Abstract
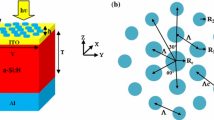
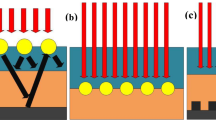
Solar plasmonics absorbers have received outstanding interest from nanotechnology. However, they have small efficiency. To overcome this challenge, we have used two ways in this proposed paper. In the first method, two types of nanoparticle including gold and silver are used on the superstate silica layer in the form of an insulating metal structure. Additionally, to analyze the structure, finite difference time domain (FDTD) is proposed. As a result, at all wavelengths, more than 50% of sunlight will be absorbed. On the other hand, by combining the light to the boundary between nanoparticles and insulation and applying optimization method in Lumerical software, surface plasmons will be stimulated and the possibility of modeling in nanodimensions is provided. It was clearly obvious that by increasing the diameter of the nanoparticles from 10 to 15 nm the amount of light absorption is increased, and by reaching the diameter nanoparticles to 20 nm, light absorption decreases. Regarding to the standard account (100 mW cm2, AM 1.5), maximum short-circuit current of 20 mA, open-circuit voltage of 0.65 V and filling coefficient 60 percent, the amount of light conversion will be 8.45%.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari, F., et al.: Long-term durability of bromide-incorporated perovskite solar cells via a modified vapor-assisted solution process. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 1(11), 6018–6026 (2018)
Wang, H., Alshehri, H., Su, H., Wang, L.: Design, fabrication and optical characterizations of large-area lithography-free ultrathin multilayer selective solar coatings. excellent thermal stability in air. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 174, 445–452 (2018)
Heidarzadeh, H., et al.: Design criteria for silicon nanostructures in silicon based triple junction solar cell. Opt. Quant. Electron 48(11), 510 (2016)
Jangjoy, A., Bahador, H., Heidarzadeh, H.: Design of an ultra-thin silicon solar cell using Localized Surface Plasmonic effects of embedded paired nanoparticles. Opt. Commun. 450, 216–221 (2019)
Heidarzadeh, H.: Transition metal-doped 3C-SiC as a promising material for intermediate band solar cells. Opt. Quant. Electron 51(1), 32 (2019)
Daryani, M., et al.: High efficiency solar cells using quantum interferences. Opt. Quant. Electron 49(7), 255 (2017)
Heidarzadeh, H., et al.: A new proposal for Si tandem solar cell: significant efficiency enhancement in 3C–SiC/Si. Optik Int. J. Light Electron. Opt 125(3), 1292–1296 (2014)
Doriani, M., Dehdashti Jahromi, H., Sheikhi, M.H.: A highly efficient thin film CuInGaSe2 solar cell. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 137(6), 064501 (2015)
Danaie, M., Shahzadi, A.: Design of a high-resolution metal–insulator–metal plasmonic refractive index sensor based on a ring-shaped Si resonator. Plasmonics 14(6), 1453–1465 (2019)
Geravand, A., Sharbati, S., Danaie, M.: Optimize parameters of new fabricated n-CdTe/p-CdTe solar cell. In: 2017 Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE). IEEE, pp. 412–416 (2017)
Heidarzadeh, H., Tavousi, A.: Performance enhancement methods of an ultra-thin silicon solar cell using different shapes of back grating and angle of incidence light. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 240, 1–6 (2019)
Nejand, A., Bahram, V.A., Shahverdi, H.R.: New physical deposition approach for low cost inorganic hole transport layer in normal architecture of durable perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(39), 21807–21818 (2015)
Ghahremanirad, E., et al.: Improving the performance of perovskite solar cells using kesterite mesostructure and plasmonic network. Sol. Energy 169, 498–504 (2018)
Ghahremanirad, E., et al.: "Hexagonal array of mesoscopic HTM-based perovskite solar cell with embedded plasmonic nanoparticles. Phys. Status Solidi 255(3), 1700291 (2018)
Najafi, L., et al.: "Mos2 quantum dot/graphene hybrids for advanced interface engineering of a ch3nh3pbi3 perovskite solar cell with an efficiency of over 20%. ACS Nano 12(11), 10736–10754 (2018)
Teymourinia, H., et al.: "Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots from corn powder and their application as down conversion effect in quantum dot-dye-sensitized solar cell. J. Mol. Liq. 251, 267–272 (2018)
Moosakhani, S., et al.: "Platelet CuSbS2 particles with a suitable conduction band position for solar cell applications. Mater. Lett. 215, 157–160 (2018)
Zamiri, G., Bagheri, S.: Fabrication of green dye-sensitized solar cell based on ZnO nanoparticles as a photoanode and graphene quantum dots as a photo-sensitizer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 511, 318–324 (2018)
