Abstract
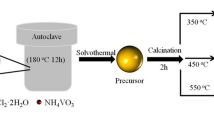
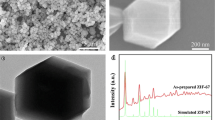
Hollow and porous structures grant fantastic physicochemical properties and widespread application in electrochemical energy storage. Here, hollow/porous Co3O4 nanospheres were synthesized using carbon spheres as the sacrificial templates and a metal-organic framework (MOF)–assisted strategy by a simple immersion method, followed by an annealing treatment in air. By virtue of their structure, the products exhibited excellent electrochemical performance when evaluated as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). Specifically, it delivered a high discharge reversible specific capacity of ~ 550 mA h g−1 after 520 cycles at the current density of 100 mA g−1; it also exhibits excellent cycling stability and rate capability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma FX, Wu HB, Sun XY (2017) Hierarchical Mn3O4 microplates composed of stacking porous nanosheets for high-performance lithium storage. ChemElectroChem 4(10):2703–2708
Zhang CY, Zhang PG, Dai J (2016) Facile synthesis and electrochemical properties of MoO2/reduced graphene oxide hybrid for efficient anode of lithium-ion battery. Ceram Int 42(2):3618–3624
Lux L, Williams K, Ma S (2015) Heat-treatment of metal–organic frameworks for green energy applications. CrystEngComm 17(1):10–22
Liu M, Deng X, Ma Y (2017) Well-designed hierarchical Co3O4 architecture as a long-life and ultrahigh rate capacity anode for advanced lithium-ion batteries. Adv Mater Interfaces 4(19):1700553
Tan Y, Gao Q, Yang C (2015) One-dimensional porous nanofibers of Co3O4 on the carbon matrix from human hair with superior lithium ion storage performance. Sci Rep 5(1):12382
Huang H, Zhu W, Tao X (2012) Nanocrystal-constructed mesoporous single crystalline Co3O4 nanobelts with superior rate capability for advanced lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(11):5974–5980
Li Y, Fu Y, Liu W (2019) Hollow Co-Co3O4 @ CNTs derived from ZIF-67 for lithium ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 784:439–446
Liu W, Fu Y, Li Y (2019) Three-dimensional carbon foam surrounded by carbon nanotubes and Co-Co3O4 nanoparticles for stable lithium-ion batteries. Compos Part B 163:464–470
Yu L, Yu XY, Lou XW (2018) The design and synthesis of hollow micro- nanostructures: present and future trends. Adv Mater 30(38):1800939
Zou F, Chen YM, Liu K (2015) Metal organic frameworks derived hierarchical hollow NiO/Ni/graphene composites for lithium and sodium storage. ACS Nano 10:377–386
Mao D, Wan J, Wang J (2018) Sequential templating approach: a groundbreaking strategy to create hollow multishelled structures. Adv Mater 2018:1802874
Wang J, Cui Y, Wang D (2018) Design of hollow nanostructures for energy storage, conversion and production. Adv Mater 2018:1801993
Li D, Zhao X, Yu R (2018) Formation of multi-shelled nickel-based sulfide hollow spheres for rechargeable alkaline batteries. Inorg Chem Front 5(3):535–540
Wang J, Tang H, Wang H (2017) Multi-shelled hollow micro−/nanostructures: promising platforms for lithium-ion batteries. Mater Chem Front 1(3):414–430
Zhao X, Yu R, Tang H (2017) Formation of septuple-shelled (Co2/3Mn1/3) (Co5/6Mn1/6)2O4 hollow spheres as electrode material for alkaline rechargeable battery. Adv Mater 29(34):1700550
Li H, Ma H, Yang M (2017) Highly controlled synthesis of multi-shelled NiO hollow microspheres for enhanced lithium storage properties. Mater Res Bull 87:224–229
Zhang J, Ren H, Wang J (2016) Engineering of multi-shelled SnO2 hollow microspheres for highly stable lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 4(45):17673–17677
Wang J, Tang H, Zhang L (2016) Multi-shelled metal oxides prepared via an anion adsorption mechanism for lithium-ion batteries. Nat Energy 1(5):16050
Chen M, Wang J, Tang H (2016) Synthesis of multi-shelled MnO2 hollow microspheres via an anion-adsorption process of hydrothermal intensification. Inorg Chem Front 3(8):1065–1070
Ren H, Sun J, Yu R (2016) Controllable synthesis of mesostructures from TiO2 hollow to porous nanospheres with superior rate performance for lithium ion batteries. Chem Sci 7(1):793–798
Qi J, Lai X, Wang J (2015) Multi-shelled hollow micro−/nanostructures. Chem Soc Rev 44(19):6749–6773
Ren H, Yu R, Wang J (2014) Multishelled TiO2 hollow microspheres as anodes with superior reversible capacity for lithium ion batteries. Nano Lett 14(11):6679–6684
Ke F, Luo G, Chen P (2016) Porous metal–organic frameworks adsorbents as a potential platform for defluoridation of water. J Porous Mater 23(4):1065–1073
Fu Y, Li Y, Zhou R (2018) Co3O4 nanoparticles @ MOF-5-derived porous carbon composites as anode materials with superior lithium storage performance. J Alloys Compd 749:645–651
Nai J, Lou XW (2018) Hollow structures based on prussian blue and its analogs for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Adv Mater 2018:1706825
Zhang CY, Dai J, Zhang PG (2016) Porous Fe2O3/ZnO composite derived from MOFs as an anode material for lithium ion batteries. Ceram Int 42(1):1044–1049
Sun X, Li Y (2004) Colloidal carbon spheres and their core/shell structures with noble-metal nanoparticles. Angew Chem 116(5):607–611
Lü Y, Zhan W, He Y (2014) MOF-templated synthesis of porous Co3O4 concave nanocubes with high specific surface area and their gas sensing properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(6):4186–4195
Ye W, Li W, Wang K (2018) ZIF-67@ Se@ MnO2: a novel co-MOF-based composite cathode for lithium–selenium batteries. J Phys Chem C 123:2048–2055
Huang G, Zhang F, Du X (2015) Metal organic frameworks route to in situ insertion of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in Co3O4 polyhedra as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Nano 9(2):1592–1599
Qi W, Li X, Li H (2017) Sandwich-structured nanocomposites of N-doped graphene and nearly monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles as high-performance Li-ion battery anodes. Nano Res 10(9):2923–2933
Ding R, Liu K, Liu X (2019) Hollow Co3O4 nanosphere surrounded by N-doped graphitic carbon filled within multilayer-sandwiched graphene network: a high-performance anode for lithium storage. Inorg Chem 58(5):3416–3424
Sultana I, Rahman MM, Ramireddy T (2015) Understanding structure–function relationship in hybrid Co3O4–Fe2O3/C lithium-ion battery electrodes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(37):20736–20744
Zhang SL, Guan BY, Wu HB (2018) Metal–organic framework-assisted synthesis of compact Fe2O3 nanotubes in Co3O4 host with enhanced lithium storage properties. Nano-Micro Lett 10(3):44
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21671001 and 21571002), the Scientific Research Foundation of Anhui Agricultural University (Grant No. Wd2018-05), the Key Research Project of Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Provincial Universities (Grant No. KJ2019A0216 and KJ2018A0161), and Provincial Undergraduate Training Programs for Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Anhui Agriculture University (201710364062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 235 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Ke, F., Xiao, H. et al. Well-designed hollow and porous Co3O4 microspheres used as an anode for Li-ion battery. J Solid State Electrochem 23, 2477–2482 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04333-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04333-2