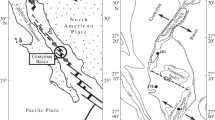
Abstract
The consolidation properties of clay samples from a marine environment were examined. Index, triaxial and odeometer tests were performed on the undisturbed/disturbed clay samples from 13 boreholes in the Gemlik Gulf (Bursa-Turkey). Laboratory tests indicated that the clays are soft and have a high moisture content and hence are highly compressible. The majority of the clays are unconsolidated due to the accretion rate being faster than the dissipation of pore water.
Abstract
Les propriétés de consolidation d’argiles prélevées en environnement marin ont été étudiées. Les indices de plasticité ont été déterminés, des essais triaxiaux et oedométriques ont été réalisés sur des échantillons intacts ou remaniés, provenant de 13 forages dans le golfe de Gemlik (Bursa, Turquie). Les essais de laboratoire ont montré que les argiles étaient des argiles molles, présentaient de fortes teneurs en eau et étaient très compressibles. La plupart de ces argiles sont non consolidées du fait d’un taux de sédimentation élevé comparativement à la vitesse de dissipation des pressions interstitielles.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyürek B (1987) 1:500 000 ölçekli jeoloji haritası (İstanbul). M.T.A. Genel Müdürlüğü Yayınları, Ankara, pp 1–105 (in Turkish)
ASTM (1990) Annual book of ASTM standards (ASTM D-2435), Soil and Rock Sec 4, Vol 04.08
Brattli B, Broch E (1995) Stability problems in water tunnels caused by expandable minerals, swelling pressure measurements and mineralogical analyses. Eng Geol, 39:151–169
Casagrande A (1936) Determination of the pre-consolidation load and its practical significance. Proceedings 1st Int. Conf. on Soil Mech and Found Eng, Cambridge, Mass. 3:60–64
Dai F, Lee CF, Wang S, Feng Y (1999) Stress-strain behaviour of a loosely compacted volcanic-derived soil and its significance to rainfall induced fill slope failures. Eng Geol 53(3–4):359–370
Feda J (1998) Fragmentary clay—a difficult waste material. Eng Geol 51(2):77–88
Giraud A, Rousset G (1996) Time-dependent behaviour of deep clays. Eng Geol 41(1–4):181–195
Leonards GA (1962) Foundation engineering. McGraw Hill
Rohrlich V, Wiseman G, Komornik A (1995) Overconsolidated clays from the Israeli Mediterranean coast and inner shore. Eng Geol 39(1–2):87–90
Spangler MG, Handy RL (1982) Soil engineering, 4th edn. Harper and Row, New York
Tomlinson MJ (1986) Foundation design and construction, 5th edn. Pitman, London
U.S.B.R. (1974) Earth manual. A Water Resources Tech Publ, U.S. Dept of Interior Bureau of Reclamation
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yilmaz, I., Üstünkaya, M. Unconsolidated clays from the inner shore of the Gemlik Gulf in the Marmara Sea (Bursa-Turkey). Bull Eng Geol Environ 63, 133–139 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-004-0229-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-004-0229-6