Yavari, M., et al.: "Greener, nonhalogenated solvent systems for highly efficient perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 8(21), 1800177 (2018)
Gholizadeh, A., et al.: Enhancement of Si solar cell efficiency using ZnO nanowires with various diameters. Matter Res. Express 5(1), 015040 (2018)
Imahori, H., Umeyama, T., Ito, S.: Large π-aromatic molecules as potential sensitizers for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Acc. Chem. Res. 42(11), 1809–1818 (2009)
Qarony, W., Hossain, M.I., Hossain, M.K., Uddin, M.J., Haque, A., Saad, A.R., Tsang, Y.H.: Efficient amorphous silicon solar cells: characterization, optimization, and optical loss analysis. Results Phys. 7, 4287–4293 (2017)
Blakers, A., Zin, N., McIntosh, K.R., Fong, K.: High efficiency silicon solar cells. Energy Procedia 33, 1–10 (2013)
De La Mora, M.B., Amelines-Sarria, O., Monroy, B.M., Hernández-Pérez, C.D., Lugo, J.E.: Materials for downconversion in solar cells: perspectives and challenges. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 165, 59–71 (2017)
Feldmann, F., Bivour, M., Reichel, C., Hermle, M., Glunz, S.W.: Passivated rear contacts for high-efficiency n-type Si solar cells providing high interface passivation quality and excellent transport characteristics. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 120, 270–274 (2014)
Holman, Z.C., Filipič, M., Lipovšek, B., De Wolf, S., Smole, F., Topič, M., Ballif, C.: Parasitic absorption in the rear reflector of a silicon solar cell: Simulation and measurement of the sub-bandgap reflectance for common dielectric/metal reflectors. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 120, 426–430 (2014)
Mack, I., Stuckelberger, J., Wyss, P., Nogay, G., Jeangros, Q., HorzelLöper, J.P.: Properties of mixed phase silicon-oxide-based passivating contacts for silicon solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 181, 9–14 (2018)
Sharma, V., Kumar, P., Kumar, A., Asokan, K., Sachdev, K.: High-performance radiation stable ZnO/Ag/ZnO multilayer transparent conductive electrode. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 169, 122–131 (2017)
Taguchi, M., Yano, A., Tohoda, S., Matsuyama, K., Nakamura, Y., Nishiwaki, T., Maruyama, E.: 24.7% record efficiency HIT solar cell on thin silicon wafer. IEEE. J. Photovolt. 4(1), 96–99 (2013)
Yamamoto, K., Yoshikawa, K., Uzu, H., Adachi, D.: High-efficiency heterojunction crystalline Si solar cells. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 57(8), 08RB20 (2018)
Masuko, K., Shigematsu, M., Hashiguchi, T., Fujishima, D., Kai, M., YoshimuraYamanishi, N.T.: Achievement of more than 25% conversion efficiency with crystalline silicon heterojunction solar cell. IEEE J. Photovolt. 4(6), 1433–1435 (2014)
Richter, A., Benick, J., Feldmann, F., Fell, A., Hermle, M., Glunz, S.W.: n-Type Si solar cells with passivating electron contact: Identifying sources for efficiency limitations by wafer thickness and resistivity variation. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 173, 96–105 (2017)
Hussain, B., Ebong, A., Ferguson, I.: Zinc oxide as an active n-layer and antireflection coating for silicon based heterojunction solar cell. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 139, 95–100 (2015)
Grabmann, M., Wallner, G., Grabmayer, K., Buchberger, W., Nitsche, D.: Effect of thickness and temperature on the global aging behavior of polypropylene random copolymers for seasonal thermal energy storages. Sol. Energy 172, 152–157 (2018)
Ho, W.J., Sue, R.S., Lin, J.C., Syu, H.J., Lin, C.F.: Optical and electrical performance of MOS-structure silicon solar cells with antireflective transparent ITO and plasmonic indium nanoparticles under applied bias voltage. Materials 9(8), 682 (2016)
Li, W., Wu, T., Jiao, R., Zhang, B.P., Li, S., Zhou, Y., Li, L.: Effects of silver nanoparticles on the firing behavior of silver paste on crystalline silicon solar cells. Colloids Surf. A 466, 132–137 (2015)
Ko, M.D., Rim, T., Kim, K., Meyyappan, M., Baek, C.K.: High efficiency silicon solar cell based on asymmetric nanowire. Sci. Rep. 5, 11646 (2015)
Ghosh, H., Mitra, S., Siddiqui, M.S., Saxena, A.K., Chaudhuri, P., Saha, H., Banerjee, C.: Back scattering involving embedded silicon nitride (SiN) nanoparticles for c-Si solar cells. Opt. Commun. 413, 63–72 (2018)
Movla, H., et al.: "Photocurrent and surface recombination mechanisms in the In_xGa_ 1–x N\slashGaN different-sized quantum dot solar cells. Turk. J. Phys. 34(2), 97–106 (2011)
Gorji, N., Es’haghi, et al.: "The effects of recombination lifetime on efficiency and J-V characteristics of InxGa1− xN/GaN quantum dot intermediate band solar cell. Physica E 42(9), 2353–2357 (2010)
