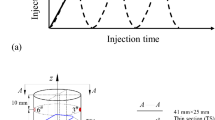
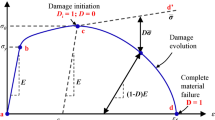
Abstract
The present study investigated the dynamic fatigue damage of thermally shocked granite with cyclic impact load. Firstly, cyclic impact tests were performed with a split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) device to study the dynamic stress–strain relationship of water-cooled granite at various temperatures and cyclic numbers. Subsequently, the dynamic stress, elastic modulus, maximum strain and strain rate affected by temperature and cyclic number were further discussed, the energy evolution and cumulative damage during cyclic impact were revealed. Finally, the crack propagation, failure mode and fatigue life (the maximum impact number) of granite were analyzed, a fatigue life prediction model was proposed. The results show that the dynamic stress, elastic modulus and transmitted energy of granite exponentially decrease, while the maximum strain, strain rate, reflection energy, absorption energy and cumulative damage exponentially increase as the cycle number increases with a fixed thermal treatment temperature. In addition, microcracks first appear in the longitudinal section, then develop into macrocracks and penetrate to cause granite failure as the impact number increases. Granite exhibits different failure modes after cyclic impact. Split tensile single fracture surface failure before 600 °C and multiple fracture surface failure at 800 °C. The fatigue life decreases as the temperature and impact pressure increase.
Highlights
-
1.
Dynamic fatigue properties deterioration rate increases as cycle number increases.
-
2.
Microcracks develop into macrocracks and penetrate to cause granite failure.
-
3.
Single-fracture failure mode to multi-fracture failure mode occurs at 800 ℃.
-
4.
Fatigue life decreases as impact pressure and temperature increase.
-
5.
A model for predicting fatigue life is developed.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data was used for the research described in the article.
References
Ambrosini D, Luccioni B (2020) Effects of underground explosions on soil and structures. Undergr Space 5(4):324-338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.undsp.2019.09.002
Cerfontaine B, Collin F (2018) Cyclic and fatigue behaviour of rock materials: review, interpretation and research perspectives. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(2):391–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1337-5
Dai F, Huang S, Xia KW, Tan ZY (2010) Some fundamental issues in dynamic compression and tension tests of rocks using split Hopkinson pressure bar. Rock Mech Rock Eng 43(6):657–666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-010-0091-8
Ersoy H, Kolaylı H, Karahan M, Karahan HH, Sunnetci MO(2019) Effect of thermal damage on mineralogical and strength properties of basic volcanic rocks exposed to high temperatures. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78(3):1515–1525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1208-z
Fan LF, Wang M, Wu ZJ (2020) A split three-characteristics method for stress wave propagation through a rock mass with double-scale discontinuities. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(12):5767-5779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02233-w
Fan LF, Wu ZJ, Wan Z, Gao JW (2017) Experimental investigation of thermal effects on dynamic behavior of granite. Appl Therm Eng 125:94–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.07.007
Fan LF, Yang KC, Wang M, Wang LJ, Wu ZJ (2021) Experimental study on wave propagation through granite after high-temperature treatment. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 148:104946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104946
Fan LF, Yang QH, Du XL (2023c) Spall characteristics of high-temperature treated granitic rock at different strain rates. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.05.016
Fan LF, Yang QH, Wang M, Du XL (2023b) A short-bar combined-wave method for wave propagation coefficient determination. Rock Mech Rock Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03647-y
Fan LF, Qiu B, Gao JW, Du XL (2023a) A real-time visual investigation on microscopic progressive fatigue deterioration of granite under cyclic loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56(7):5133-5147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03326-y
Feng G, Kang Y, Wang XC, Hu YQ, Li XH (2020) Investigation on the failure characteristics and fracture classification of shale under brazilian test conditions. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:3325–3340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02110-6
Fuenkajorn K, Phueakphum D (2010) Effects of cyclic loading on mechanical properties of Maha Sarakham salt. Eng Geol 112(1):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.01.002
Gao JY, Fan LF, Wan Z (2021) Thermal cycling effects on the dynamic behavior of granite and microstructural observations. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:8711–8723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02462-5
Ge Z, Sun Q (2018) Acoustic emission (AE) characteristic of granite after heating and cooling cycles. Eng Fract Mech 200:418–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.08.011
Huang S, Xia KW (2015) Effect of heat-treatment on the dynamic compressive strength of Longyou sandstone. Eng Geol 191:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.03.007
Jha MK, Verma AK, Maheshwar S, Chauhan A (2016) Study of temperature effect on thermal conductivity of Jhiri shale from upper Vindhyan, India. Bull Eng Geol Environ 75(4):1657–1668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-015-0829-3
Kim K, Kemeny J, Nickerson M (2014) Effect of rapid thermal cooling on mechanical rock properties. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47:2005–2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0523-3
Kumari WGP, Ranjith PG, Perera MSA, Chen BK, Abdulagatov IM (2017) Temperature-dependent mechanical behaviour of Australian Strathbogie granite with different cooling treatments. Eng Geol 229:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.09.012
