Abstract
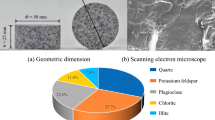
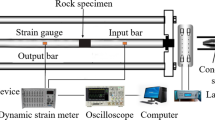
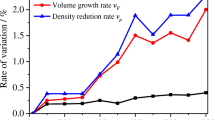
This study investigated the thermal cycling effects on the dynamic behavior of granite and described its microstructure. The specimens were subjected to various numbers of thermal cycles (0, 1, 3, 5, and 7 cycles) at temperatures ranging from 25 to 500 °C. Then, ultrasonic wave tests and split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) tests (with different impact gas pressures of 0.25, 0.28, and 0.31 MPa) were performed to study the thermal cycling effects on the P-wave velocity, P-wave modulus, dynamic compressive strength, and impact failure pattern of the granite specimens. Finally, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was performed to analyze the micromechanism of the dynamic property degeneration of the granite specimens. The results show that the dynamic properties of the P-wave velocity, P-wave modulus, and dynamic compressive strength exponentially decrease as the number of thermal cycles increases. The decreases in the dynamic properties mainly occur during the first thermal cycle, and the P-wave modulus and dynamic strength decrease by 67.5% and 8.4–16.3%, respectively. Moreover, a higher dynamic compressive strength, smaller fragments, and more fine powder are generated by impact failure with a larger strain rate. Smaller fragments and more fine powder are observed after impact failure as the number of thermal cycles increases. The tests further reveal that the dynamic properties of thermally damaged granite are closely related to the microcracks induced by thermal cycling.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MF, Waqas U, Arshad M, Rogers JD (2018) Effect of heat treatment on dynamic properties of selected rock types taken from the Salt Range in Pakistan. Arab J Geosci 11(22):728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4058-5
Chen L, Fang Q, Jiang XQ, Ruan Z, Hong J (2015) Combined effects of high temperature and high strain rate on normal weight concrete. Int J Impact Eng 86:40–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.07.002
Chen Y, Wang C (1980) Thermally induced acoustic-emission in Westerly granite. Geophys Res Lett 7(12):1089–1092. https://doi.org/10.1029/GL007i012p01089
Dai F, Huang S, Xia KW, Tan ZY (2010) Some fundamental issues in dynamic compression and tension tests of rocks using split Hopkinson pressure bar. Rock Mech Rock Eng 43(6):657–666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-010-0091-8
Deng XF, Zhu JB, Chen SG, Zhao ZY, Zhou YX, Zhao J (2014) Numerical study on tunnel damage subject to blast-induced shock wave in jointed rock masses. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 43:88–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2014.04.004
Fan LF, Gao JW, Wu ZJ, Yang SQ, Ma GW (2018) An investigation of thermal effects on micro-properties of granite by X-ray CT technique. Applied Thermal Engineering 140:505–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.05.074
Fan LF, Gao JW, Wu ZJ, Yang SQ, Ma GW (2020) Spatial gradient distributions of thermal shock-induced damage to granite. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 12(5):917–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2020.05.004
Fan LF, Wang M, Du XL (2021) Dual-mesh three characteristic lines method for stress wave propagation through micro-defected rock mass with thin layer filled macro-joint. Rock Mech Rock Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02644-3
Fan LF, Wu ZJ, Wan Z, Gao JW (2017) Experimental investigation of thermal effects on dynamic behavior of granite. Appl Therm Eng 125:94–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.07.007
Frew DJ, Forrestal MJ, Chen W (2002) Pulse shaping techniques for testing brittle materials with a split Hopkinson pressure bar. Exp Mech 42(1):93–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02411056
Gautam PK, Dwivedi R, Kumar A, Kumar A, Verma AK (2021) Damage characteristics of Jalore granitic rocks after thermal cycling effect for nuclear waste repository. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54(1):235–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02260-7
Ge ZL, Sun Q (2018) Acoustic emission (AE) characteristics of granite after heating and cooling cycles. Eng Fract Mech 200:418–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.08.011
Huang S, Xia KW (2015) Effect of heat-treatment on the dynamic compressive strength of Longyou sandstone. Eng Geol 191:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.03.007
Jin PH, Hu YQ, Shao JX, Zhao GK, Zhu XZ, Li C (2019) Influence of different cycling treatments on the physical, mechanical and transport properties of granite. Geothermics 78:118–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.12.008
Ju MH, Li JC, Li J, Zhao J (2020) Loading rate effects on anisotropy and crack propagation of weak bedding plane-rich rocks. Eng Fract Mech 230:106983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.106983
Kolsky H (1964) Stress waves in solids. J Sound Vib 1(1):88–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-460X(64)90008-2
