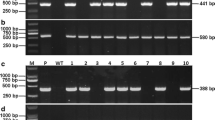
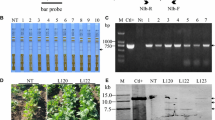
Abstract
Rice stripe virus (RSV) is a viral disease that seriously impacts rice production in East Asia, most notably in Korea, China, and Japan. Highly RSV-resistant transgenic japonica rice plants were generated using a dsRNAi construct designed to silence the entire sequence region of the RSV-CP gene. Transgenic rice plants were inoculated with a population of viruliferous insects, small brown planthoppers (SBPH), and their resistance was evaluated using ELISA and an infection rate assay. A correlation between the expression of the RSV-CP homologous small RNAs and the RSV resistance of the transgenic rice lines was discovered. These plants were also analyzed by comparing the expression pattern of invading viral genes, small RNA production and the stable transmission of the RSV resistance trait to the T3 generation. Furthermore, the agronomic trait was stably transmitted to the T4 generation of transgenic plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andika, I.B., Kondo, H., and Tamada, T. (2005). Evidence that RNA silencing-mediated resistance to Beet necrotic yellow vein virus is less effective in roots than in leaves. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 18, 194–204.
Andika, I.B., Kondo, H., Rahim, M.D., and Tamada, T. (2006). Lower levels of transgene silencing in roots is associated with reduced DNA methylation levels at non-symmetrical sites but not at symmetrical sites. Plant Mol. Biol. 60, 423–435.
Atabekov, J.G. (1975). Host specificity of plant viruses. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 13, 127–145.
Bernstein, E., Caudy, A.A., Hammond, S.M., and Hannon, G.J. (2001). Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409, 363–366.
Chang, C.I., Kang, H.S., Ban, C., Kim, S., and Lee, D.K. (2009). Dual-target gene silencing by using, synthetic siRNA duplexes without triggering antiviral responses. Mol. Cells 27, 689–695.
Chen, Y.K., Dick, L., Rob, G., and Marcel, P. (2004). High frequency induction of RNA-mediated resistance against Cucumber mosaic virus using inverted repeat constructs. Mol. Breed. 14, 215–226.
Choi, C.W., Qu, F., Ren, T., and Morris, T.J. (2004). Relationship between plant viral encoded suppressor to post-transcriptional gene silencing and elicitor to R gene-specific host resistance. Plant Pathol. J. 20, 22–29.
Dasgupta, I., Malathi, V.G., and Mukherjee, S.K. (2003). Genetic engineering for virus resistance. Curr. Sci. 84, 341–354.
Deleris, A., Gallego-Bartolome, J., Bao, J., Kasschau, K.D., Carrington, J.C., and Voinnet, O. (2006). Hierarchical action and inhibition of plant Dicer-like proteins in antiviral defense. Science 313, 68–71.
Di Nicola-Negri, E., Brunetti, A., Tavazza, M., and Ilardi, V. (2005). Hairpin RNA-mediated silencing of Plum pox virus P1 and HCPro genes for efficient and predictable resistance to the virus. Transgenic Res. 14, 989–994.
Falk, B.W., and Tsai, J.H. (1998). Biology and molecular biology of viruses in the genus Tenuivirus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 36, 139–163.
Fuentes, A., Ramos, P.L., Fiallo, E., Callard, D., Sanchez, Y., Peral, R., Rodriguez, R., and Pujol, M. (2006). Intron-hairpin RNA derived from replication associated protein C1 gene confers immunity to Tomato yellow leaf curl virus infection in transgenic tomato plants. Transgenic Res. 15, 291–304.
Goto, K., Kanazawa, A., Kusaba, M., Masutaaj, C., and Baulcombe, D.C. (2003). A simple and rapid method to detect plant siRNAs using Nonradioactive probes. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 21, 51–58.
Gu, K.L., Wang, Z.L., Yang, G., Ma, L., and Xu, J.J. (2005). The consequence of outbreak of the small brown planthopper (Laodelphax striatellus Fallén) and rice stripe virus and their control measures. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 33, 44.
