Abstract
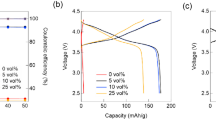
In this study, Li–S batteries were fabricated using 9(15NaI∙NaBH4)∙LiI as the solid electrolyte, and their charge–discharge properties were investigated. The composition of the cathode, consisting of sulfur, solid electrolyte, and carbon, was optimized from the viewpoint of microstructure and charge–discharge performance. For the cathode composite with sulfur, solid electrolyte, and carbon in a weight ratio of 2:7:1, an initial discharge capacity of 1480 mAh/g was obtained, and 760 mAh/g was maintained for the subsequent cycles at 0.006 C. The discharge capacities did not change significantly when the discharge rate was increased to 0.03 C. This indicates that the overvoltage originates mainly from the IR drop of the solid electrolyte at a low rate. On the other hand, the discharge capacity was dropped to 380 mAh/g at 0.06 C, which could be due to insufficient electronic conduction in the composite and/or the homogeneity of the composite. This is a pioneering study of the functioning of a Na-compound-based Li+ conductor as a solid electrolyte for Li–S batteries. The results of this study show the potential of the all-solid-state Li–S battery using the Li+-doped Na compound as the solid electrolyte and strongly indicate that a suitable solid electrolyte for Li–S batteries can be developed from the existing Na compounds.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ji X, Nazar LF (2010) J Mater Chem 20:9821–9826
Rauh RD, Shuker FS, Marston JM, Brummer SB (1977) J Inorg Nucl Chem 39:1761–1766
Zhou W, Chen H, Yu Y, Wang D, Cui Z, Disalvo FJ, Abruña HD (2013) ACS Nano 7:8801–8808
Li Y, Guo XT, Zhang ST, Pang H (2021) Rare Met 40:417–424
Zhang K, Chen Z, Ning R, Xi S, Tang W, Du Y, Liu C, Ren Z, Chi X, Bai M, Shen C, Li X, Wang X, Zhao X, Leng K, Pennycook SJ, Li H, Xu H, Loh KP et al (2019) ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:25147–25154
Liao J, Liu Z, Liu X, Ye Z (2018) J Phys Chem C 122:25917–25929
Wang ZY, Wang L, Liu S, Li GR, Gao XP (2019). Adv Funct Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201901051
Yang T, Qian T, Liu J, Xu N, Li Y, Grundish N, Yan C, Goodenough JB (2019) ACS Nano 13:9067–9073
Pan H, Cheng Z, He P, Zhou H (2020) Energy Fuels 34:11942–11961
Umeshbabu E, Zheng B, Yang Y (2019) Recent progress in all-solid-state lithium−sulfur batteries using high Li-ion conductive solid electrolytes. Electrochem Energ Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41918-019-00029-3
Yang Q, Deng N, Zhao Y, Gao L, Cheng B, Kang W (2023) Chem Eng J 451:38532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138532
Yi J, Chen L, Liu Y, Geng H, Fan LZ (2019) ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:36774–36781
Ahmad N, Zhou L, Faheem M, Tufail MK, Yang L, Chen R, Zhou Y, Yang W (2020) ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:21548–21558
Machida N, Kobayashi K, Nishikawa Y, Shigematsu T (2004) Solid State Ionics 175:247–250
Kinoshita S, Okuda K, Machida N, Naito M, Sigematsu T (2014) Solid State Ionics 256:97–102
Kim PJ, Narayanan S, Xue J, Thangadurai V, Pol VG (2018) ACS Appl Energy Mater 1:3733–3741
Lu Y, Huang X, Song Z, Rui K, Wang Q, Gu S, Yang J, Xiu T, Badding ME, Wen Z (2018) Energy Storage Mater 15:282–290
Shaomao X, Dennis MW, Lei Z, Greg HT, Changwei W, Zhaohui M, Chaoji C, Wei L, Jiaqi D, Yudi K, Emily HM, Kun F, Yunhui G, Eric WD, Liangbing H (2018) Energy Storage Mater 15:458–464
Din MMU, Murugan R (2018) Electrochem commun 93:109–113
Das S, Ngene P, Norby P, Vegge T, de Jongh PE, Blanchard D (2016) J Electrochem Soc 163:A2029–A2034
Miyazaki R, Sakaguchi I, Hihara T (2021) J Solid State Electrochem 25:1927–1936
Miyazaki R, Hihara T (2022) Mater Lett 312:131646
Choi YS, Lee YS, Choi DJ, Chae KH, Oh KH, Cho YW (2017) J Phys Chem C 121:26209–26215
Shannon RD (1976) Acta Cryst A32:751–767
Maekawa H, Matsuo M, Takamura H, Ando M, Noda Y, Karahashi T, Orimo S (2009) J Am Chem Soc 131:894–895
Liang CC (1973) J Electrochem Soc 120:1289
Maier J (1987) Solid State Ionics 23:59–67
Ji X, Lee KT, Nazar LF (2009) Nat Mater 8:500–506
Miyazaki R, Hihara T (2019) J Power Sources 427:15–20
Sakuda A, Takeuchi T, Shikano M, Sakaebe H, Kobayashi H (2016) Front Energy Res 4:1–7
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the JSPS KAKENHI grant numbers JP22H02179, JP22K04871, and the Naito Science & Engineering Foundation. The FIB-SEM observation and EDS analyses were supported by the Equipment Sharing Division, Organization for Co-Creation Research and Social Contributions, Nagoya Institute of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Miyazaki, R., Onishi, K. & Hihara, T. Charge–discharge performances of Li–S battery using NaI–NaBH4–LiI solid electrolyte. J Solid State Electrochem 27, 1195–1201 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-023-05437-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-023-05437-6