Li JC, Li NN, Li HB, Zhao J (2017) An SHPB test study on wave propagation across rock masses with different contact area ratios of joint. Int J Impact Eng 105:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.12.011
Li M, Mao XB, Cao LL, Pu H, Mao RR, Lu AH (2016) Effects of thermal treatment on the dynamic mechanical properties of coal measures sandstone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(9):3525–3539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-0981-5
Li SH, Li PF, Zhang MJ (2021) Analysis of additional stress for a curved shield tunnel. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 107:103675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2020.103675
Li YB, Zhai Y, Wang CS, Meng FD, Lu M (2020a) Mechanical properties of Beishan granite under complex dynamic loads after thermal treatment. Eng Geol 267:105481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105481
Li ZW, Xu JY, Bai E (2012) Static and dynamic mechanical properties of concrete after high temperature exposure. Mat Sci Eng A-Struct 544:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.02.058
Li ZH, Wong LNY, Tech CI (2020b) Influence of thermal and mechanical loading on development of microcracks in granite. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(5):2035–2051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-02030-0
Liu QS, Qian ZC, Wu ZJ (2019) Micro/macro physical and mechanical variation of red sandstone subjected to cyclic heating and cooling: an experimental study. B Eng Geol Environ 78:1485–1499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1196-z
Liu S, Xu JY (2015) An experimental study on the physico-mechanical properties of two post-high-temperature rocks. Eng Geol 18:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.11.013
Mardoukhi A, Mardoukhi Y, Hokka M, Kuokkala VT (2017) Effects of heat shock on the dynamic tensile behavior of granitic rocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(5):1171–1182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1168-4
Ma GW, Fan LF, Li JC (2013) Evaluation of equivalent medium methods for stress wave propagation in jointed rock mass. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 37(7):701–715. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.1118
McCartney JS, Sanchez M, Tomac I (2016) Energy geotechnics: advances in subsurface energy recovery, storage, exchange, and waste management. Comput Geotech 75:244–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.01.002
Peng J, Rong G, Tang ZC, Sha S (2019) Microscopic characterization of microcrack development in marble after cyclic treatment with high temperature. B Eng Geol Environ 78(8):5965–5976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01494-2
Qin Y, Tian H, Xu NX, Chen Y (2020) Physical and mechanical properties of granite after high-temperature treatment. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(1):305–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01919-0
Rathnaweera TD, Ranjith PG, Gu X, Perera MSA, Kumari WGP, Wanniarachchi WAM, Haque A, Li JC (2018) Experimental investigation of thermomechanical behaviour of clay-rich sandstone at extreme temperatures followed by cooling treatments. Int J Rock Mech Min 107:208–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.04.048
Rong G, Peng J, Cai M, Yao MD, Zhou CB, Sha S (2018) Experimental investigation of thermal cycling effect on physical and mechanical properties of bedrocks in geothermal fields. Appl Therm Eng 141:174–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.05.126
Rong G, Sha S, Li BW, Chen ZH, Zhang ZY (2021) Experimental investigation on physical and mechanical properties of granite subjected to cyclic heating and liquid nitrogen cooling. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54(5):2383–2403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02390-6
Sano O, Kudo Y, Mizuta Y (1992) Experimental determination of elastic constants of Oshima granite, Barre granite, and Chelmsford granite. J Geophys Res 97:3367–3379. https://doi.org/10.1029/91JB02934
Takemura T, Golshani A, Oda M, Suzuki K (2003) Preferred orientations of open microcracks in granite and their relation with anisotropic elasticity. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40:443–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00014-5
Thill RE, Bur TR, Steckley RC (1973) Velocity anisotropy in dry and saturated rock spheres and its relation to rock fabric. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 10:535–557
Waqas U, Ahmed MF, Arshad M (2020a) Classification of the intact carbonate and silicate rocks based on their degree of thermal cracking using discriminant analysis. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79(5):2607–2619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01727-9
Waqas U, Ahmed MF (2020b) Prediction modeling for the estimation of dynamic elastic Young’s modulus of thermally treated sedimentary rocks using linear-nonlinear regression analysis, regularization, and ANFIS. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(12):5411–5428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02219-8
Waqas U, Ahmed MF, Rogers JD (2018) Effect of loading frequencies on the dynamic properties of thermally treated rock samples. In 52nd US Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium. American Rock Mechanics Association.