Yang, L., Yu, X., Hu, W., Wu, X., Zhao, Y., Yang, D.: An 8.68% efficiency chemically-doped-free graphene–silicon solar cell using silver nanowires network buried contacts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(7), 4135–4141 (2015)
Xu, Z., Qiao, H., Huangfu, H., Li, X., Guo, J., Wang, H.: Optical absorption of several nanostructures arrays for silicon solar cells. Opt. Commun. 356, 526–529 (2015)
Saravanan, S., Dubey, R.S.: Optical absorption enhancement in 40 nm ultrathin film silicon solar cells assisted by photonic and plasmonic modes. Opt. communi. 377, 65–69 (2016)
Azad, A.K., Kort-Kamp, W.J., Sykora, M., Weisse-Bernstein, N.R., Luk, T.S., Taylor, A.J., Chen, H.T.: Metasurface broadband solar absorber. Sci. Rep. 6, 20347 (2016)
Han, S., Shin, J.H., Jung, P.H., Lee, H., Lee, B.J.: Broadband solar thermal absorber based on optical metamaterials for high-temperature applications. Adv. Opt. Mater. 4(8), 1265–1273 (2016)
Farmani, A.: Three-dimensional FDTD analysis of a nanostructured plasmonic sensor in the near-infrared range. JOSA B 36(2), 401–407 (2019)
Moradiani, F., Farmani, A., Mozaffari, M.H., Seifouri, M., Abedi, K.: Systematic engineering of a nanostructure plasmonic sensing platform for ultrasensitive biomaterial detection. Opt. Commun. 474, 126178 (2020)
Amoosoltani, N., Yasrebi, N., Farmani, A., Zarifkar, A.: A plasmonic nano-biosensor based on two consecutive disk resonators and unidirectional reflectionless propagation effect. IEEE Sens. J. 20(16), 9097–9104 (2020)
Mozaffari, M.H., Farmani, A.: On-chip single-mode optofluidic microresonator dye laser sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 20(7), 3556–3563 (2019)
Farmani, A., Soroosh, M., Mozaffari, M.H., Daghooghi, T.: Optical nanosensors for cancer and virus detections. In: Han, B., Tomer, V.K., Nguyen, T.A., Farmani, A., Singh, P.K. (eds.) Nanosensors for Smart Cities, pp. 419–432. Elsevier (2020)
Amoosoltani, N., Zarifkar, A., Farmani, A.: Particle swarm optimization and finite-difference time-domain (PSO/FDTD) algorithms for a surface plasmon resonance-based gas sensor. J. Comput. Electron. 18(4), 1354–1364 (2019)
Han, B., Tomer, V., Nguyen, T.A., Farmani, A., Singh, P.K. (eds.): Nanosensors for Smart Cities. Elsevier, (2020)
Amoosoltani, N., Mehrabi, K., Zarifkar, A., Farmani, A., Yasrebi, N.: Double-ring resonator plasmonic refractive index sensor utilizing dual-band unidirectional reflectionless propagation effect. Plasmonics 16(4), 1277–1285 (2021)
Khosravian, E., Mashayekhi, H.R., Farmani, A.: Tunable plasmonics photodetector in near-infrared wavelengths using graphene chemical doping method. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 127, 153472 (2020)
Farmani, H., Farmani, A.: Graphene sensing nanostructure for exact graphene layers identification at terahertz frequency. Physica E 124, 114375 (2020)
Ogawa, S., Kimata, M.: Metal-insulator-metal-based plasmonic metamaterial absorbers at visible and infrared wavelengths: a review. Materials 11(3), 458 (2018)
Li, Y., Li, D., Zhou, D., Chi, C., Yang, S., Huang, B.: Efficient, scalable, and high-temperature selective solar absorbers based on hybrid-strategy plasmonic metamaterials. Solar RRL 2(8), 1800057 (2018)
Huang, Z., Li, S., Cui, X., Wan, Y., Xiao, Y., Tian, S., Lee, C.S.: A broadband aggregation-independent plasmonic absorber for highly efficient solar steam generation. J. Mater. Chemis. A 8(21), 10742–10746 (2020)
Raeen, M.S., Nella, A., Rajagopal, M.: Design and analysis of a miniaturized UWB plasmonic absorber in visible light spectrum. Optik (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.169090
Wang, Y., Chen, K., Lin, Y.S., Yang, B.R.: Plasmonic metasurface with quadrilateral truncated cones for visible perfect absorber. Physica E 139, 115140 (2022)
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies.
Data availability and materials.
All data included in this paper are available upon request by contact with the contact corresponding author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AF and AH took part in validation, data curation, writing—original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This is a numerical study on plasmonics solar cell.
Consent to publish
All authors of this paper agree to publish our theoretical research.
Consent to participate
This is a theoretical study on design of plasmonics solar cell.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farmani, A., Hamidi, A. Smart inverters with broadband light absorption enhancement of nanostructure plasmonic solar absorber using PSO algorithms and FDTD method. Opt Rev 29, 327–334 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-022-00749-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-022-00749-w