Hamilton, A.J., and Baulcombe, D.C. (1999). A species of small antisense RNA in post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 286, 950–952.
Hayakawa, T., Zhu, Y., Itoh, K., Kimura, Y., Izawa, T., Shimamoto, K., and Toriyama, S. (1992). Genetically engineered rice resistant to rice stripe virus, an insect-transmitted virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 9865–9869.
Hayano-Saito, Y., Tsuji, T., Fujii, K., Saito, K., Iwasaki, M., and Saito, A. (1998). Localization of the rice stripe disease resistance gene, Stvb-i, by graphical genotyping and linkage analyses with molecular markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 101, 59–63.
Hibino, H. (1996). Biology and epidemiology of rice viruses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 34, 249–274.
Hutvagner, G., Mlynarova, L., and Nap, J. (2000). Detailed characterization of the post-transcriptional gene-silencing-related small RNA in a GUS gene-silenced tobacco. RNA 6, 1445–1454.
Jang, I.C., Choi, W.B., Lee, K.H., Song, S.I., Nahm, B.H., and Kim, J.K. (2002). High-level and ubiquitous expression of the rice cytochrome c gene (OsCc1) and its promoter activity in transgenic plants provides a useful promoter for transgenesis of monocots. Plant Physiol. 129, 1473–1481.
Jari, P., and Valkonen, T. (2003). Plant resistance to Infection with viruses. eLS on line library. DOI: 10.1038/npg.els.0000757.
Jonson, G.-M., Choi, H.-S., Kim, J.-S., Choi, I.-R., and Kim, K.-H. (2009a). Sequence and phylogenetic analyses of the RNA1 and RNA2 segments of Korean Rice stripe virus isolates and comparison with those of China and Japan. Arch. Virol. 154, 1705–1708.
Jonson, G.-M., Choi, H.-S., Kim, J.-S., Choi, I.-R., and Kim, K.-H. (2009b). Complete genome sequence of the RNAs 3 and 4 segments of rice stripe virus isolates in Korea and their phylogenetic relationships with Japan and China isolates. Plant Pathol. J. 25, 142–150.
Jonson, G.-M., Lian, S., Choi, H.S., Lee, G.-S., Kim, C.S., and Kim, K.H. (2011). Genetic reassortment of Rice stripe virus RNA segments detected by RT-PCR restriction enzyme analysis-based method. Plant Pathol. J. 27, 148–155.
Kim, Y.H., Park, H.M., Choi, M.S., Yun, H.T., Choi, I.S., Shin, D.B., Kim, C.K., and Lee, J.Y. (2009). The effects of co-cultivation medium and culture conditions on rice transformation efficiency. Korean J. Breed. Sci. 41, 252–260.
Kumar, P., Lee, S.K., Shankar, P., and Manjunath, N. (2006). A single siRNA suppresses fatal encephalitis induced by two different fl aviviruses. PLoS Med. 3, 505–514.
Lee, B.C., Hong, Y.K., Kawk, D.Y., Park, S.T., Choi, J.M., and Lee, K.W. (2004). Cloning and sequencing of the Korean isolate of rice stripe virus. Plant Pathol. J. 20, 313–315.
Lennefors, B.L., Yndgaard, F., van Roggen, P., Savenkov, E.I., and Valkonen, J.P.T. (2008). Efficient dsRNA-mediated transgenic resistance to Beet necrotic yellow vein virus in sugar beets is not affected by other soilborne and aphid-transmitted viruses. Transgenic Res. 17, 219–228.
Liang, D., Qu, Z., Ma, X., and Hull, R. (2005). Detection and localization of rice stripe virus gene products in vivo. Virus Genes 31, 211–221.
Ma, J., Song, Y., Wu, B., Jiang, M., Li, K., Zhu, C., and Wen, F. (2011). Production of transgenic rice new germplasm with strong resistance against two isolations of rice stripe virus by RNA interference. Transgenic Res. DOI 10.1007/s11248-011-9502-1.
Mansoor, S., Amin, I., Hussain, M., Zafar, Y., and Briddon, R.W. (2006). Engineering novel traits in plants through RNA-interference. Trends Plant Sci. 11, 559–565.