Wang ZL, Hao SY, Zheng J, Tian NC, Zha FS, Shi H (2019a) Study on energy properties and failure behaviors of heat-treated granite under static and dynamic compression. Mech Adv Mater Struc 27(6):462–472. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2018.1479808
Wang P, Xu JY, Fang XY, Wen M, Zheng GH, Wang PX (2017) Dynamic splitting tensile behaviors of red-sandstone subjected to repeated thermal shocks: Deterioration and micro-mechanism. Eng Geol 223:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.04.012
Wang P, Xu JY, Liu SH, Wang HY (2016) Dynamic mechanical properties and deterioration of red-sandstone subjected to repeated thermal shocks. Eng Geol 212:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.07.015
Wang P, Yin TB, Li XB, Zhang SS, Lv B (2019b) Dynamic properties of thermally treated granite subjected to cyclic impact loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(4):991–1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1606-y
Wong LNY, Li ZH, Kang HM, Teh CI (2017) Dynamic loading of Carrara marble in a heated state. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(6):1487–1505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1170-x
Wong LNY, Zhang YH, Wu ZJ (2020) Rock strengthening or weakening upon heating in the mild temperature range? Eng Geol 272:105619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105619
Xu JH, Kang Y, Wang ZF, Wang XC, Zeng DP, Su DF (2020) Dynamic mechanical behavior of granite under the effects of strain rate and temperature. Int J Geomech 20(2):04019177. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001583
Yang CF, Yang SY, Su N (2016) Stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in mineral-bound water and the indication for chemical weathering intensity. Chem Geol 441:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.08.015
Yang SQ, Huang YH, Tian WL, Ying PF, Jing HW (2019) Effect of high temperature on deformation failure behavior of granite specimen containing a single fissure under uniaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(7):2087–2107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1725-5
Yang SQ, Ranjith PG, Jing HW, Tian WL, Ju Y (2017) An experimental investigation on thermal damage and failure mechanical behavior of granite after exposure to different high temperature treatments. Geothermics 65:180–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.09.008
Yavuz H (2011) Effect of freeze-thaw and thermal shock weathering on the physical and mechanical properties of an andesite stone. B Eng Geol Environ 70(2):187–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0302-2
Yin TB, Bai L, Li X, Li XB, Zhang SS (2018) Effect of thermal treatment on the mode I fracture toughness of granite under dynamic and static coupling load. Eng Fract Mech 199:143–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.05.035
Yu LY, Su HJ, Liu RC, Jing HW, Li GL, Li M (2018) Effect of thermal treatment on the dynamic behaviors at a fixed loading rate of limestone in quasi-vacuum and air-filled environments. Lat Am J Solids Stru 15(3):e25. https://doi.org/10.1590/1679-78254021
Zhang WQ, Sun Q, Hao SQ, Geng JS, Lv C (2016) Experimental study on the variation of physical and mechanical properties of rock after high temperature treatment. Appl Therm Eng 98:1297–1304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.01.010
Zhang ZX, Yu J, Kou SQ, Lindqvist PA (2001) Effects of high temperatures on dynamic rock fracture. Int J Rock Mech Min 38(2):211–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(00)00071-X
Zhou ZL, Li XB, Ye ZY, Liu KW (2010) Obtaining constitutive relationship for rate-dependent rock in SHPB tests. Rock Mech Rock Eng 43(6):697–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-010-0096-3
Zhou YX, Xia KW, Li XB, Li HB, Ma GW, Zhao J, Zhou ZL, Dai F (2012) Suggested methods for determining the dynamic strength parameters and mode-I fracture toughness of rock materials. Int J Rock Mech Min 49:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.10.004
Zhu ZN, Tian H, Chen J, Jiang GS, Dou B, Xiao P, Mei G (2019) Experimental investigation of thermal cycling effect on physical and mechanical properties of heated granite after water cooling. B Eng Geol Environ 79(5):2457–2465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01705-w
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NOs. 12172019, 41831281 and 51778021) and Beijing Natural Science Foundation (JQ20039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Fan, L. & Wan, Z. Thermal cycling effects on the dynamic behavior of granite and microstructural observations. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80, 8711–8723 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02462-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02462-5