Abstract
Background
Incisional hernia (IH) is a common complication after abdominal surgery. Prevention of IH is matter of intense research. Prophylactic mesh reinforcement (PMR) has been shown to be promising in the minimization of IH risk after elective midline laparotomy.
Methods
Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing PMR vs. primary suture closure (PSC). Risk ratio (RR) and standardized mean difference (MD) were used as pooled effect size measures whereas 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) were used to assess relative inference.
Results
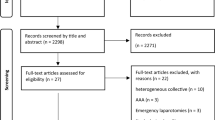
Fourteen RCTs (2332 patients) were included. Overall, 1280 (54.9%) underwent PMR while 1052 (45.1%) PSC. Postoperative follow-up ranged from 12 to 67 months. The incidence of IH was reduced for PMR vs. PSC (13.4% vs. 27.5%). The estimated pooled IH RR for PMR vs. PSC is 0.38 (95% CI 0.24–0.58; p < 0.001). Stratified subgroup analysis according to mesh location shows a risk reduction for intraperitoneal (RR = 0.65; 95% CI 0.48–0.89), preperitoneal (RR = 0.18; 95% CI 0.04–0.81), retromuscular (RR = 0.47; 95% CI 0.24–0.92) and onlay (RR = 0.24; 95% CI 0.12–0.51) compared to PSC. The seroma RR was higher for PMR (RR = 2.05; p = 0.0008). No differences were found for hematoma (RR = 1.49; p = 0.34), surgical site infection (SSI) (RR = 1.17; p = 0.38), operative time (OT) (MD = 0.27; p = 0.413), and hospital length of stay (HLOS) (MD = -0.03; p = 0.237).
Conclusions
PMR seems effective in reducing the risk of IH after elective midline laparotomy compared to PSC in the medium-term follow-up. While the risk of postoperative seroma appears higher for PMR, hematoma, SSI, HLOS and OT seems comparable.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data generated at a central, large-scale facility, available upon request.
References
Mudge M, Hughes LE (1985) Incisional hernia: a 10-year prospective study of incidence and attitudes. Br J Surg 72:70–71
Millbourn D, Cengiz Y, Israelsson LA (2009) Effect of stitch length on wound complications after closure of midline incisions: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Surg 144:1056–1059
Bosanquet DC, Ansell J, Abdelrahman T, Cornish J, Harries R, Stimpson A et al (2015) Systematic review and meta-regression of factors affecting midline incisional hernia rates: analysis of 14 618 patients. PLoS ONE 10:e0138745
Muysoms FE, Antoniou SA, Bury K, Campanelli G, Conze J, Cuccurullo D, de Beaux AC, Deerenberg EB, East B, Fortelny RH, Gillion JF, Henriksen NA, Israelsson L, Jairam A, Jänes A, Jeekel J, López-Cano M, Miserez M, Morales-Conde S, Sanders DL, Simons MP, Śmietański M, Venclauskas L, Berrevoet F, European Hernia Society (2015) European Hernia Society guidelines on the closure of abdominal wall incisions. Hernia 19(1):1–24
Diener MK, Voss S, Jensen K, Büchler MW, Seiler CM (2010) Elective midline laparotomy closure: the INLINE systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg 251(5):843–856
Pans A, Elen P, Dewé W, Desaive C (1998) Long-term results of polyglactin mesh for the prevention of incisional hernias in obese patients. World J Surg 22:479–482
Gutiérrez de la Peña C, Medina Achirica C, Domínguez-Adame E, Medina Díez J (2003) Primary closure of laparotomies with high risk of incisional hernia using prosthetic material: analysis of usefulness. Hernia 7:134–136
Strzelczyk JM, Szymański D, Nowicki ME, Wilczyński W, Gaszynski T, Czupryniak L (2006) Randomized clinical trial of postoperative hernia prophylaxis in open bariatric surgery. Br J Surg 93:1347–1350
El-Khadrawy OH, Moussa G, Mansour O, Hashish MS (2009) Prophylactic prosthetic reinforcement of midline abdominal incisions in high-risk patients. Hernia 13:267–274
Bevis PM, Windhaber RA, Lear PA, Poskitt KR, Earnshaw JJ, Mitchell DC (2010) Randomized clinical trial of mesh versus sutured wound closure after open abdominal aortic aneurysm surgery. Br J Surg 97:1497–1502
Abo-Ryia MH, El-Khadrawy OH, Abd-Allah HS (2013) Prophylactic preperitoneal mesh placement in open bariatric surgery: a guard against incisional hernia development. Obes Surg 23:1571–1574
Bali C, Papakostas J, Georgiou G, Kouvelos G, Avgos S, Arnaoutoglou E et al (2015) A comparative study of sutured versus bovine pericardium mesh abdominal closure after open abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Hernia 19:267–271
Deerenberg EB, Harlaar JJ, Steyerberg EW, Lont HE, van Doorn HC, Heisterkamp J et al (2015) Small bites versus large bites for closure of abdominal midline incisions (STITCH): a double-blind, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 386:1254–1260
van Ramshorst GH, Eker HH, Hop WC, Jeekel J, Lange JF (2012) Impact of incisional hernia on health-related quality of life and body image: a prospective cohort study. Am J Surg 204:144–150