Li JC (2013) Wave propagation across non-linear rock joints based on time-domain recursive method. Geophys J Int 193:970–985. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggt020
Li BY, Ju F (2018) Thermal stability of granite for high temperature thermal energy storage in concentrating solar power plants. Appl Therm Eng 138:409–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.04.071
Li XB, Lok TS, Zhao J (2005) Dynamic characteristics of granite subjected to intermediate loading rate. Rock Mech Rock Eng 38(1):21–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-004-0030-7
Li JC, Li HB, Jiao YY, Liu YQ, Xia X, Yu C (2014a) Analysis for oblique wave propagation across filled joints based on thin-layer interface model. J Appl Geophy 102:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2013.11.014
Li XB, Zou Y, Zhou ZL (2014b) Numerical simulation of the rock SHPB test with a special shape striker based on the discrete element method. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47(5):1693–1709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0484-6
Li JC, Li HB, Zhao J (2015) An improved equivalent viscoelastic medium method for wave propagation across layered rock masses. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 73:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.10.008
Li JC, Li NN, Li HB, Zhao J (2017) An SHPB test study on wave propagation across rock masses with different contact area ratios of joint. Int J Impact Eng 105:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.12.011
Li SH, Zhu WC, Niu LL, Yu M, Chen CF (2018) Dynamic characteristics of green sandstone subjected to repetitive impact loading: phenomena and mechanisms. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:1921–1936. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1449-6
Li JC, Rong LF, Li HB, Hong SN (2019) An SHPB test study on stress wave energy attenuation in jointed rock masses. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:403–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1586-y
Li Q, Yin TB, Li XB, Zhang SS (2020) Effects of rapid cooling treatment on heated sandstone: a comparison between water and liquid nitrogen cooling. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79(1):313-327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01571-6
Li X, Xia KW, Yao W, Xu Y (2022) Investigation on the dynamic tensile behaviour of rubberized mortar using the Brazilian disc method. Theor Appl Fract Mech 119:103339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2022.103339
Liu S, Xu JY (2015) Effect of strain rate on the dynamic compressive mechanical behaviors of rock material subjected to high temperatures. Mech Mater 82:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2014.12.006
Liu EL, Huang RQ, He SM (2012) Effects of frequency on the dynamic properties of intact rock samples subjected to cyclic loading under confining pressure conditions. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45:89–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-011-0185-y
Liu XY, Dai F, Liu Y, Pei PD, Yan ZL (2021) Experimental investigation of the dynamic tensile properties of naturally saturated rocks using the coupled static-dynamic flattened Brazilian disc method. Energies 14:4784. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14164784
Lu YL, Wang LG, Sun XK, Wang J (2017) Experimental study of the influence of water and temperature on the mechanical behavior of mudstone and sandstone. Bull Eng Geol Environ 76(2):645–660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0851-0
Luo XD, Jiang N, Wang MY, Xu Y (2016) Response of Leptynite subjected to repeated impact loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(10):4137–4141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0896-6
Ma LJ, Liu XY, Wang MY, Xu HF, Hua RP, Fan PX, Jiang SR, Wang GA, Yi QK (2013) Experimental investigation of the mechanical properties of rock salt under triaxial cyclic loading. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 62:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2013.04.003
Momeni A, Karakus M, Khanlari GR, Heidari M (2015) Effects of cyclic loading on the mechanical properties of a granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 77:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.03.029
Santos JPLD, Rosa LG, Amaral PM (2011) Temperature effects on mechanical behaviour of engineered stones. Constr Build Mater 25(1):171–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.06.042
Sha S, Rong G, Chen ZH, Li BW, Zhang ZY (2020) Experimental evaluation of physical and mechanical properties of geothermal reservoir rock after different cooling treatments. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02200-5
Sirdesai NN, Mahanta B, Ranjith PG, Singh TN (2019) Effects of thermal treatment on physico-morphological properties of Indian fine-grained sandstone. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78(2):883–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1149-6
Sun B, Zhu ZD, Shi C, Luo ZH (2017) Dynamic mechanical behavior and fatigue damage evolution of sandstone under cyclic loading. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 94:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.03.003
Tian H, Mei G, Jiang GS, Qin Y (2017) High-temperature influence on mechanical properties of diorite. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(6):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1185-3
Wang F, Konietzky H (2019) Thermo-mechanical properties of granite at elevated temperatures and numerical simulation of thermal cracking. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:3737–3755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01837-1
Wang ZL, Tian NC, Wang JG, Liu JC, Hong L (2018) Experimental study on damage, mechanical characteristics of heat-treated granite under repeated impact. Am Soc Civil Eng 30(11):04018274. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002465
