Abstract
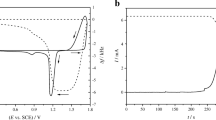
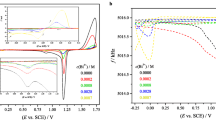
Thick lead dioxide layers were electrodeposited on gold and platinum substrates from aqueous solutions of Pb(NO3)2 dissolved in nitric acid and perchloric acid, respectively. The electrodeposition was carried out using cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry experiments. The mass changes during PbO2-film formation and dissolution were followed by in situ electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM). The electrodeposition of lead dioxide on several types of substrates and in different electrolytes has been widely investigated; however, the mechanism of its dissolution has not been explored, yet. The rate of the reactions occurring during the reduction of the film can be very different depending on the substrates, the electrolytes, the applied potential, and the scan rate. The sweep rate and pH have a small effect on reversibility but highly influences the properties and the deposited mass of lead dioxide layer. At lower concentrations of nitric acid, the PbO2 can be reduced in a larger potential range which is most likely related to the variation of the conductivity of the deposited layer as well as on the nature of the intermediate species.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karami H, Shamsipur M, Ghasemi S, Mousavi MF (2007) Lead–acid bipolar battery assembled with primary chemically formed positive pasted electrode. J Power Sources 164(2):896–904
Petersson I, Berghult B, Ahlberg E (1998) Thin lead dioxide electrodes for high current density applications in semi-bipolar batteries. J Power Sources 74(1):68–76
Johnson DC, Feng J, Houk LL (2000) Direct electrochemical degradation of organic wastes in aqueous media. Electrochim Acta 46(2–3):323–330
Amadelli R, Armelao L, Velichenko AB, Nikolenko NV, Girenko DV, Kovalyov SV, Danilov FI (1999) Oxygen and ozone evolution at fluoride modified lead dioxide electrodes. Electrochim Acta 45(4–5):713–720
Devilliers D, Dinh Thi MT, Mahé E, Le Xuan Q (2003) Cr(III) oxidation with lead dioxide-based anodes. Electrochim Acta 48(28):4301–4309
Taguchi M, Sugita H (2002) Analysis for electrolytic oxidation and reduction of PbSO4/Pb electrode by electrochemical QCM technique. J Power Sources 109(2):294–300
Inguanta R, Rinaldo E, Piazza S, Sunseri C (2012) Formation of lead by reduction of electrodeposited PbO2: comparison between bulk films and nanowires fabrication. J Solid State Electrochem 16(12):3939–3946
Pech D, Brousse T, Bélanger D, Guay D (2009) EQCM study of electrodeposited PbO2: investigation of the gel formation and discharge mechanisms. Electrochim Acta 54(28):7382–7388
Derafa I, Zerroual L, Matrakova M (2018) On the electrochemical activity of β-lead dioxide in sulfuric acid solution: a comparative study between the chemical and electrochemical routes. J Solid State Electrochem 22(4):1175–1183
Pavlov D (2011) Lead-acid batteries: science and technology. Elsevier, Oxford
Yao Y, Zhao M, Zhao C, Ma L (2014) Influence of duty cycle on the structure and electrocatalytic properties of pulse electrodeposited lead dioxide electrodes. J Solid State Electrochem 18(3):721–727
Shmychkova O, Luk’yanenko TV, Piletska A, Velichenko A, Gladyshevskii R, Demchenko P, Amadelli R (2015) Electrocrystallization of lead dioxide: influence of early stages of nucleation on phase composition. J Electroanal Chem 746:57–61
Chang H, Johnson DC (1989) Electrocatalysis of anodic oxygen‐transfer reactions: chronoamperometric and voltammetric studies of the nucleation and electrodeposition of β‐lead dioxide at a rotated gold disk electrode in acidic media. J Electrochem Soc 136(1):17–22
Burazer S, Sopčić S, Mandić Z (2016) Anodic deposition of lead dioxide at Nafion® covered gold electrode. J Solid State Electrochem 20(11):3053–3059
Hwang BJ, Santhanam R, Chang YW (2002) Mechanism of electrodeposition of PbO2 at a Pt sheet/rotating disk electrode. Electroanalysis 14(5):363–367
González-García J, Gallud F, Iniesta J, Montiel V, Aldaz A, Lasia A (2001) Kinetics of electrocrystallization of PbO2 on glassy carbon electrodes: influence of the electrode rotation. Electroanalysis 13(15):1258–1264
