Chen S, Zhang D (2019a) Damage Constitutive Model Based on Energy Dissipation for Frozen Sandstone Under Triaxial Compression Revealed by X-Ray Tomography. Exp Tech 43(5):545–560
Zhang G, Liu E, Chen S, Zhang D, Liu X, Yin X, Song B (2019b) Effects of uniaxial and triaxial compression tests on the frozen sandstone combining with CT scanning. Int J Phys Model 19(5):261–274
Zhang W, Zhou H, Guo W (2019c) Experimental Study on Seepage Characteristics of Fractured Rock Mass and Its Electrical Response. J Hydrol Eng 24(7)
Zhao X, Zhou G (2013) Experimental study on the creep behavior of frozen clay with thermal gradient. Cold Reg Sci Technol 86:127–132
Zhao Y, Zhang L, Wang W et al (2017) Creep Behavior of Intact and Cracked Limestone Under Multi-Level Loading and Unloading Cycles. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50:1409–1424
Zhou Z, Ma W, Zhang S, Du H, Mu Y, Li G (2016) Multiaxial creep of frozen loess. Mech Mater 95:172–191
Zhu Z, Luo F, Zhang Y, Zhang D, He J (2019) A creep model for frozen sand of Qinghai-Tibet based on Nishihara model. Cold Reg Sci Technol 167
Funding
This work was supported by the LiaoNing Revitalization Talents Program (Grant No. XLYC1905015), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52078093 and 51678101), and the Doctoral Innovation Program of Dalian Maritime University (Grant No. BSCXXM015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Jiang, A. & Guo, X. Effects of water content and temperature on creep properties of frozen red sandstone: an experimental study. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81, 51 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02553-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02553-3