van Ramshorst GH, Eker HH, van der Voet JA, Jeekel J, Lange JF (2013) Long-term outcome study in patients with abdominal wound dehiscence: a comparative study on quality of life, body image, and incisional hernia. J Gastrointest Surg 17:1477–1484
Holihan JL, Alawadi Z, Martindale RG, Roth JS, Wray CJ, Ko TC, Kao LS, Liang MK (2015) Adverse events after ventral hernia repair: the vicious cycle of complications. J Am Coll Surg 221(2):478–485
Fischer JP, Basta MN, Mirzabeigi MN, Bauder AR, Fox JP, Drebin JA et al (2016) A risk model and cost analysis of incisional hernia after elective, abdominal surgery based upon 12,373 cases: the case for targeted prophylactic intervention. Ann Surg 263:1010–1017
Bhangu A, Fitzgerald JE, Singh P, Battersby N, Marriott P, Pinkney T (2013) Systematic review and meta-analysis of prophylactic mesh placement for prevention of incisional hernia following midline laparotomy. Hernia 17(4):445–455
Payne R, Aldwinckle J, Ward S (2017) Meta-analysis of randomised trials comparing the use of prophylactic mesh to standard midline closure in the reduction of incisional herniae. Hernia 21(6):843–853
Borab ZM, Shakir S, Lanni MA, Tecce MG, MacDonald J, Hope WW, Fischer JP (2017) Does prophylactic mesh placement in elective, midline laparotomy reduce the incidence of incisional hernia? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgery 161(4):1149–1163
Timmermans L, de Goede B, Eker HH, van Kempen BJ, Jeekel J, Lange JF (2013) Meta-analysis of primary mesh augmentation as prophylactic measure to prevent incisional hernia. Dig Surg 30(4–6):401–409
Wang XC, Zhang D, Yang ZX, Gan JX, Yin LN (2017) Mesh reinforcement for the prevention of incisional hernia formation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Surg Res 209:17–29
Ahmed J, Hasnain N, Fatima I, Malik F, Chaudhary MA, Ahmad J, Malik M, Malik L, Osama M, Baig MZ, Khosa F, Bhora F (2020) Prophylactic mesh placement for the prevention of incisional hernia in high-risk patients after abdominal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus 12(9):e10491
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339:b2700. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700
Goossen K, Tenckhoff S, Probst P et al (2018) Optimal literature search for systematic reviews in surgery. Langenbecks Arch Surg 403(1):119–129
Parker SG, Halligan S, Liang MK, Muysoms FE, Adrales GL, Boutall A, de Beaux AC, Dietz UA, Divino CM, Hawn MT, Heniford TB, Hong JP, Ibrahim N, Itani KMF, Jorgensen LN, Montgomery A, Morales-Conde S, Renard Y, Sanders DL, Smart NJ, Torkington JJ, Windsor ACJ (2020) International classification of abdominal wall planes (ICAP) to describe mesh insertion for ventral hernia repair. Br J Surg 107(3):209–217
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Cochrane Bias Methods Group, Cochrane Statistical Methods Group et al (2011) The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 343:d5928
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7(3):177–188
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JP, Rothstein HR (2010) A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods 1(2):97–111
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560
Aiolfi A, Tornese S, Bonitta G, Rausa E, Micheletto G, Bona D (2019) Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis comparing open, laparoscopic, and robotic approach. Surg Obes Relat Dis 15(6):985–994
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21(11):1539–1558
R Development Core Team (2015) A language and enviroment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Sarr MG, Hutcher NE, Snyder S, Hodde J, Carmody B (2014) A prospective, randomized, multicenter trial of Surgisis Gold, a biologic prosthetic, as a sublay reinforcement of the fascial closure after open bariatric surgery. Surgery 156:902–908
García-Ureña MÁ, López-Monclús J, Hernando LA, Montes DM, Valle de Lersundi AR, Pavón CC et al (2015) Randomized controlled trial of the use of a large-pore polypropylene mesh to prevent incisional hernia in colorectal surgery. Ann Surg 261:876–881
Muysoms FE, Detry O, Vierendeels T, Huyghe M, Miserez M (2016) Ruppert M et al Prevention of incisional hernias by prophylactic mesh-augmented reinforcement of midline laparotomies for abdominal aortic aneurysm treatment: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg 263:638–645
Jairam AP, Timmermans L, Eker HH, Pierik REGJM, van Klaveren D, Steyerberg EW, PRIMA Trialist Group et al (2017) Prevention of incisional hernia with prophylactic onlay and sublay mesh reinforcement versus primary suture only in midline laparotomies (PRIMA): 2-year follow-up of a multicentre, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 390:567–576