Zakharchuk N, Meyer S, Lange B, Scholz F (2000) A comparative study of lead oxide modified graphite paste electrodes and solid graphite electrodes with mechanically immobilized lead oxides. Croat Chem Acta 73:667–704
Lee J, Varela H, Uhm S, Tak Y (2000) Electrodeposition of PbO2 onto Au and Ti substrates. Electrochem Commun 2(9):646–652
Pereira JF, Figueiredo RS, Ponce-de-León C, Bertazzoli R (2016) Platinum-free lead dioxide electrode for electrooxidation of organic compounds. J Solid State Electrochem 20(4):1167–1173
Laitinen HA, Watkins NH (1976) Mechanism of anodic deposition and cathodic stripping of PbO2 on conductive tin oxide. J Electrochem Soc 123(6):804–809
Velayutham D, Noel M (1991) The influence of electrolyte media on the deposition-dissolution behaviour of lead dioxide on glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim Acta 36(13):2031–2035
Velichenko AB, Baranova EA, Girenko DV, Amadelli R, Kovalev SV, Danilov FI (2003) Mechanism of electrodeposition of lead dioxide from nitrate solutions. Russ J Electrochem 39(6):615–621
Velichenko AB, Girenko DV, Danilov FI (1995) Electrodeposition of lead dioxide at an Au electrode. Electrochim Acta 40(17):2803–2807
Fleischmann M, Liler M (1958) The anodic oxidation of solutions of plumbous salts: Part 1.–the kinetics of deposition of α-lead dioxide from acetate solutions. Trans Faraday Soc 54(0):1370–1381
Velichenko AB, Amadelli R, Gruzdeva EV, Luk’yanenko TV, Danilov FI (2009) Electrodeposition of lead dioxide from methanesulfonate solutions. J Power Sources 191:103–110
Hu X, Yu Y, Yang L (2015) Electrocatalytic activity of Ce-PbO2/C anode for acid red B reduction in aqueous solution. J Solid State Electrochem 19(6):1599–1609
Knysh V, Luk’yanenko T, Shmychkova O, Amadelli R, Velichenko A (2017) Electrodeposition of composite PbO2–TiO2 materials from colloidal methanesulfonate electrolytes. J Solid State Electrochem 21(2):537–544
Beck F (1975) Cyclic behaviour of lead dioxide electrodes in tetrafluorborate solutions. J Electroanal Chem 65(1):231–243
Campbell SA, Peter LM (1991) Detection of soluble intermediates during deposition and reduction of lead dioxide. J Electroanal Chem 306(1-2):185–194
Velichenko AB, Girenko DV, Danilov FI (1996) Mechanism of lead dioxide electrodeposition. J Electroanal Chem 405(1-2):127–132
Velichenko AB, Luk’yanenko T, Nikolenko NV, Amadelli R, Danilov FI (2007) Nafion effect on the lead dioxide electrodeposition kinetics. Russ J Electrochem 43:121–124
Velichenko AB, Devilliers D (2007) Electrodeposition of fluorine-doped lead dioxide. J Fluor Chem 128(4):269–276
Sauerbrey G (1959) Verwendung von Schwingquarzen zur Wägung dünner Schichten und zur Mikrowägung. Z Phys 155(2):206–222
Kanazawa KK, Gordon JG (1985) The oscillation frequency of a quartz resonator in contact with a liquid. Anal Chim Acta 175:99–105
Doménech-Carbó A, Doménech-Carbó MT, Gimeno-Adelentado JV, Moya-Moreno M, Bosch-Reig F (2000) Voltammetric identification of lead(II) and (IV) in mediaeval glazes in abrasion-modified carbon paste and polymer film electrodes: application to the study of alterations in archaeological ceramic. Electroanalysis 12(2):120–127
Pavlov D (1987) Effect of chemisorbed water on the electrical capacity of the lead-acid battery positive plate. J Power Sources 19(1):15–25
Pavlov D (1992) The lead-acid battery lead dioxide active mass: a gel-crystal system with proton and electron conductivity. J Electrochem Soc 139(11):3075–3080
Carr JP, Hampson NA (1972) The lead dioxide electrode. Chem Rev 72(6):679–703
Mark HB, Vosburgh WC (1961) The discharge mechanism of certain oxide electrodes. J Electrochem Soc 108(7):615–621
Dawber JG, Wyatt PAH (1960) The Hammett acidity function in aqueous nitric acid. J Chem Soc :3589–3593
Devilliers D, Dinh Thi MT, Mahé E, Dauriac V, Lequeux N (2004) Electroanalytical investigations on electrodeposited lead dioxide. J Electroanal Chem 573(2):227–239
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broda, B., Inzelt, G. Microgravimetric study of electrodeposition and dissolution of lead dioxide on gold and platinum substrates. J Solid State Electrochem 22, 3921–3931 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-4097-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-4097-6