Wang P, Yin TB, Li XB, Zhang SS, Bai L (2019) Dynamic properties of thermally treated granite subjected to cyclic impact loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(4):991–1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1606-y
Wang F, Konietzky H, Frühwirt T, Li YW, Dai YJ (2020) The infuence of temperature and high-speed heating on tensile strength of granite and the application of digital image correlation on tensile failure processes. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:1935–1952. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-02022-0
Wang JT, Zuo JP, Sun YJ, Wen JH (2021) The effects of thermal treatments on the fatigue crack growth of Beishan granite: an in situ observation study. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:1541–1555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01966-w
Wu XG, Huang ZW, Song HY, Zhang SK, Cheng Z, Li R, Wen HT, Huang PP, Dai XW (2019) Variations of physical and mechanical properties of heated granite after rapid cooling with LN2. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(7):2123–2139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1727-3
Xia KW, Yao W (2015) Dynamic rock tests using split Hopkinson (Kolsky) bar systeme-a review. J Rock Mech Geotech 7(1):27–59
Xia KW, Yao W, Wu BB (2017) Dynamic rock tensile strengths of Laurentian granite: experimental observation and micromechanical model. J Rock Mech Geotech 9:116–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.08.007
Xiao JQ, Ding DX, Xu G, Jiang FL (2009) Inverted S-shaped model for nonlinear fatigue damage of rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(3):643–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.11.002
Xu T, Tang CA, Zhao J, Li JC, Heap MJ (2012) Modelling the time-dependent rheological behaviour of heterogeneous brittle rocks. Geophys J Int 189(3):1781–1796. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05460.x
Xue YM, Dai B, Chen Y, Zhang L, He GC, Zhang ZJ (2020) Experimental study on the mechanical properties and damage evolution of hollow cylindrical granite specimens subjected to cyclic coupled static-dynamic Loads. Geofluids 2020:8881936. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8881936
Yan ZL, Dai F, Liu Y, Du HB, Luo J (2020) Dynamic strength and cracking behaviors of single-flawed Rock subjected to coupled static-dynamic compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:4289–4298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02165-5
Yang RZ, Xu Y, Chen PY, Wang J (2020) Experimental study on dynamic mechanics and energy evolution of rubber concrete under cyclic impact loading and dynamic splitting tension. Constr Build Mater 262:120071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120071
Yang QH, Fan LF, Du XL (2022) Determination of wave propagation coefficients of the granite by high-speed digital image correlation (HDIC). Rock Mech Rock Eng 55(7):4497-4505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02894-9
Yin TB, Li XB, Xia KW, Huang S (2012) Effect of thermal treatment on the dynamic fracture toughness of Laurentian Granite. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45(6):1087–1094. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0240-3
Yin TB, Bai L, Li X, Li XB, Zhang SS (2018) Effect of thermal treatment on the mode I fracture toughness of granite under dynamic and static coupling load. Eng Fract Mech 199:143–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.05.035
Zhang QB, Zhao J (2014) A review of dynamic experimental techniques and mechanical behaviour of rock materials. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47(4):1411–1478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0463-y
Zhang H, Song HP, Kang YL, Huang GY, Qu CY (2013) Experimental analysis on deformation evolution and crack propagation of rock under cyclic indentation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 46:1053–1059. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0309-z
Zhang F, Zhang YH, Yu YD, Hu DW, Shao JF (2020) Influence of cooling rate on thermal degradation of physical and mechanical properties of granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 129:104285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104285
Zhao Z (2016) Thermal influence on mechanical properties of granite: a microcracking perspective. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(3):747–762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0767-1
Zhao J, Li HB (2000) Experimental determination of dynamic tensile properties of a granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 37(5):861–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(00)00015-0
Zhao YS, Feng ZJ, Xi BP, Wan ZJ, Yang D, Liang WG (2015) Deformation and instability failure of borehole at high temperature and high pressure in hot dry rock exploitation. Renew Energ 77:159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2014.11.086
Zhong WL, Fan LF, Zhang YH (2022) Experimental research on the dynamic compressive properties of lightweight slag based geopolymer. Ceram Int 48:20426–20437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.03.328
Zhou T, Dong SL, Zhao GF, Zhang R, Wu SY, Zhu JB (2018) An Experimental study of fatigue behavior of granite under low cycle repetitive compressive impacts. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:3157–3166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1515-0
Zhu ZN, Tian H, Chen J, Jiang GS, Dou B, Xiao P, Mei G (2020) Experimental investigation of thermal cycling effect on physical and mechanical properties of heated granite after water cooling. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:2457–2465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01705-w
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.12172019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, L., Li, H., Xi, Y. et al. Effect of Cyclic Impact on the Dynamic Behavior of Thermally Shocked Granite. Rock Mech Rock Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-024-03819-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-024-03819-4