Kohler A, Lavanchy JL, Lenoir U, Kurmann A, Candinas D, Beldi G (2019) Effectiveness of prophylactic intraperitoneal mesh implantation for prevention of incisional hernia in patients undergoing open abdominal surgery: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Surg 154(2):109–115
Glauser PM, Brosi P, Speich B, Käser SA, Heigl A, Rosenberg R, Maurer CA (2019) Prophylactic intraperitoneal onlay mesh following midline laparotomy-long-term results of a randomized controlled trial. World J Surg 43(7):1669–1675
Caro-Tarrago A, Olona C, Millán M, Olona M, Espina B, Jorba R (2019) Long-term results of a prospective randomized trial of midline laparotomy closure with onlay mesh. Hernia 23(2):335–340
Goodenough CJ, Ko TC, Kao LS, Nguyen MT, Holihan JL, Alawadi Z, Nguyen DH, Flores JR, Arita NT, Roth JS, Liang MK (2015) Development and validation of a risk stratification score for ventral incisional hernia after abdominal surgery: hernia expectation rates in intra-abdominal surgery (the HERNIA Project). J Am Coll Surg 220(4):405–413
Tsuruta M, Abe Y, Ishida T, Matsui S, Kitagawa Y (2016) Age, preoperative subcutaneous fat area, and open laparotomy are risk factors for incisional hernia following colorectal cancer surgery. Ann Surg Oncol 23(Suppl 2):S236–S241
Ooms LS, Verhelst J, Jeekel J, Ijzermans JN, Lange JF, Terkivatan T (2016) Incidence, risk factors, and treatment of incisional hernia after kidney transplantation: An analysis of 1,564 consecutive patients. Surgery 159(5):1407–1411
Cavalli M, Aiolfi A, Bruni PG, Manfredini L, Lombardo F, Bonfanti MT, Bona D, Campanelli G (2021) Prevalence and risk factors for diastasis recti abdominis: a review and proposal of a new anatomical variation. Hernia 25(4):883–890
Poole GV Jr (1985) Mechanical factors in abdominal wound closure: the prevention of fascial dehiscence. Surgery 97(6):631–640
Fortelny RH, Andrade D, Schirren M, Baumann P, Riedl S, Reisensohn C, Kewer JL, Hoelderle J, Shamiyeh A, Klugsberger B, Maier TD, Schumacher G, Köckerling F, Pession U, Hofmann A, Albertsmeier M (2022) Effects of the short stitch technique for midline abdominal closure on incisional hernia (ESTOIH): randomized clinical trial. Br J Surg. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjs/znac194
Albertsmeier M, Hofmann A, Baumann P, Riedl S, Reisensohn C, Kewer JL, Hoelderle J, Shamiyeh A, Klugsberger B, Maier TD, Schumacher G, Köckerling F, Pession U, Weniger M, Fortelny RH (2022) Effects of the short-stitch technique for midline abdominal closure: short-term results from the randomised-controlled ESTOIH trial. Hernia 26(1):87–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-021-02410-y
Kroese LF, Sneiders D, Kleinrensink GJ, Muysoms F, Lange JF (2018) Comparing different modalities for the diagnosis of incisional hernia: a systematic review. Hernia 22(2):229–242
Jairam AP, López-Cano M, Garcia-Alamino JM, Pereira JA, Timmermans L, Jeekel J, Lange J, Muysoms F (2020) Prevention of incisional hernia after midline laparotomy with prophylactic mesh reinforcement: a meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. BJS Open 4(3):357–368
Olavarria OA, Dhanani NH, Bernardi K, Holihan JL, Bell CS, Ko TC, Liang MK (2020) Prophylactic mesh reinforcement for prevention of midline incisional hernias: a publication bias adjusted meta-analysis. Ann Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000004729
Gillion JF, Sanders D, Miserez M, Muysoms F (2016) The economic burden of incisional ventral hernia repair: a multicentric cost analysis. Hernia 20:819–830
Aiolfi A, Cavalli M, Ferraro SD, Manfredini L, Bonitta G, Bruni PG, Bona D, Campanelli G (2021) Treatment of inguinal hernia: systematic review and updated network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Surg 274(6):954–961
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of article ethical approval is not required, because it does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Human and animal rights
This study does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent was not necessary.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10029_2022_2660_MOESM2_ESM.tiff
Supplementary file2 (TIFF 2390 KB) Figure 1. Risk of bias for Randomized Controlled Trials (RCT) was assessed with use of the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool. Green circle: Low risk of Bias. Red circle: High Risk of Bias. Yellow circle: Unclear Risk of Bias
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aiolfi, A., Cavalli, M., Gambero, F. et al. Prophylactic mesh reinforcement for midline incisional hernia prevention: systematic review and updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hernia 27, 213–224 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-022-02660-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-022-02660-4