Abstract
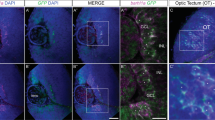
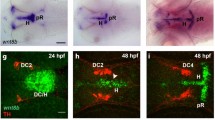
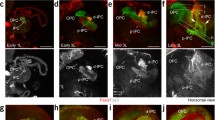
Previous studies have shown that Notch signaling not only regulates the number of early differentiating neurons, but also maintains proliferating neural precursors in the neural tube. Although it is well known that Notch signaling is closely related to the differentiation of adult neural stem cells, none of transgenic zebrafish provides a tool to figure out the relationship between Notch signaling and the differentiation of neural precursors. The goal of this study was to characterize Her4-positive cells by comparing the expression of a fluorescent Her4 reporter in Tg[her4-dRFP] animals with a GFAP reporter in Tg[gfap-GFP] adult zebrafish. BrdU incorporation indicated that dRFP-positive cells were proliferating and a double labeling assay revealed that a significant fraction of the Her4-dRFP positive population was also GFAP-GFP positive. Our observations suggest that a reporter line with Notch-dependent gene expression can provide a tool to examine proliferating neural precursors and/or neuronal/glial precursors in the development of the adult nervous system to examine the model in which Notch signaling maintains proliferating neural precursors in the neural tube.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernardos, R.L., and Raymond, P.A. (2006). GFAP transgenic zebrafish. Gene Expr. Pattern 6, 1007–1013.
Dam, T.M., Kim, H.T., Moon, H.Y., Hwang, K.S., Jeong, Y.M., You, K.H., Lee, J.S., and Kim, C.H. (2011). Neuron-specific expression of scratch genes during early zebrafish development. Mol. Cells 31, 471–475.
Eng, L.F., Ghirnikar, R.S., and Lee, Y.L. (2000). Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969–2000). Neurochem. Res. 25, 1439–1451.
Grandbarbe, L., Bouissac, J., Rand, M., Hrabe de Angelis, M., Artavanis-Tsakonas, S., and Mohier, E. (2003). Delta-Notch signaling controls the generation of neurons/glia from neural stem cells in a stepwise process. Development 130, 1391–1402.
Gwak, J.W., Kong, H.J., Bae, Y.K., Kim, M.J., Lee, J., Park, J.H., and Yeo, S.Y. (2010). Proliferating neural progenitors in the developing CNS of zebrafish require Jagged2 and Jagged1b. Mol. Cells 30, 155–159.
Kempermann, G., Jessberger, S., Steiner, B., and Kronenberg, G. (2004). Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus. Trends Neurosci. 27, 447–452.
Lam, C.S., Marz, M., and Strahle, U. (2009). gfap and nestin reporter lines reveal characteristics of neural progenitors in the adult zebrafish brain. Dev. Dyn. 238, 475–486.
Lendahl, U., Zimmerman, L.B., and McKay, R.D. (1990). CNS stem cells express a new class of intermediate filament protein. Cell 60, 585–595.
Ma, D.K., Ming, G.L., and Song, H. (2005). Glial influences on neural stem cell development: cellular niches for adult neurogenesis. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 15, 514–520.
Ninkovic, J., and Götz, M. (2007). Signaling in adult neurogenesis: from stem cell niche to neuronal networks. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 17, 338–344.
So, J.H., Chun, H.S., Bae, Y.K., Kim, H.S., Park, Y.M., Huh, T.L., Chitnis, A.B., Kim, C.H., and Yeo, S.Y. (2009). Her4 is necessary for establishing peripheral projections of the trigeminal ganglia in zebrafish. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 379, 22–26.
Yeo, S.Y., and Chitnis, A.B. (2007). Jagged-mediated Notch signaling maintains proliferating neural progenitors and regulates cell diversity in the ventral spinal cord. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 5913–5918.
Yeo, S.Y., Kim, M., Kim, H.S., Huh, T.L., and Chitnis, A.B. (2007). Fluorescent protein expression driven by her4 regulatory elements reveals the spatiotemporal pattern of Notch signaling in the nervous system of zebrafish embryos. Dev. Biol. 301, 555–567.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to the work.
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, SH., Kim, HS., Ryu, JH. et al. Her4-positive population in the tectum opticum is proliferating neural precursors in the adult zebrafish brain. Mol Cells 33, 627–632 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-0091-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-0091-5