Miki, D., and Shimamoto, K. (2004). Simple RNAi vectors for stable and transient suppression of gene function in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 45, 490–495.
Phillips, R.L., Kaeppler, S.M., and Olhoft, P. (1994). Genetic instability of plant tissue cultures: breakdown of normal controls. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 5222–5226.
Rogers, S.O., and Bendich, A.J. (1985). Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol. Biol. 5, 69–76.
Shimizu, T., Nakazono-Nagaoka, E., Uehara-Ichiki, T., Sasaya, T., and Omura, T. (2010). Targeting specific genes for RNA interference is crucial to the development of strong resistance to rice stripe virus. Plant Biotechnol. J. 9, 503–512.
Takahashi, M., Toriyama, S., Hamamatsu, C., and Ishihama, A. (1993). Nucleotide sequence and possible ambisense coding strategy of rice stripe virus RNA segment 2. J. Gen. Virol. 74, 769–773.
Toriyama, S. (2000). Rice stripe virus. CMI/AAB Description of Plant Viruses. No. 375
Toriyama, S., and Watanabe, Y. (1989). Characterization of single- and double stranded RNAs in particles of rice stripe virus. J. Gen. Virol. 70, 505–511.
Toriyama, S., Takahashi, M., Sano, Y., Shimizu, T., and Ishihama, A. (1994). Nucleotide sequence of RNA1, the largest genomic segment of rice stripe virus, the prototype of the tenuiviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 75, 3569–3579.
Voinnet, O. (2005). Induction and suppression of RNA silencing: Insights from viral infections. Nat. Rev. Genet. 6, 206–221.
Washio, O., Ezuka, A., Toriyama, K., and Sakurai, Y. (1968). Testing method for genetics of and breeding for resistance to rice stripe disease. Bull. Chugoku Agric. Exp. Sta. Ser. A 16, 39–197.
Waterhouse, P.M., Graham, M.W., and Wang, M.B. (1998). Virus resistance and gene silencing in plants can be induced by simultaneous expression of sense and antisense RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 13959–13964.
Wei, T.Y., Yang, J.G., Liao, F.R., Gao, F.L., Lu, L.M., Zhang, X.T., Li, F., Wu, Z.J., Lin, Q.Y., Xie, L.H., et al. (2009). Genetic diversity and population structure of rice stripe virus in China. J. Gen. Virol. 90, 1025–1034.
Wu, S.J., Zhong, H., Zuo, H., Gu, M.H., and Liang, G.H. (2006). Research progress in molecular biology of rice stripe virus and gene engineering of virus resistance. Acta Agric. Jiangxi. 18, 72–77.
Xiong, R.Y., Cheng, Z.B., Wu, J.X., Zhou, Y.J., Zhou, T., and Zhou, X.P. (2008a). First report of an outbreak of Rice stripe virus on wheat in China. Plant Pathol. 57, 397.
Xiong, R., Wu, J., Zhou, Y., and Zhou, X. (2008b). Identification of movement protein of the Tenuivirus rice stripe virus. J. Virol. 82, 12304–12311.
Xiong, R., Wu, J., Zhou, Y., and Zhou, X. (2009). Characterization and subcellular localization of an RNA silencing suppressor encoded by rice stripe tenuivirus. Virology 387, 29–40.
Zhu, Y., Hayakawa, T., Toriyama, S., and Takahashi, M. (1991). Complete nucleotide sequence of RNA 3 of rice stripe virus: an ambisense coding strategy. J. Gen. Virol. 72, 763–767.
Zhu, Y., Hayakawa, T., and Toriyama, S. (1992). Complete nucleotide sequence of RNA4 of rice stripe virus isolate T and comparison with another isolate and with maize stripe virus. J. Gen. Virol. 73, 1309–1312.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, HM., Choi, MS., Kwak, DY. et al. Suppression of NS3 and MP is important for the stable inheritance of RNAi-mediated Rice Stripe Virus (RSV) resistance obtained by targeting the fully complementary RSV-CP gene. Mol Cells 33, 43–51 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-2185-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-2185-5