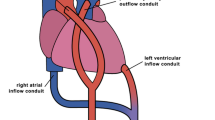
Abstract
Papillary muscle rupture is a fatal complication with a high operative mortality. Most patients experience cardiogenic shock and hypoxia due to pulmonary edema caused by severe mitral regurgitation. Although preoperative stabilization using a mechanical assist device potentially improves surgical outcomes, an appropriate strategy has not yet been established. ECPELLA, combining venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and Impella, has the potential to stabilize preoperative status and improve outcome in patients with refractory cardiogenic shock due to papillary muscle rupture. Herein, we present 3 cases involving the efficacy of ECPELLA and our tips of surgical and ECPELLA management in patients with papillary muscle rupture.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei JY, Hutchins GM, Bulkley BH. Papillary muscle rupture in fatal acute myocardial infarction, a potentially treatable form of cardiogenic shock. Ann Intern Med. 1979;90:149–53.
Thompson CR, Buller CE, Sleeper LA, et al. Cardiogenic shock due to severe mitral regurgitation complicating acute myocardial infarction: a report from the shock trial registry. J Am Coll Cardior. 2000;36:1104–9.
Russo A, Suri RM, Grigioni F, et al. Clinical outcome after surgical correction of mitral regurgitation due to papillary muscle rupture. Circulation. 2008;118:1528–34.
Schroeter T, Lehmann S, Misfeld M, et al. Clinical outcome after mitral valve surgery due to ischemic papillary muscle rupture. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;95:820–4.
Sultan I, Aranda-Michel E, Gleason TG, et al. Mitral valve surgery for acute papillary muscle rupture. J Card Surg. 2018;33:484–8.
Jalil B, El-Kersh K, Frizzell J, et al. Impella percutaneous left ventricular assist device for severe acute ischemic mitral regurgitation as a bridge to surgery. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2017-219749.
Harmon L, Boccalandro F. Cardiogenic shock secondary acute ischemic mitral regurgitation managed with an Impella 2.5 percutaneous left ventricular assist device. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;79:1129–34.
Hryniewicz K, Sandoval Y, Samara M, et al. Percutaneous venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for refractory cardiogenic shock is associated with improved short- and long-term survival. ASAIO J. 2016;62:397–402.
Pappalardo F, Shulte C, Pieri M, et al. Concomitant implantation Impella on top of veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation may improve survival of patients with cardiogenic shock. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016;19:404–12.
Patel SM, Lipinski J, Al-Kindi SG, et al. Simultaneous venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and percutaneous left ventricular decompression therapy with Impella is associated with improved outcomes in refractory cardiogenic shock. ASAIO J. 2019;65:21–8.
Basir MB, Schreiber T, Dixon S, et al. Feasibility of early mechanical circulatory support in acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock: the Detroit cardiogenic shock initiative. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;91:454–61.
Kaku Y, Nakano J, Pham DT. Successful support of cardiogenic shock due to ruptured papillary muscle using Impella 5.0. Artif Organs. 2020;44:900–1.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. This study was approved by the institutional ethics committee (Kurume University IRB No.: 2020 103).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Takagi, K., Shojima, T., Kono, T. et al. ECPELLA as the bridge to surgery in patients with cardiogenic shock due to post-infarct papillary muscle rupture: management of mechanical circulatory support during operation. J Artif Organs 26, 237–241 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-022-01365-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-022-01365-w