Abstract:
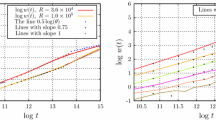
In this work, we introduce a restricted ballistic deposition model with symmetric growth rules that favors the formation of local finite slopes. It is the simplest model which, even without including a diffusive relaxation mode of the interface, leads to a macroscopic groove instability. By employing a finite-size scaling of numerical simulation data, we determine the scaling behavior of the surface structure grown over a one-dimensional substrate of linear size L. We found that the surface profile develops a macroscopic groove with the asymptotic surface width scaling as , with . The early-time dynamics is governed by the scaling law , with . We further investigate the sensitivity to initial conditions of the present model by applying damage spreading techniques. We find that the early-time distance between two initially close surface configurations grows in a ballistic fashion as , but a slower Brownian-like scaling () sets up for evolution times much larger than a characteristic time scale .
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 26 May 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, R., Lyra, M., da Silva, C. et al. Roughness scaling and sensitivity to initial conditions in a symmetric restricted ballistic deposition model. Eur. Phys. J. B 17, 693–697 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510070110
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510070110